Equilibrium is a term that finds its roots in the Latin word "aequilibrium," which means "equal balance." In the simplest of terms, it refers to a state of balance or stability where opposing forces or influences are of equal strength. This concept of balance is essential in numerous fields, including physics, chemistry, economics, and even in our daily lives. Understanding equilibrium can help us navigate the complexities of various systems and appreciate the stability it brings to our world.
In the realm of science, equilibrium is a crucial concept that helps explain the behavior of systems at rest or in a state of constant motion. It is the state where the sum of forces acting on a system is zero, resulting in no net change in the system's condition. This balance is not only applicable to physical systems but also to chemical reactions, where it signifies a condition where the rates of forward and reverse reactions are equal. Thus, equilibrium is a fundamental aspect of understanding the stability and predictability of scientific phenomena.
Beyond the scientific domain, equilibrium is a metaphor for balance and harmony in our personal and professional lives. It signifies the need for balance between various aspects of life such as work and leisure, stress and relaxation, and personal and professional commitments. Achieving equilibrium in life can lead to improved mental health, increased productivity, and overall well-being. As we delve deeper into the concept of equilibrium, we will explore its multifaceted applications and its profound impact on different areas of our lives.
Read also:Niki Taylor A Luminary In The Fashion World
Table of Contents
- What is Equilibrium?
- Types of Equilibrium
- Equilibrium in Physics
- How Does Chemical Equilibrium Work?
- Equilibrium in Economics
- Biological Equilibrium
- Equilibrium in Daily Life
- How is Mental Equilibrium Maintained?
- Importance of Equilibrium in Relationships
- Equilibrium in Art and Design
- What Role Does Equilibrium Play in Technology?
- Equilibrium in Literature and Philosophy
- Achieving Equilibrium in the Modern World
- Equilibrium in Environmental Science
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
What is Equilibrium?
Equilibrium, in its broadest sense, refers to a state of balance where different forces or influences are equal. This concept is pivotal in understanding various systems and phenomena across different fields. Whether we talk about the balance of forces in physics, the stability of chemical reactions, or the equilibrium in social and economic systems, the core idea remains the same: achieving a stable state where change is minimal or non-existent.
In physics, equilibrium is achieved when all the forces acting on a body are balanced, resulting in no net force and no acceleration. In chemistry, equilibrium describes a state where the concentrations of reactants and products remain constant over time, indicating that the forward and reverse reactions occur at the same rate. Economically, equilibrium is a condition where supply matches demand, leading to stable prices and markets.
Moreover, equilibrium is not only limited to scientific or economic contexts; it also plays a vital role in our daily lives. Achieving a balance between work and personal life, maintaining mental stability, and fostering harmonious relationships are all about finding equilibrium. By understanding this concept, we can better navigate the complexities of life and work towards a more stable and balanced existence.
Types of Equilibrium
Equilibrium can be classified into several types, each pertaining to different fields and contexts. Some of the most common types of equilibrium include static equilibrium, dynamic equilibrium, chemical equilibrium, and thermal equilibrium. Each type has its own characteristics and applications, providing a comprehensive understanding of balance and stability across various domains.
Static Equilibrium
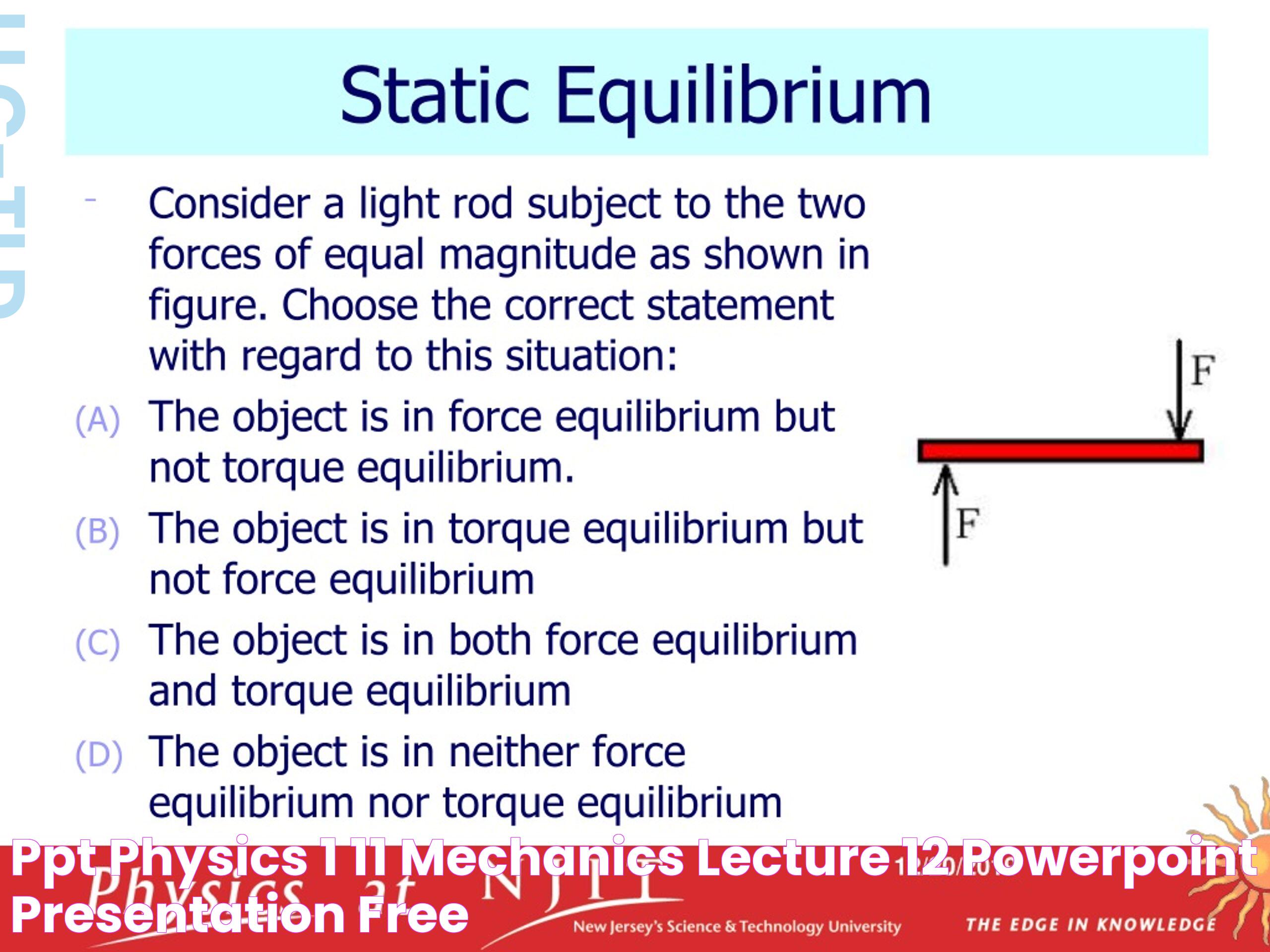
Static equilibrium refers to a state where a system is at rest, and the sum of all forces and torques acting on it is zero. This type of equilibrium is commonly observed in structures and objects that remain stationary, such as a book resting on a table or a building standing firm against gravity.
Dynamic Equilibrium
Dynamic equilibrium, on the other hand, describes systems in motion that maintain a constant speed or direction. In this state, the forces acting on the system are balanced, resulting in no net change in motion. Examples of dynamic equilibrium include a car cruising at a constant speed or a planet orbiting the sun.
Read also:Secrets Of Success At Sephora Appleton A Beauty Haven
Chemical Equilibrium
Chemical equilibrium occurs in reversible chemical reactions when the rates of the forward and reverse reactions are equal. At this point, the concentrations of reactants and products remain constant, indicating a state of balance in the chemical system. This concept is crucial in understanding reaction dynamics and chemical processes.
Thermal Equilibrium
Thermal equilibrium is achieved when two objects or systems at different temperatures reach the same temperature, resulting in no net heat transfer between them. This principle is fundamental in thermodynamics and is essential for understanding heat exchange and energy transfer processes.
Equilibrium in Physics
In physics, equilibrium is a fundamental concept that helps explain the behavior of objects and systems at rest or in constant motion. It is the state where the sum of forces acting on an object is zero, resulting in no net change in its state of motion. This balance is essential for understanding the stability and predictability of physical systems.
Equilibrium in physics can be classified into three main categories: stable, unstable, and neutral equilibrium. Each type has its own characteristics and implications for the behavior of physical systems.
Stable Equilibrium
Stable equilibrium occurs when a system, if disturbed, returns to its original position. This type of equilibrium is common in systems with a low center of gravity, such as a pendulum at rest or a marble in a concave bowl. The system tends to resist changes and returns to its initial state after a disturbance.
Unstable Equilibrium
Unstable equilibrium is observed in systems that, when disturbed, move further away from their original position. An example of this is a pencil balanced on its tip or a ball on top of a hill. Once disturbed, the system is unable to return to its initial state and instead moves to a new equilibrium position.
Neutral Equilibrium
Neutral equilibrium describes systems that, when disturbed, neither return to their original position nor move further away. An example is a ball on a flat surface, where any disturbance results in a new equilibrium position without affecting the system's overall stability.
Understanding these types of equilibrium in physics is essential for analyzing the behavior of systems and predicting their responses to external forces. It provides a foundation for studying mechanics, dynamics, and other areas of physics where stability and balance play a crucial role.
How Does Chemical Equilibrium Work?
Chemical equilibrium is a fundamental concept in chemistry that describes the state of a reversible chemical reaction where the rates of the forward and reverse reactions are equal. At this point, the concentrations of reactants and products remain constant, indicating a state of balance in the chemical system. Understanding chemical equilibrium is crucial for studying reaction dynamics and predicting the behavior of chemical processes.
- Reversible Reactions: Chemical equilibrium occurs in reversible reactions, where the reactants can form products, and the products can reform reactants.
- Equilibrium Constant: The equilibrium constant (K) is a numerical value that represents the ratio of the concentrations of products to reactants at equilibrium. It provides insight into the position of equilibrium and the extent of the reaction.
- Le Chatelier's Principle: This principle states that if a system at equilibrium is subjected to a change in concentration, temperature, or pressure, the system will adjust to partially counteract the change and restore equilibrium.
The concept of chemical equilibrium is essential for understanding various chemical processes, including industrial reactions, biochemical pathways, and environmental systems. It provides valuable insights into reaction kinetics, thermodynamics, and the conditions necessary for achieving a balanced state in chemical systems.
Equilibrium in Economics
In economics, equilibrium is a critical concept that describes a state where supply and demand are balanced, resulting in stable prices and market conditions. It is a condition where the quantity of goods and services supplied equals the quantity demanded, leading to an optimal allocation of resources and minimal waste.
There are several types of economic equilibrium, each with its own implications for market behavior and economic stability:
Market Equilibrium
Market equilibrium occurs when the quantity of goods supplied equals the quantity demanded at a particular price. It is the point where the demand curve intersects the supply curve, resulting in a stable market condition with no excess supply or demand.
General Equilibrium
General equilibrium refers to a state where all markets in an economy are in equilibrium simultaneously. It represents an overall balance in the economy, with all resources optimally allocated and no market imbalances.
Partial Equilibrium
Partial equilibrium focuses on the equilibrium condition in a single market or sector, without considering the interactions with other markets. It is useful for analyzing specific market conditions and the impact of changes in supply and demand on prices and quantities.
Understanding equilibrium in economics is essential for analyzing market dynamics, predicting price changes, and developing policies to achieve economic stability. It provides a framework for understanding the interactions between supply and demand, resource allocation, and the factors influencing market behavior.
Biological Equilibrium
Biological equilibrium, also known as homeostasis, refers to the ability of living organisms to maintain a stable internal environment despite external changes. It is a dynamic process that involves the regulation of physiological systems to achieve a balance between various factors such as temperature, pH, and nutrient levels.
Homeostasis is achieved through complex feedback mechanisms that involve various physiological processes and systems. These include:
- Temperature Regulation: The ability of organisms to maintain a stable body temperature despite external temperature fluctuations.
- pH Balance: The regulation of acidity and alkalinity levels in the body to ensure optimal functioning of enzymes and metabolic processes.
- Fluid and Electrolyte Balance: The maintenance of proper hydration and electrolyte levels to support cellular functions and metabolic processes.
The concept of biological equilibrium is essential for understanding the mechanisms that enable organisms to adapt to changing environments and maintain optimal health. It provides insights into the complex interactions between physiological systems and the factors that influence their stability and balance.
Equilibrium in Daily Life
Equilibrium is a concept that extends beyond scientific and economic contexts to encompass various aspects of daily life. Achieving balance in personal and professional life is essential for overall well-being and success. It involves finding a harmonious equilibrium between work, leisure, relationships, and personal goals.
Some strategies for achieving equilibrium in daily life include:
- Time Management: Prioritizing tasks and allocating time effectively to balance work and leisure activities.
- Stress Management: Identifying stressors and implementing techniques such as meditation, exercise, and relaxation to maintain mental and emotional equilibrium.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Adopting a balanced diet, regular exercise, and sufficient rest to support physical and mental well-being.
Understanding and applying the concept of equilibrium in daily life can lead to improved mental health, increased productivity, and overall satisfaction. It encourages a holistic approach to life, emphasizing the importance of balance and harmony in achieving personal and professional fulfillment.
How is Mental Equilibrium Maintained?
Mental equilibrium, or emotional balance, is a crucial aspect of overall well-being. It involves maintaining a stable and positive mental state, despite external challenges and stressors. Achieving mental equilibrium requires a proactive approach to managing emotions, thoughts, and behaviors.
Some strategies for maintaining mental equilibrium include:
- Mindfulness and Meditation: Practicing mindfulness and meditation to increase self-awareness and reduce stress.
- Positive Thinking: Cultivating a positive mindset and focusing on strengths and achievements rather than negative thoughts.
- Social Support: Building and maintaining strong relationships with family and friends for emotional support and encouragement.
Maintaining mental equilibrium is essential for overall health and well-being. It enables individuals to cope with challenges, build resilience, and achieve a balanced and fulfilling life.
Importance of Equilibrium in Relationships
Equilibrium is a vital aspect of healthy and successful relationships. It involves finding a balance between individual needs and the needs of the relationship, ensuring that both partners feel valued, respected, and supported. Achieving equilibrium in relationships requires effective communication, mutual understanding, and compromise.
Some key elements of equilibrium in relationships include:
- Communication: Open and honest communication is essential for understanding each other's needs and resolving conflicts.
- Mutual Respect: Recognizing and valuing each other's individuality and perspectives.
- Compromise: Finding solutions that satisfy both partners' needs and maintaining a balanced dynamic.
Equilibrium in relationships fosters trust, intimacy, and long-term satisfaction. It encourages a supportive and harmonious connection, enabling both partners to thrive and grow together.
Equilibrium in Art and Design
In art and design, equilibrium refers to the balance and harmony achieved through the arrangement of visual elements. It is an essential principle that guides the composition and aesthetics of artworks, ensuring that they are pleasing to the eye and evoke a sense of stability and unity.
Equilibrium in art and design can be achieved through various techniques, including:
- Symmetry: The use of symmetrical elements to create a balanced and harmonious composition.
- Asymmetry: The arrangement of elements in an asymmetrical manner to achieve visual balance and interest.
- Proportion: The use of proportionate elements to create a sense of balance and harmony in the composition.
Understanding and applying the principles of equilibrium in art and design can enhance the aesthetic appeal and effectiveness of visual works. It encourages creativity and innovation while maintaining a sense of balance and harmony.
What Role Does Equilibrium Play in Technology?
Equilibrium plays a significant role in the development and application of technology. It is a critical concept in various technological fields, including engineering, computing, and telecommunications. Achieving equilibrium in technology involves balancing performance, efficiency, and sustainability to ensure optimal functionality and long-term viability.
Some areas where equilibrium is essential in technology include:
- Energy Efficiency: Balancing energy consumption and output to achieve optimal performance and reduce environmental impact.
- System Stability: Ensuring that technological systems are stable and resilient to external disturbances and changes.
- Resource Allocation: Optimizing the use of resources to achieve a balance between cost, performance, and sustainability.
Understanding the role of equilibrium in technology is crucial for developing innovative solutions and advancing technological progress. It encourages the integration of balance and sustainability principles in technological design and application.
Equilibrium in Literature and Philosophy
Equilibrium is a recurring theme in literature and philosophy, representing the balance and harmony between opposing forces or elements. It is often used as a metaphor for the struggle between good and evil, order and chaos, and reason and emotion.
In literature, equilibrium is explored through character development, plot structure, and thematic elements. It is used to convey the complexities of human nature and the challenges of achieving balance in life and society.
In philosophy, equilibrium is a central concept in various philosophical traditions and schools of thought. It is associated with the pursuit of truth, justice, and the good life, emphasizing the importance of balance and harmony in achieving personal and societal fulfillment.
Understanding the concept of equilibrium in literature and philosophy provides insights into the human experience and the quest for balance and harmony in life. It encourages reflection and contemplation on the nature of existence and the pursuit of meaning and purpose.
Achieving Equilibrium in the Modern World
Achieving equilibrium in the modern world is a complex and multifaceted challenge. It involves balancing various aspects of life, including work, family, health, and personal growth, in an increasingly fast-paced and interconnected world.
Some strategies for achieving equilibrium in the modern world include:
- Prioritization: Identifying and focusing on the most important aspects of life to achieve balance and fulfillment.
- Adaptability: Embracing change and being flexible in the face of new challenges and opportunities.
- Mindfulness: Practicing mindfulness and self-awareness to maintain mental and emotional equilibrium.
Achieving equilibrium in the modern world requires a proactive and holistic approach to life. It encourages individuals to embrace balance and harmony, fostering personal growth, well-being, and success in an ever-changing world.
Equilibrium in Environmental Science
In environmental science, equilibrium refers to the balance and stability of ecosystems and natural systems. It is a critical concept for understanding the interactions between living organisms and their environment and the factors that influence ecological balance and sustainability.
Equilibrium in environmental science is achieved through various processes, including:
- Natural Succession: The gradual and predictable changes in ecosystems over time, leading to a stable and balanced state.
- Resource Cycling: The continuous movement and recycling of nutrients and resources within ecosystems to maintain balance and sustainability.
- Biodiversity: The variety and abundance of different species in an ecosystem, contributing to its stability and resilience.
Understanding equilibrium in environmental science is essential for developing sustainable solutions and practices to protect and preserve natural systems. It encourages the integration of ecological balance principles in environmental management and conservation efforts.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the equilibrium meaning in simple terms?
The equilibrium meaning refers to a state of balance or stability where opposing forces or influences are of equal strength, resulting in no net change.
How is equilibrium achieved in a chemical reaction?
Equilibrium in a chemical reaction is achieved when the rates of the forward and reverse reactions are equal, resulting in constant concentrations of reactants and products.
What are the types of equilibrium in physics?
In physics, equilibrium can be classified into stable, unstable, and neutral equilibrium, each describing the behavior of systems under different conditions.
Why is equilibrium important in economics?
Equilibrium is important in economics because it represents a state where supply and demand are balanced, leading to stable prices and efficient resource allocation.
How does biological equilibrium affect health?
Biological equilibrium, or homeostasis, affects health by maintaining a stable internal environment, essential for optimal physiological functioning and well-being.
What role does equilibrium play in personal relationships?
Equilibrium in personal relationships involves finding a balance between individual needs and the needs of the relationship, ensuring both partners feel valued and supported.
Conclusion
Equilibrium is a multifaceted concept that encompasses various fields and aspects of life, from physics and chemistry to economics and personal well-being. Understanding and achieving equilibrium is essential for stability, balance, and harmony in different contexts. Whether it is maintaining a stable internal environment in biological systems, achieving market balance in economics, or finding personal equilibrium in daily life, the concept of equilibrium plays a vital role in promoting well-being, sustainability, and success. As we continue to navigate the complexities of the modern world, embracing the principles of equilibrium can help us achieve a more balanced and fulfilling life.