Lupus is a complex autoimmune disease that affects millions of individuals worldwide, with women being disproportionately represented. It can manifest in a myriad of ways, often mimicking other conditions, which makes early diagnosis challenging. Recognizing the symptoms of lupus in women is crucial for timely intervention and management, as it can significantly impact one's quality of life. For many women, the journey to diagnosis can be fraught with confusion and frustration due to the disease's unpredictable nature and diverse presentation. Understanding the symptoms and how they affect women differently than men is essential for raising awareness and improving patient outcomes.
The symptoms of lupus in women can range from mild to severe, fluctuating over time with periods of remission and flare-ups. Women may experience a combination of systemic and organ-specific symptoms, including fatigue, joint pain, skin rashes, and more. It's important to note that lupus is a highly individualized disease, and no two cases are identical. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the symptoms of lupus in women, offering valuable insights into recognizing and managing this condition effectively.
Through this article, we will delve into the various symptoms of lupus in women, examine their impact on daily life, and explore the challenges faced by those living with the disease. We will also discuss the importance of seeking medical advice and support, as well as strategies for managing symptoms and improving overall well-being. By increasing our understanding of lupus, we hope to empower women to advocate for their health and improve their quality of life.
Read also:The Intriguing Blend Taurus Sun Sign Libra Rising
Table of Contents
- What is Lupus?
- Why are Women More Affected?
- Common Symptoms in Women
- How Does Lupus Affect the Skin?
- Impact on Joints and Muscles
- Fatigue and Its Challenges
- Organ-Specific Symptoms
- Emotional and Mental Health
- How is Lupus Diagnosed?
- Treatment Options for Women
- Lifestyle Changes and Management
- Support Systems and Resources
- Can Diet Affect Lupus Symptoms?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
What is Lupus?
Lupus is a chronic autoimmune disease where the body's immune system becomes hyperactive and attacks normal, healthy tissues. This results in inflammation, swelling, and damage to joints, skin, kidneys, blood, heart, and lungs. Lupus is characterized by periods of illness, called flares, and periods of wellness, or remission. It is a disease of varying severity and can be life-threatening.
The exact cause of lupus is unknown, but it is believed to be linked to genetic, environmental, and hormonal factors. Certain triggers such as sunlight, infections, and stress can instigate symptom flare-ups. Lupus can affect anyone, but it is most prevalent in women, particularly those of African, Hispanic, Asian, and Native American descent.
Why are Women More Affected?
Approximately 90% of lupus patients are women, and the reasons are believed to be related to hormonal differences. Estrogen, a female hormone, may contribute to the onset and severity of lupus. Studies have shown that women are more likely to develop lupus during their childbearing years, suggesting a link between hormone levels and the disease.
Genetic predisposition also plays a role, as lupus tends to run in families. Women with a family history of lupus or other autoimmune diseases are at a higher risk. Environmental factors, such as exposure to certain drugs or sunlight, can also affect women differently due to biological differences.
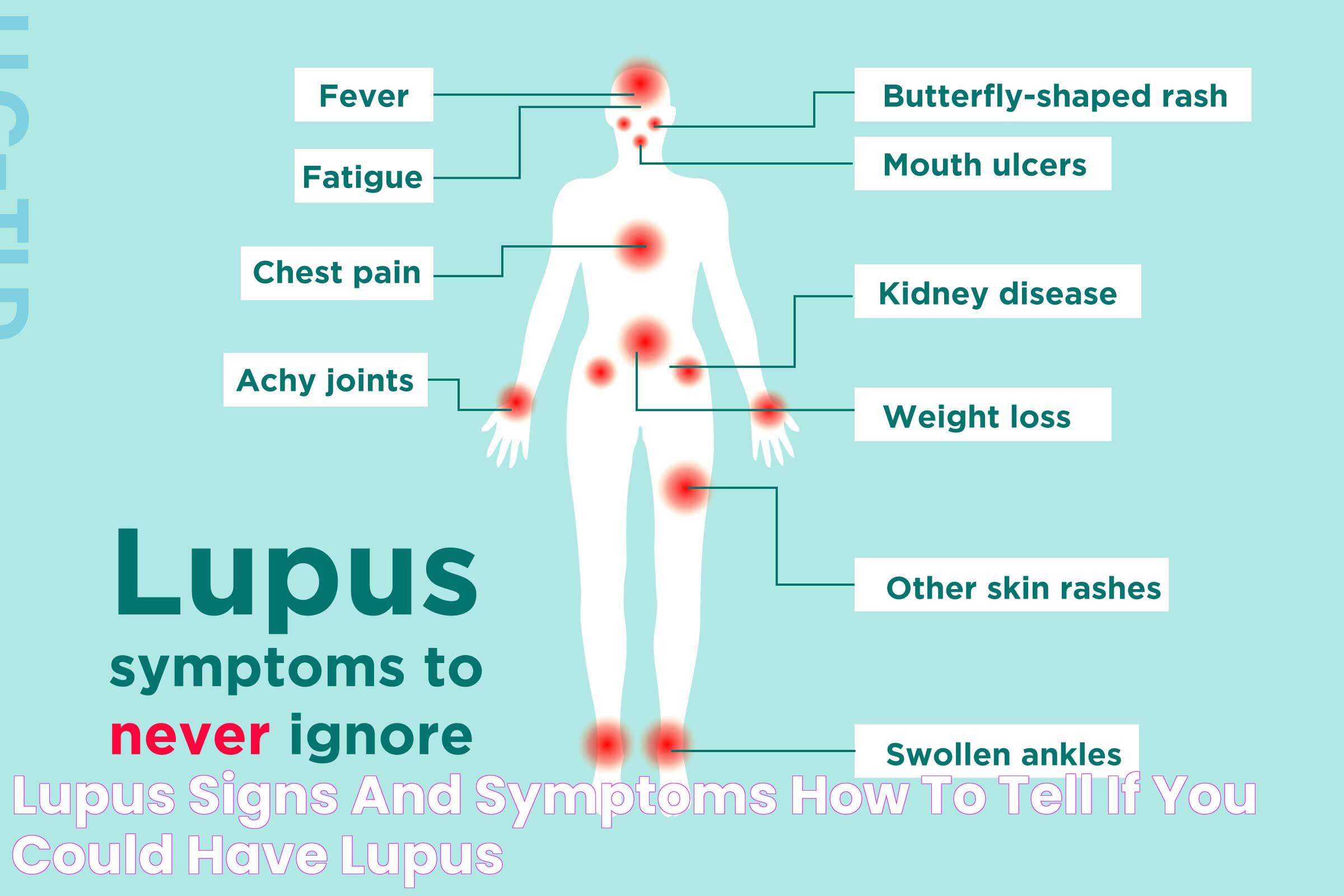
Common Symptoms in Women
The symptoms of lupus in women can vary greatly, making it a difficult condition to diagnose. Some of the most common symptoms include:
- Fatigue: A profound and persistent sense of tiredness and lack of energy.
- Joint Pain and Swelling: Inflammation leading to stiffness and pain, often in the hands, wrists, and knees.
- Skin Rashes: The "butterfly" rash across the cheeks and nose is a classic sign.
- Fever: Low-grade fevers without any obvious cause.
- Hair Loss: Thinning hair or hair falling out in clumps.
- Photosensitivity: Sensitivity to sunlight causing skin rash or triggering other symptoms.
Women may experience these symptoms to varying degrees, and they can change over time. It's important to monitor these symptoms and consult a healthcare provider if they persist or worsen.
Read also:Red Spots On Thighs Causes Treatment And Prevention Tips
How Does Lupus Affect the Skin?
Lupus can manifest in several ways on the skin. The most recognizable is the malar, or "butterfly," rash, which appears across the bridge of the nose and cheeks. Other skin issues include discoid rashes, subacute cutaneous lupus lesions, and photosensitivity.
Discoid rashes are red, scaly patches that can occur on the face, scalp, or anywhere on the body. They can cause scarring and discoloration. Subacute cutaneous lupus lesions are red, ring-shaped lesions that primarily appear on sun-exposed areas of the body. Photosensitivity can lead to a worsening of these rashes and other lupus symptoms upon exposure to ultraviolet rays.
Impact on Joints and Muscles
Joint and muscle pain is a common symptom of lupus in women. The pain is often accompanied by swelling and stiffness, particularly in the morning. Lupus-related arthritis can affect any joint, but it most commonly affects the fingers, wrists, and knees.
Unlike rheumatoid arthritis, lupus rarely causes permanent joint damage. However, the inflammation can cause significant discomfort and limit mobility. Muscle pain and weakness, particularly in the upper arms and thighs, are also common symptoms experienced by women with lupus.
Fatigue and Its Challenges
Fatigue is one of the most debilitating symptoms of lupus and can significantly impact a woman's quality of life. It is not merely feeling tired; it is a profound and persistent exhaustion that doesn't improve with rest. This fatigue can make it challenging to perform daily tasks, maintain employment, and engage in social activities.
Managing fatigue requires a comprehensive approach, including adequate rest, stress management, and sometimes medication. Understanding the nature of lupus-related fatigue is crucial for both patients and their support systems.
Organ-Specific Symptoms
Lupus can affect various organs in the body, leading to a wide range of symptoms. Some of the organ-specific symptoms include:
- Kidneys: Lupus nephritis can cause inflammation in the kidneys, leading to proteinuria, swelling, and high blood pressure.
- Heart: Inflammation of the heart muscle (myocarditis) or the surrounding tissue (pericarditis) can occur.
- Lungs: Pleuritis, inflammation of the lining of the lungs, can cause chest pain and difficulty breathing.
- Brain and Nervous System: Neurological symptoms such as headaches, dizziness, seizures, and cognitive dysfunction.
These symptoms can be severe and require prompt medical attention to manage and prevent complications.
Emotional and Mental Health
The impact of lupus extends beyond physical symptoms, affecting emotional and mental health. Women with lupus may experience depression, anxiety, and mood swings. The chronic nature of the disease, coupled with the unpredictability of flares, can lead to feelings of frustration and hopelessness.
It is essential to address these emotional challenges as part of a comprehensive lupus management plan. Counseling, support groups, and stress-relief techniques can be beneficial in managing the mental health aspects of lupus.
How is Lupus Diagnosed?
Diagnosing lupus can be challenging due to the variability of symptoms. There is no single test for lupus; instead, doctors rely on a combination of clinical evaluation, laboratory tests, and patient history. Common diagnostic tests include:
- Antinuclear Antibody (ANA) Test: Indicates the presence of autoantibodies in the blood.
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): Checks for anemia and other blood abnormalities.
- Urinalysis: Detects protein and blood cells in the urine, indicating kidney involvement.
- Biopsy: Skin or kidney biopsies can confirm the presence of lupus.
Early and accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment and management of lupus.
Treatment Options for Women
Treatment for lupus in women involves managing symptoms and preventing flares. The treatment plan is individualized, depending on the severity of the disease and the specific symptoms present. Common treatments include:
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Used to reduce inflammation and pain.
- Corticosteroids: Powerful anti-inflammatory drugs used to control severe flares.
- Antimalarial Drugs: Help control skin and joint symptoms and prevent flares.
- Immunosuppressants: Used in severe cases to suppress the immune system's attack on the body.
Regular monitoring and communication with healthcare providers are essential to adjust treatment plans as needed.
Lifestyle Changes and Management
In addition to medication, lifestyle changes can help manage lupus symptoms and improve quality of life. These include:
- Healthy Diet: Consuming a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in low-impact activities like walking or swimming.
- Stress Management: Practicing relaxation techniques such as yoga or meditation.
- Sun Protection: Wearing protective clothing and using sunscreen to prevent photosensitivity reactions.
Adopting these lifestyle changes can reduce the frequency of flares and enhance overall well-being.
Support Systems and Resources
Living with lupus can be challenging, but support systems and resources are available to help women cope with the disease. These include:
- Support Groups: Connecting with others who have lupus can provide emotional support and practical advice.
- Educational Resources: Accessing information about lupus can empower women to manage their condition effectively.
- Healthcare Team: Building a team of healthcare providers, including rheumatologists, dermatologists, and mental health professionals, is crucial for comprehensive care.
Utilizing these resources can make a significant difference in managing lupus and improving quality of life.
Can Diet Affect Lupus Symptoms?
Diet can play a role in managing lupus symptoms, although there is no specific "lupus diet." A healthy, balanced diet can help reduce inflammation and support overall health. Some dietary considerations for women with lupus include:
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Found in fish and flaxseeds, they may help reduce inflammation.
- Calcium and Vitamin D: Important for bone health, as lupus and its treatments can increase the risk of osteoporosis.
- Avoiding Triggers: Identifying and avoiding foods that trigger symptoms, such as gluten or dairy.
Consulting with a nutritionist can help create a personalized diet plan that supports lupus management.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the early signs of lupus in women?
Early signs can include fatigue, joint pain, skin rashes, and unexplained fevers. It's important to consult a doctor if these symptoms persist.
2. How does lupus affect pregnancy in women?
While many women with lupus have successful pregnancies, there is an increased risk of complications. Close monitoring and a healthcare team familiar with lupus are essential.
3. Can lupus go into remission?
Yes, lupus can go into remission, where symptoms are minimal or absent. Remission can be achieved through effective treatment and lifestyle management.
4. Is there a cure for lupus?
Currently, there is no cure for lupus, but treatments are available to manage symptoms and reduce the frequency of flares.
5. How can I support someone with lupus?
Offer emotional support, help with daily tasks when needed, and encourage adherence to treatment plans. Educating yourself about the disease can also be beneficial.
6. What lifestyle changes can help manage lupus symptoms?
Lifestyle changes such as a healthy diet, regular exercise, stress management, and sun protection can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
Conclusion
Understanding the symptoms of lupus in women is vital for early diagnosis and effective management. While lupus presents unique challenges, with the right treatment and support, women can lead fulfilling lives. Recognizing the symptoms and seeking medical advice promptly can prevent complications and improve outcomes. By making informed lifestyle choices and utilizing available resources, women with lupus can take control of their health and well-being.