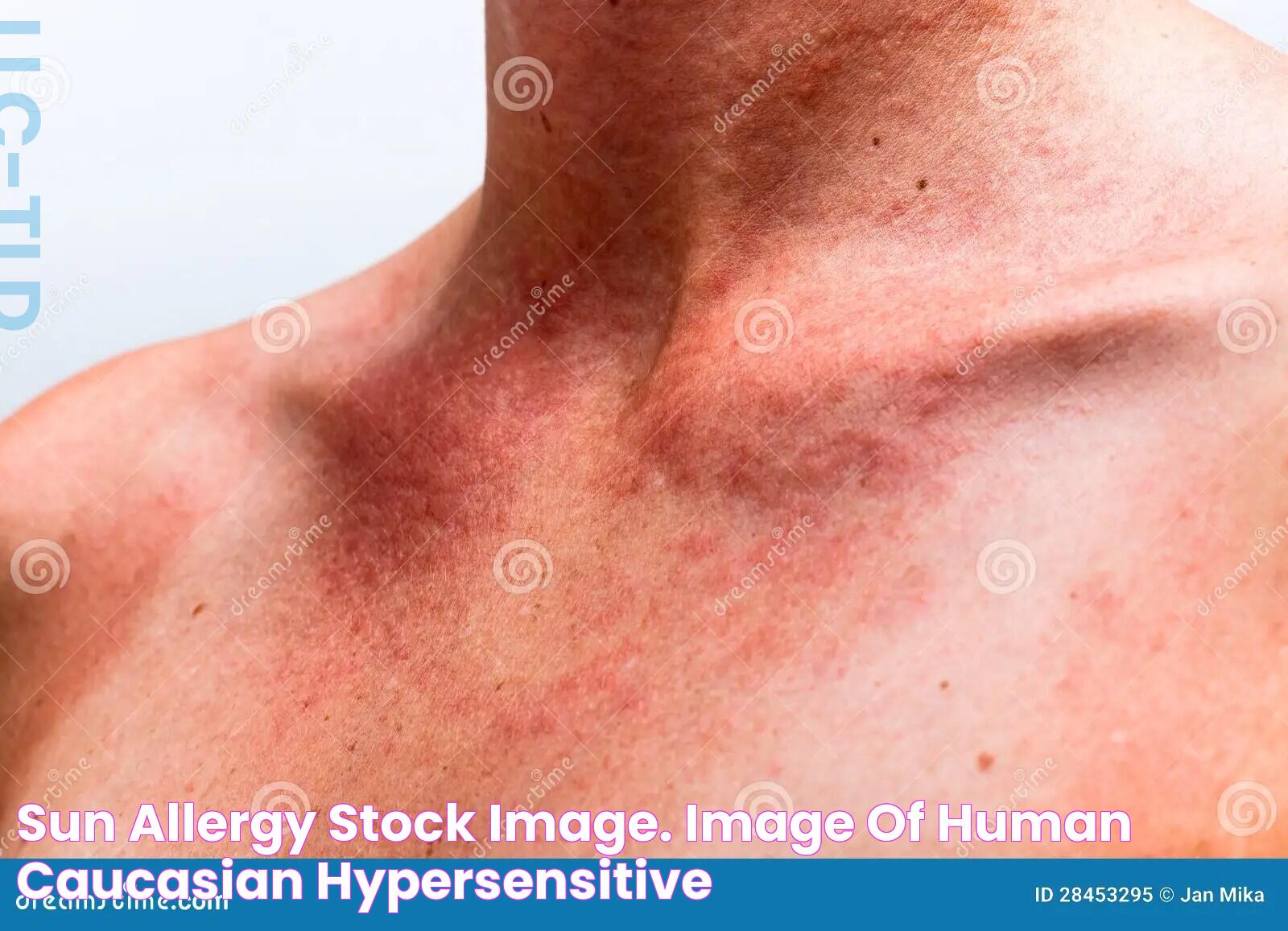
Allergy to the sun, also known as photosensitivity, is a condition that affects a significant number of individuals worldwide. This condition can cause discomfort, skin irritations, and even more severe reactions when exposed to sunlight. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and management strategies for sun allergies is crucial for those affected. This guide aims to provide a detailed exploration of sun allergies, offering expert insights and practical advice to help manage this challenging condition effectively.
Sun allergies can manifest in various forms, ranging from mild itching and rashes to severe blisters and hives. Often, individuals with sun allergies may find it difficult to enjoy outdoor activities, especially during peak sunlight hours. This guide delves into the science behind sun allergies, helping readers comprehend the biological mechanisms that trigger these reactions. Additionally, it highlights the importance of early detection and timely intervention to prevent complications and improve the quality of life for those affected by this condition.
As we explore the intricacies of sun allergies, we will also discuss the latest advancements in medical research and treatments available for managing photosensitivity. From lifestyle modifications to medical interventions, there are numerous strategies to help mitigate the impact of sun allergies. This comprehensive guide is designed to empower readers with the knowledge and tools needed to navigate sun allergies confidently and effectively, enabling them to lead a fulfilling and active life despite the challenges posed by this condition.
Read also:Buoyant Bucolic Timeless Charm Of Rural Bliss
Table of Contents
- What is an Allergy to the Sun?
- Symptoms and Signs of Sun Allergy
- Causes and Risk Factors
- Types of Sun Allergies
- How is Sun Allergy Diagnosed?
- Treatment Options for Sun Allergy
- Lifestyle Modifications for Managing Sun Allergy
- Can Sun Allergy Be Prevented?
- Sun Protection Tips for Sensitive Skin
- Understanding Photosensitivity
- Impact of Sun Allergy on Daily Life
- Sun Allergy in Children
- Latest Research and Developments
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
What is an Allergy to the Sun?
An allergy to the sun, medically referred to as photosensitivity, is an immune system reaction triggered by sunlight exposure. Unlike sunburn, which is a direct result of UV radiation damaging the skin, sun allergies involve an immune response that causes rashes, itching, and other symptoms. This reaction can occur within minutes to hours after sun exposure and varies in severity among individuals.
Photosensitivity can be classified into several types, each with distinct characteristics. The most common types include polymorphic light eruption (PMLE), solar urticaria, and photoallergic reactions. Understanding these different forms of sun allergies is crucial for identifying the appropriate management and treatment strategies.
Sun allergies are more prevalent in certain demographics, particularly among fair-skinned individuals and those with a family history of photosensitivity. However, anyone can develop a sun allergy, regardless of skin type or genetic predisposition. The key to managing sun allergies effectively lies in understanding the underlying causes and implementing preventive measures to minimize sun exposure.
Symptoms and Signs of Sun Allergy
The symptoms of a sun allergy can vary widely depending on the type and severity of the reaction. Common signs include:
- Redness and inflammation of the skin
- Itching or burning sensations
- Rashes or hives
- Blisters or welts
- Peeling or flaking skin
In some cases, sun allergies can also lead to more systemic symptoms such as headaches, nausea, or fatigue. These symptoms are often a result of the body's overall reaction to sun exposure rather than the localized skin response.
Identifying the symptoms early and seeking medical advice is crucial for managing sun allergies effectively. A healthcare professional can perform a thorough examination and recommend appropriate treatment options based on the individual's specific symptoms and medical history.
Read also:Alluring Belly Button Ring A Guide To Style Care And More
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of sun allergies is not well understood, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Some potential causes and risk factors include:
- Genetic predisposition: A family history of sun allergies increases the likelihood of developing the condition.
- Skin type: Fair-skinned individuals are more susceptible to sun allergies due to lower levels of melanin, which provides natural protection against UV radiation.
- Certain medications: Some medications, such as antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs, can increase photosensitivity.
- Underlying medical conditions: Conditions such as lupus or eczema can exacerbate sun allergies.
- Environmental factors: High-altitude locations or areas with intense sunlight can increase the risk of sun allergies.
Understanding these risk factors can help individuals take proactive measures to protect themselves from sun allergies. This may include avoiding peak sunlight hours, wearing protective clothing, and using sunscreen regularly.
Types of Sun Allergies
There are several types of sun allergies, each with unique characteristics and symptoms:
Polymorphic Light Eruption (PMLE)
PMLE is the most common type of sun allergy, characterized by a delayed skin reaction to sunlight. Symptoms typically appear several hours or days after sun exposure and may include red, itchy rashes and small blisters. PMLE is more prevalent in women and often occurs in the spring and early summer months.
Solar Urticaria
Solar urticaria is a rare form of sun allergy that causes immediate hives or welts upon sun exposure. The symptoms can appear within minutes and usually resolve within a few hours once the individual is out of the sun. This type of allergy can be particularly debilitating, as even brief exposure to sunlight can trigger a reaction.
Photoallergic Reactions
Photoallergic reactions occur when a chemical substance on the skin, such as sunscreen or medication, interacts with sunlight, causing an allergic response. These reactions can result in itchy, red rashes and are often mistaken for contact dermatitis.
How is Sun Allergy Diagnosed?
Diagnosing a sun allergy involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and specialized tests. A dermatologist or allergist will typically perform the following steps:
- Medical History: The doctor will inquire about the patient's symptoms, family history, and any medications or topical products used.
- Physical Examination: A thorough examination of the affected skin areas will help identify the characteristic signs of a sun allergy.
- Phototesting: This procedure involves exposing a small skin area to controlled amounts of UV light to observe the skin's reaction.
- Patch Testing: If a photoallergic reaction is suspected, patch testing may be conducted to identify the specific substance causing the allergy.
Accurate diagnosis is essential for developing an effective treatment plan and preventing future sun allergy episodes. It is important for individuals experiencing symptoms to seek medical advice promptly to avoid complications.
Treatment Options for Sun Allergy
Treating sun allergies involves a combination of preventive measures, topical treatments, and, in some cases, medications. Common treatment options include:
Topical Steroids
Topical corticosteroids can help reduce inflammation and relieve itching associated with sun allergies. These creams or ointments are often prescribed for short-term use to manage acute symptoms.
Antihistamines
Oral antihistamines can help alleviate itching and other allergic symptoms by blocking the action of histamine, a chemical released during an allergic reaction.
Phototherapy
In some cases, controlled exposure to UV light under medical supervision can help desensitize the skin and reduce the severity of sun allergy reactions. This treatment, known as phototherapy, is typically reserved for severe cases that do not respond to other therapies.
Immunosuppressants
For individuals with severe or persistent sun allergies, immunosuppressant medications may be prescribed to help modulate the immune system's response to sunlight.
It is essential to work closely with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment plan based on the individual's specific needs and medical history.
Lifestyle Modifications for Managing Sun Allergy
In addition to medical treatments, several lifestyle modifications can help manage sun allergies and reduce the risk of reactions. These include:
Avoiding Peak Sunlight Hours
Staying indoors or seeking shade during peak sunlight hours, typically between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m., can help minimize sun exposure and reduce the risk of triggering a sun allergy reaction.
Wearing Protective Clothing
- Long-sleeved shirts and pants made of tightly woven fabrics can provide a physical barrier against UV rays.
- Wide-brimmed hats and sunglasses with UV protection can protect the face and eyes from sunlight.
Using Sunscreen
Applying broad-spectrum sunscreen with a high SPF can help protect the skin from UV radiation. It is important to reapply sunscreen every two hours and after swimming or sweating.
Maintaining a Healthy Diet
A diet rich in antioxidants, such as fruits and vegetables, can help support the skin's natural defenses against UV damage.
By incorporating these lifestyle modifications, individuals with sun allergies can enjoy outdoor activities while minimizing the risk of allergic reactions.
Can Sun Allergy Be Prevented?
While it may not be possible to completely prevent sun allergies, several strategies can help reduce the risk of developing a reaction:
- Gradual Exposure: Slowly increasing sun exposure over time can help the skin build tolerance to sunlight.
- Skin Care Products: Using hypoallergenic and non-comedogenic skin care products can reduce the risk of photoallergic reactions.
- Regular Skin Checks: Regularly examining the skin for any changes or new symptoms can help detect sun allergies early and prevent complications.
By taking these preventive measures, individuals can reduce their risk of developing sun allergies and enjoy outdoor activities with greater confidence.
Sun Protection Tips for Sensitive Skin
Individuals with sensitive skin need to take extra precautions to protect themselves from the sun. Here are some tips to help safeguard sensitive skin:
Choose the Right Sunscreen
- Select a mineral-based sunscreen containing zinc oxide or titanium dioxide, which is less likely to irritate sensitive skin.
- Opt for fragrance-free and hypoallergenic formulations to minimize the risk of allergic reactions.
Test Products Before Use
Perform a patch test by applying a small amount of a new product to a discreet area of the skin to check for any adverse reactions before using it more widely.
Moisturize Regularly
Keeping the skin well-moisturized can help maintain its barrier function and reduce the risk of irritation and sensitivity.
By following these sun protection tips, individuals with sensitive skin can minimize the risk of sun allergies and enjoy outdoor activities with peace of mind.
Understanding Photosensitivity
Photosensitivity is a heightened sensitivity to sunlight that can result in skin reactions, such as rashes, blisters, or hives. This condition can be caused by various factors, including medications, medical conditions, and genetic predispositions.
Medications and Photosensitivity
Certain medications, such as antibiotics, antifungals, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), can increase photosensitivity. Individuals taking these medications should take extra precautions to protect themselves from the sun.
Medical Conditions and Photosensitivity
Conditions such as lupus, porphyria, and eczema can exacerbate photosensitivity and increase the risk of sun allergies. Individuals with these conditions should work closely with their healthcare providers to manage their symptoms and minimize sun exposure.
Understanding the factors that contribute to photosensitivity is essential for developing effective strategies to manage and prevent sun allergies.
Impact of Sun Allergy on Daily Life
Sun allergies can significantly impact an individual's daily life, affecting their ability to participate in outdoor activities and enjoy time in the sun. Common challenges faced by individuals with sun allergies include:
- Limiting Outdoor Activities: Avoiding sun exposure may restrict participation in outdoor sports, events, and hobbies.
- Social Implications: Fear of triggering a reaction can lead to social withdrawal and isolation.
- Psychological Impact: Sun allergies can cause anxiety and stress, particularly during the summer months when sun exposure is more likely.
By understanding the challenges posed by sun allergies and implementing effective management strategies, individuals can lead fulfilling lives and participate in activities they enjoy.
Sun Allergy in Children
Children are not immune to sun allergies, and their delicate skin makes them particularly susceptible to photosensitivity. Parents should take special care to protect their children from sun exposure and recognize the signs of sun allergies in young ones.
Symptoms in Children
Common symptoms of sun allergies in children include red, itchy rashes, blisters, and hives. These symptoms may appear on areas of the skin exposed to sunlight, such as the face, arms, and legs.
Protective Measures for Children
- Dressing children in lightweight, long-sleeved clothing and wide-brimmed hats can provide physical protection against UV rays.
- Applying child-friendly, broad-spectrum sunscreen with a high SPF can help shield delicate skin.
- Encouraging play in shaded areas and providing regular breaks indoors can reduce sun exposure.
By taking these protective measures, parents can help their children enjoy outdoor activities while minimizing the risk of sun allergies.
Latest Research and Developments
Ongoing research continues to advance our understanding of sun allergies and develop new treatments to manage this condition effectively. Recent developments include:
Advancements in Phototherapy
New techniques in phototherapy, such as narrowband UVB therapy, are showing promise in reducing the severity of sun allergy reactions by gradually desensitizing the skin to sunlight.
Innovations in Sunscreen Formulations
Researchers are developing new sunscreen formulations that provide enhanced protection against UV radiation while minimizing skin irritation and allergic reactions.
Genetic Research
Studies exploring the genetic factors contributing to sun allergies are helping identify individuals at higher risk and guide personalized prevention and treatment strategies.
Staying informed about the latest research and developments can empower individuals with sun allergies to make informed decisions about their health and well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common triggers for sun allergies?
Common triggers include sun exposure, certain medications, and specific skin care products. Understanding personal triggers can help manage and prevent reactions.
Can sun allergies develop suddenly?
Yes, sun allergies can develop suddenly, even in individuals who have not previously experienced photosensitivity. Factors such as medication changes or increased sun exposure can contribute to sudden onset.
Is sun allergy the same as sunburn?
No, sun allergy involves an immune system reaction, while sunburn is a direct result of UV radiation damaging the skin. Sun allergies can occur even with minimal sun exposure.
Are there long-term effects of sun allergies?
While most sun allergy symptoms resolve with treatment and sun avoidance, repeated reactions can cause long-term skin damage and increase the risk of skin cancer.
Can lifestyle changes help manage sun allergies?
Yes, lifestyle changes such as wearing protective clothing, using sunscreen, and avoiding peak sunlight hours can effectively manage sun allergies and reduce the risk of reactions.
Is it safe to use tanning beds if I have a sun allergy?
No, tanning beds emit UV radiation that can trigger sun allergy reactions and increase the risk of skin damage and cancer. It is best to avoid tanning beds and opt for safer alternatives.
Conclusion
Allergy to the sun, or photosensitivity, is a challenging condition that affects many individuals worldwide. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and management strategies for sun allergies is essential for effectively managing this condition and enjoying outdoor activities with confidence. By implementing preventive measures, seeking timely medical advice, and staying informed about the latest research, individuals with sun allergies can lead fulfilling lives and minimize the impact of sun exposure on their health and well-being.