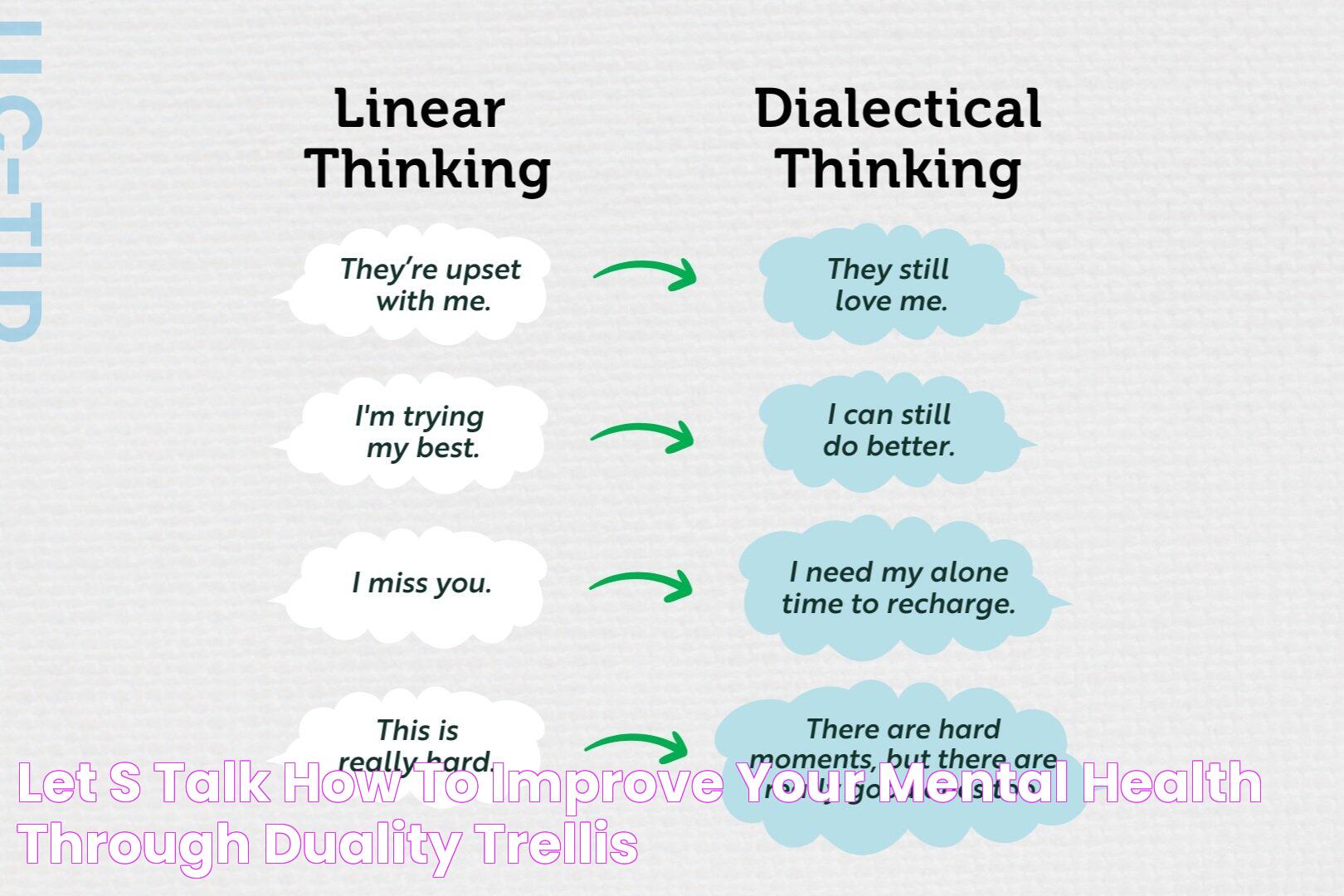
The concept of duality meaning resonates deeply across various domains – from science to philosophy, art to spirituality. It is a term that is often used to signify balance and contrast, embodying the idea that two opposing forces or ideas can coexist harmoniously. Duality is seen in nature, human behavior, and even within ourselves, suggesting a fundamental truth about the universe: that opposites are not separate, but rather interconnected.
Duality meaning is not just a philosophical concept, but a principle that finds its relevance in everyday life. It encourages us to look beyond the surface and understand the intrinsic value of opposition. By appreciating the duality within our experiences, we can gain a more nuanced understanding of the world around us. This understanding can lead to personal growth and a more harmonious existence, as we learn to balance the light and dark, the good and the bad, the joy and the sorrow.
As we delve deeper into the duality meaning, we uncover the layers of complexity that define our perceptions and realities. It challenges us to embrace contradictions and see them as complementary rather than conflicting. In this exploration, we will cover various aspects of duality, from its philosophical underpinnings to its practical implications in modern life, aiming to provide a comprehensive view that is both enlightening and thought-provoking.
Read also:Makeup Forever Cosmetics Your Ultimate Beauty Companion
Table of Contents
- Philosophical Duality: What Does It Mean?
- How Does Duality Manifest in Nature?
- Cultural Expressions of Duality: Art and Literature
- What Are the Psychological Aspects of Duality?
- Duality Meaning in Spiritual Perspectives
- Scientific Principles: The Role of Duality
- How Is Duality Represented in Mythology?
- Duality Meaning and Personal Growth
- Societal Implications of Embracing Duality
- How Is Duality Portrayed in Literature?
- Artistic Interpretations of Duality
- Duality Meaning in Religion
- Balancing Contrasts: Practical Applications of Duality
- How Does Modern Society View Duality?
- Future Trends: The Evolving Understanding of Duality
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
Philosophical Duality: What Does It Mean?
Philosophical duality refers to the idea that two fundamental, often opposing, elements exist simultaneously and are integral components of the universe. This concept is rooted in the philosophical traditions of many cultures, such as the Yin and Yang in Chinese philosophy, which symbolize the balance of opposite forces. The Greek philosopher Heraclitus also touched upon duality through his assertion that "the road up and the road down are one and the same," highlighting the interconnectedness of opposites.
In Western philosophy, duality is often discussed in terms of mind and body, good and evil, or reality and illusion. These dualities form the basis of many philosophical debates and have been explored extensively by thinkers such as Descartes, who proposed the mind-body dualism, and Kant, who examined the duality between phenomena (what we perceive) and noumena (what is beyond perception).
Understanding philosophical duality involves recognizing that these opposing elements are not in conflict but are complementary. They create a dynamic equilibrium, where each aspect is necessary for the existence and definition of the other. This balance is crucial in seeking a holistic understanding of life and the universe.
How Does Duality Manifest in Nature?
Nature is a testament to duality, presenting countless examples of balance and contrast. The cycles of day and night, the changing seasons, and the balance of ecosystems all illustrate duality in action. These natural phenomena demonstrate that duality is not about opposition but rather about harmony.
In biology, duality can be seen in the symbiotic relationships between species, where two different organisms live in close association and benefit from each other. Predator and prey dynamics also exemplify duality, where the survival of one depends on the other, maintaining ecological balance.
The concept of duality in nature extends to the molecular level with the idea of complementary base pairing in DNA, where adenine pairs with thymine and cytosine pairs with guanine. This duality is essential for the accurate replication and functioning of genetic material.
Read also:Meticulous Definition A Detailed Insight Into Precision And Accuracy
Cultural Expressions of Duality: Art and Literature
Art and literature have long been arenas where duality is explored and expressed. Artists and writers use duality to convey complex narratives and themes, often highlighting the coexistence of contrasting ideas and emotions.
In art, duality is often represented through contrasting colors, light and shadow, or symmetrical compositions. These techniques create visual tension and balance, inviting viewers to explore deeper meanings and interpretations.
Literature, on the other hand, uses duality to develop characters, plotlines, and conflicts. Classic works like Shakespeare's "Macbeth" and Dostoevsky's "Crime and Punishment" delve into the duality of human nature, exploring themes of morality, identity, and redemption.
What Are the Psychological Aspects of Duality?
Psychologically, duality is inherent in the human experience, often manifesting as internal conflicts or contrasting desires. Carl Jung, a prominent psychologist, introduced the concept of the "shadow," representing the unconscious part of the personality that contains repressed weaknesses and instincts. Recognizing and integrating this shadow self is crucial for personal development and achieving psychological balance.
The duality of emotions is another significant psychological aspect. People often experience conflicting emotions simultaneously, such as love and hate or joy and sadness. Accepting these emotional dualities can lead to greater self-awareness and emotional intelligence.
Moreover, the duality of the conscious and unconscious mind plays a vital role in shaping behavior and perceptions. Understanding this duality can help individuals navigate their thoughts and actions more effectively, leading to improved mental health and well-being.
Duality Meaning in Spiritual Perspectives
In spirituality, duality is often seen as a path to enlightenment, where the goal is to transcend dualistic thinking and realize the unity of all things. Many spiritual traditions emphasize the importance of balancing dual forces, such as light and darkness, to achieve spiritual growth and harmony.
For instance, Hinduism and Buddhism both explore the duality of samsara (the cycle of birth and death) and nirvana (liberation from the cycle). Understanding and transcending this duality is seen as essential for spiritual liberation.
Similarly, in Christianity, duality is explored through the concepts of heaven and hell, good and evil, and the material and spiritual realms. The spiritual journey involves navigating these dualities and striving for a deeper connection with the divine.
Scientific Principles: The Role of Duality
Science provides numerous examples of duality, where seemingly opposing forces or concepts coexist and complement each other. One of the most well-known examples is the wave-particle duality of light, a fundamental concept in quantum mechanics. This duality describes how light can exhibit both wave-like and particle-like properties, depending on the experimental conditions.
Another scientific principle that embodies duality is the concept of matter and antimatter. These are two forms of matter that are mirror images of each other, and their interaction can result in annihilation, releasing energy.
Duality in science is not limited to physics. In biology, the duality of nature versus nurture explores the interplay between genetic inheritance and environmental factors in shaping an individual's traits and behaviors.
How Is Duality Represented in Mythology?
Mythology from various cultures often incorporates dualities to explain natural phenomena, moral dilemmas, or human characteristics. These stories use duality to convey lessons and explore the complexities of life.
In Egyptian mythology, the duality of the god Osiris and his brother Seth represents the struggle between order and chaos. This myth encapsulates the idea that both forces are necessary for balance in the universe.
Similarly, in Norse mythology, the duality of gods and giants symbolizes the tension between creation and destruction, a recurring theme in many mythological narratives.
Duality Meaning and Personal Growth
Understanding duality can significantly impact personal growth and development. By embracing the dualities within ourselves and our experiences, we can cultivate a more balanced and fulfilling life.
Recognizing the coexistence of strengths and weaknesses allows for greater self-acceptance and humility. It encourages individuals to work on their flaws while appreciating their positive attributes.
Furthermore, understanding duality can enhance decision-making skills, as it promotes considering multiple perspectives and finding a middle ground. This approach can lead to more thoughtful and effective solutions in personal and professional contexts.
Societal Implications of Embracing Duality
Embracing duality at a societal level can promote tolerance, understanding, and cooperation among diverse groups. Acknowledging the dualities within cultural, political, and social systems can lead to more inclusive and harmonious societies.
For instance, recognizing the duality of individual rights and collective responsibilities can guide policymaking and governance, ensuring that both personal freedoms and social welfare are balanced.
Moreover, understanding duality can foster empathy and respect for different viewpoints, reducing conflicts and promoting peaceful coexistence in an increasingly interconnected world.
How Is Duality Portrayed in Literature?
In literature, duality is a powerful tool for exploring themes and character development. Authors use duality to create complex characters and narratives that reflect the multifaceted nature of human experience.
Narratives often revolve around characters facing internal or external conflicts, embodying duality through their choices, motivations, and transformations. This portrayal allows readers to engage with the story on a deeper level, as they relate to the universal struggle between opposing forces.
Literary duality also extends to thematic elements, such as the contrast between freedom and confinement, love and betrayal, or hope and despair. These dualities enrich the narrative and provide layers of meaning for readers to explore.
Artistic Interpretations of Duality
Artists have long been inspired by duality, using it as a means to convey meaning and provoke thought. Through various mediums, such as painting, sculpture, and photography, artists explore the interplay of contrasting elements to create visually and intellectually stimulating works.
In painting, duality is often expressed through the use of complementary colors, juxtaposition of light and shadow, or the balance of symmetry and asymmetry. These techniques draw the viewer's attention and invite interpretation.
Sculpture and installation art also utilize duality, playing with the contrast between materials, forms, and spaces. This approach challenges conventional perceptions and encourages viewers to engage with art in new and meaningful ways.
Duality Meaning in Religion
Religion often addresses duality through its teachings and symbols, exploring the relationship between the divine and the earthly, the sacred and the profane, or the temporal and the eternal.
In Christianity, duality is evident in the concepts of heaven and hell, sin and redemption, and the human and divine nature of Christ. These dualities underscore the spiritual journey and the choices individuals must make in their pursuit of salvation.
In Islam, the duality of seen (the visible world) and unseen (the spiritual realm) emphasizes the importance of faith and the belief in a reality beyond what is perceptible to the senses.
Balancing Contrasts: Practical Applications of Duality
The concept of duality can be applied practically in various areas of life, from personal decision-making to professional strategies. By balancing contrasts, individuals and organizations can achieve more effective and holistic outcomes.
In personal life, embracing duality can enhance relationships, as it encourages understanding and compromise between differing viewpoints or needs. It can also aid in stress management, as individuals learn to balance work and leisure, ambition, and contentment.
In the professional realm, duality can guide strategic planning and innovation, as organizations seek to balance risk and reward, short-term goals, and long-term vision. This approach can lead to sustainable growth and success in a competitive marketplace.
How Does Modern Society View Duality?
In modern society, duality is increasingly recognized as a valuable framework for understanding complexity and navigating change. As globalization and technological advancements continue to reshape the world, the ability to balance opposing forces becomes more crucial.
Contemporary discussions around duality often focus on issues such as cultural diversity, technological progress, and environmental sustainability. By acknowledging and embracing duality in these areas, societies can foster innovation, resilience, and cohesion.
Additionally, the rise of interdisciplinary approaches in education and research highlights the importance of duality in bridging gaps between different fields and fostering holistic understanding and solutions.
Future Trends: The Evolving Understanding of Duality
The understanding of duality is likely to evolve as new insights and discoveries challenge existing paradigms. As science, technology, and society continue to advance, the exploration of duality will remain a dynamic and relevant pursuit.
Emerging fields such as quantum computing, artificial intelligence, and biotechnology may offer new perspectives on duality, revealing previously unimagined connections and possibilities.
Furthermore, the integration of diverse cultural and philosophical perspectives will enrich the dialogue around duality, fostering a more inclusive and comprehensive understanding of this timeless concept.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the duality meaning in philosophy?
- How does duality manifest in nature?
- What role does duality play in art and literature?
- How can understanding duality contribute to personal growth?
- What are the societal implications of embracing duality?
- How is duality explored in modern scientific principles?
In philosophy, duality refers to the presence and interplay of two fundamental, often opposing, elements or forces within the universe. It is a concept explored in various philosophical traditions, such as Eastern philosophies' Yin and Yang and Western mind-body dualism.
Duality in nature is evident in phenomena such as day and night, predator-prey relationships, and the complementary base pairing in DNA. These examples illustrate the balance and harmony achieved through duality.
In art and literature, duality is used to explore complex themes and characters. Artists and writers employ contrasting elements to create tension, balance, and deeper meaning in their works.
Understanding duality can enhance personal growth by promoting self-awareness, acceptance, and balance. It encourages individuals to embrace their strengths and weaknesses and consider multiple perspectives in decision-making.
Embracing duality at a societal level can promote tolerance, empathy, and cooperation among diverse groups. It can guide policymaking and governance, ensuring a balance between individual rights and collective responsibilities.
Modern scientific principles, such as wave-particle duality in quantum mechanics and the interplay of matter and antimatter, illustrate the dualities present in the natural world. These principles highlight the coexistence and complementarity of opposing forces.
Conclusion
Duality meaning is a profound concept that transcends disciplines and domains, offering a lens through which we can explore the complexities of life and the universe. By understanding and embracing duality, we can achieve balance, harmony, and deeper insights into our existence.
From philosophy to nature, art to science, and personal growth to societal progress, duality provides a framework for navigating the dynamic interplay of opposing forces. As we continue to explore this concept, we open ourselves to new possibilities and a richer understanding of the world around us.
In a rapidly changing world, the ability to recognize and balance dualities will be crucial for fostering innovation, resilience, and cohesion. Embracing duality is not just about acknowledging the coexistence of opposites but about finding the harmony that lies within their interaction.