PTSD means, or Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder, is a complex mental health condition that emerges after an individual experiences or witnesses a traumatic event. It is a severe psychological response that can significantly impact daily life, affecting emotional well-being, relationships, and overall quality of life. This disorder can manifest through various symptoms, including flashbacks, nightmares, severe anxiety, and uncontrollable thoughts about the event. Understanding PTSD means recognizing its profound effects and the importance of seeking appropriate treatment and support.
In recent years, awareness about PTSD means has grown substantially, largely due to increased research and advocacy efforts. This disorder is not limited to military personnel; it affects people from all walks of life, including survivors of accidents, natural disasters, assaults, and other traumatic experiences. The impact of PTSD means is far-reaching, influencing not only the individuals who experience it but also their families, communities, and society at large. It is crucial to shed light on the realities of PTSD means to foster empathy, understanding, and support for those affected.
As we delve deeper into the topic of PTSD means, this article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the disorder, including its symptoms, causes, and treatment options. By exploring various aspects of PTSD means, we hope to offer valuable insights and resources for individuals seeking to understand or manage this condition. Whether you are directly affected by PTSD means or know someone who is, this guide is designed to offer hope and practical guidance for navigating the challenges associated with this disorder.
Read also:Silk Pillow Case Elevate Your Sleep Experience With Luxurious Comfort
Table of Contents
- What is PTSD?
- Symptoms of PTSD
- Causes of PTSD
- What are the Risk Factors for PTSD?
- How is PTSD Diagnosed?
- Treatment Options for PTSD
- Coping Strategies for Living with PTSD
- Impact of PTSD on Daily Life
- PTSD in Children and Adolescents
- Importance of Support Systems
- PTSD and Co-occurring Disorders
- Future Research and Developments in PTSD
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
What is PTSD?
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) is a mental health condition that can occur after experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event. The disorder involves a range of symptoms that can significantly disrupt a person's life. PTSD means dealing with persistent mental and emotional distress triggered by past experiences. It is classified as an anxiety disorder, and its symptoms can vary widely among individuals.
PTSD means experiencing symptoms such as flashbacks, where the individual relives the traumatic event, and nightmares that disturb sleep. People with PTSD may also experience severe anxiety, emotional numbness, and a heightened state of alertness known as hyperarousal. These symptoms can interfere with daily activities and relationships, making it challenging to maintain a sense of normalcy.
Understanding PTSD means recognizing that it is a genuine and serious mental health condition that requires appropriate attention and treatment. It is not a sign of weakness or a character flaw, and individuals affected by PTSD should not be stigmatized or blamed for their condition. With proper diagnosis and treatment, many people with PTSD can find relief from their symptoms and regain control over their lives.
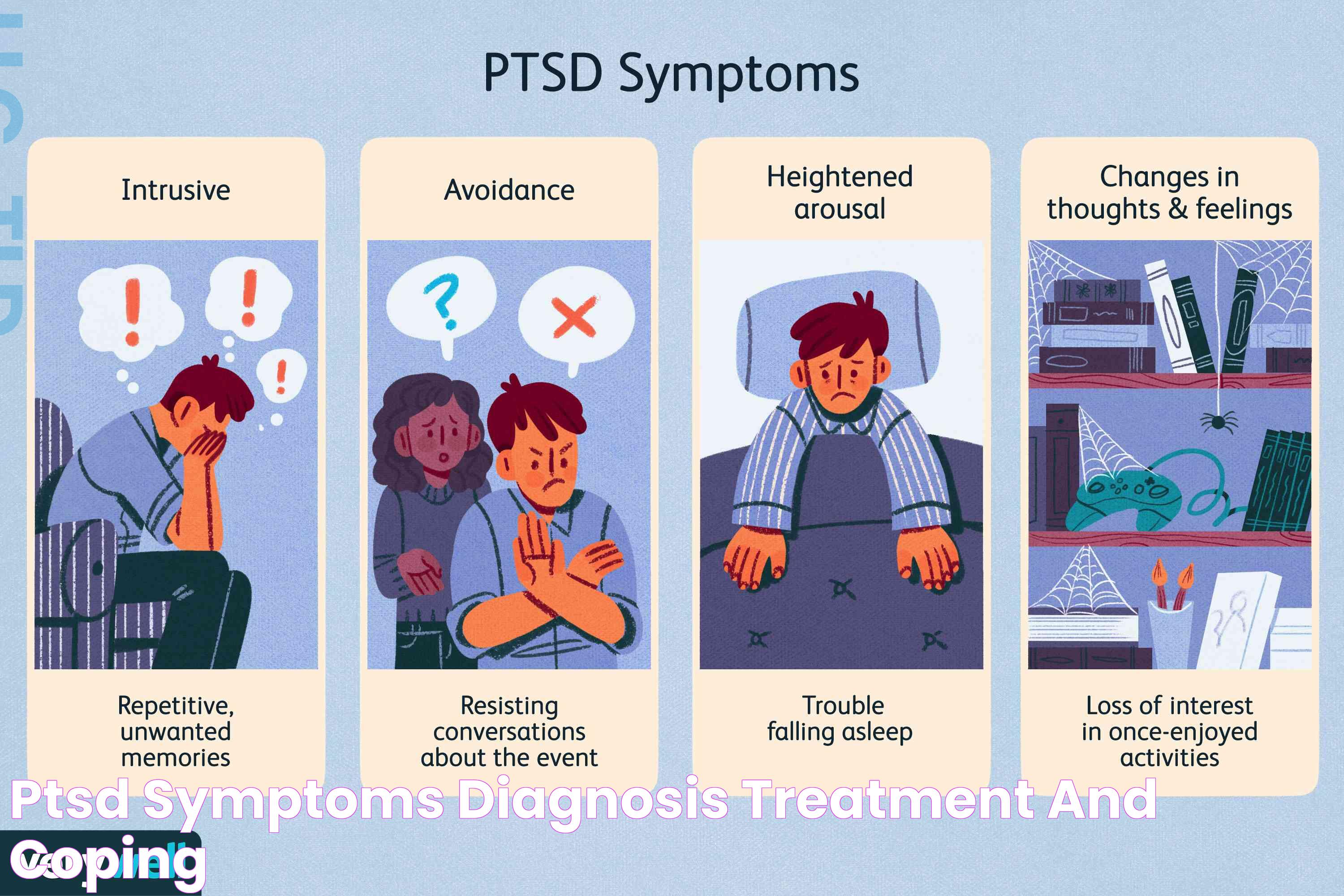
Symptoms of PTSD
PTSD symptoms are categorized into four main types: intrusive memories, avoidance, negative changes in thinking and mood, and changes in physical and emotional reactions. These symptoms can vary in intensity and duration, affecting each individual differently.
Intrusive Memories
- Recurrent, unwanted distressing memories of the traumatic event
- Flashbacks, or reliving the traumatic event as if it were happening again
- Upsetting dreams or nightmares about the traumatic event
- Severe emotional distress or physical reactions to reminders of the trauma
Avoidance
- Efforts to avoid thinking about or discussing the traumatic event
- Avoidance of places, activities, or people that remind one of the trauma
Negative Changes in Thinking and Mood
- Negative thoughts about oneself, others, or the world
- Hopelessness about the future
- Memory problems, including difficulty remembering important aspects of the traumatic event
- Difficulty maintaining close relationships
- Feeling detached or estranged from family and friends
- Lack of interest in activities once enjoyed
- Difficulty experiencing positive emotions
Changes in Physical and Emotional Reactions
- Being easily startled or frightened
- Always being on guard for danger
- Self-destructive behavior, such as drinking too much or driving too fast
- Trouble sleeping
- Trouble concentrating
- Irritability, angry outbursts, or aggressive behavior
- Overwhelming guilt or shame
PTSD symptoms can vary over time and may intensify during periods of stress or when exposed to reminders of the traumatic event. It is crucial to seek professional help if symptoms persist or interfere with daily functioning, as early intervention can significantly improve outcomes.
Causes of PTSD
PTSD means understanding that the disorder results from a complex interplay of factors rather than a single cause. Although the primary trigger is exposure to a traumatic event, several other factors can contribute to the development of PTSD.
Read also:Horoscope June 21st A Guide To Celestial Insights
Traumatic events that may lead to PTSD include:
- Combat exposure
- Childhood physical abuse
- Sexual violence
- Physical assault
- Being threatened with a weapon
- Accidents
- Natural disasters
Not everyone who experiences trauma will develop PTSD. PTSD means recognizing that certain risk factors can increase the likelihood of developing the disorder, such as a family history of mental health issues, previous traumatic experiences, and the presence of other mental health conditions.
Research suggests that PTSD may be linked to an imbalance in brain chemicals that regulate stress responses. Genetic factors may also play a role, as some individuals may be more susceptible to developing PTSD due to inherited traits. Additionally, environmental factors, such as a lack of social support, can influence the onset and severity of PTSD symptoms.
What are the Risk Factors for PTSD?
PTSD means identifying certain risk factors that can increase an individual's vulnerability to developing the disorder. These factors can be biological, psychological, or social in nature, and they may interact in complex ways.
Biological Risk Factors
- Genetic predisposition to anxiety or mood disorders
- Differences in brain structure or function
- Hormonal imbalances that affect stress responses
Psychological Risk Factors
- Previous history of trauma or abuse
- Existing mental health conditions, such as depression or anxiety
- Personality traits, such as a high degree of neuroticism
Social Risk Factors
- Lack of social support or isolation
- Exposure to ongoing stress or adversity
- Cultural or societal factors that stigmatize mental health issues
Understanding these risk factors is essential for identifying individuals who may be at a higher risk of developing PTSD and implementing preventive measures. Early intervention and support can mitigate the impact of these risk factors and improve outcomes for those affected by PTSD.
How is PTSD Diagnosed?
Diagnosis of PTSD means a comprehensive evaluation by a mental health professional, who will assess the individual's symptoms, history, and the impact of the traumatic event. The process typically involves several steps:
Clinical Interview
The mental health professional will conduct a thorough interview to gather information about the individual's experiences, symptoms, and how these affect daily life. This conversation helps determine whether the symptoms align with PTSD criteria as outlined in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5).
Psychological Assessment
In some cases, standardized questionnaires or psychological tests may be used to assess the severity of symptoms and identify any co-occurring mental health conditions.
Medical Evaluation
A medical evaluation may be necessary to rule out any physical conditions that could be contributing to the symptoms. This evaluation may include lab tests or imaging studies to assess overall health and identify any underlying issues.
Once a diagnosis is confirmed, the mental health professional will work with the individual to develop a personalized treatment plan. Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial for managing PTSD effectively and improving long-term outcomes.
Treatment Options for PTSD
Treating PTSD means addressing the disorder through a combination of therapeutic approaches tailored to the individual's needs. Effective treatment can significantly reduce symptoms and improve quality of life. Common treatment options for PTSD include:
Psychotherapy
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): This form of therapy helps individuals change negative thought patterns and behaviors. It often includes exposure therapy, which involves confronting the traumatic memories in a safe environment to reduce their impact.
- Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR): EMDR is a structured therapy that encourages the individual to recall traumatic memories while focusing on external stimuli, such as eye movements. This process can help reprocess the memories and reduce distress.
- Group Therapy: Sharing experiences with others who have similar challenges can provide support and validation. Group therapy also offers a sense of community and opportunities to learn coping strategies from peers.
Medication
Medications can be prescribed to manage symptoms of PTSD, such as depression, anxiety, and sleep disturbances. Common medications include:
- Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs)
- Serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs)
- Prazosin for managing nightmares and sleep disturbances
Medications are often used in conjunction with psychotherapy to enhance treatment outcomes. The choice of medication and dosage should be carefully monitored by a healthcare professional to minimize side effects and ensure effectiveness.
Alternative and Complementary Therapies
- Mindfulness and Meditation: Mindfulness practices can help individuals become more aware of their thoughts and feelings, reducing stress and promoting relaxation.
- Yoga and Physical Exercise: Physical activity can improve mood, reduce anxiety, and enhance overall well-being.
- Acupuncture: This traditional Chinese medicine technique may help alleviate some symptoms of PTSD by promoting relaxation and reducing stress.
Combining different treatment approaches can provide comprehensive care for individuals with PTSD, addressing both the psychological and physiological aspects of the disorder.
Coping Strategies for Living with PTSD
Living with PTSD means finding effective coping strategies to manage symptoms and improve quality of life. While professional treatment is essential, self-help strategies can also play a significant role in the recovery process. Here are some practical coping strategies for individuals with PTSD:
Building a Support Network
- Reach out to family and friends for emotional support.
- Join support groups or online communities for individuals with PTSD.
- Engage in open communication with loved ones about your experiences and needs.
Practicing Self-Care
- Maintain a regular sleep schedule and create a calming bedtime routine.
- Engage in regular physical activity to reduce stress and improve mood.
- Eat a balanced diet to support overall health and well-being.
- Incorporate relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing or progressive muscle relaxation, into your daily routine.
Managing Stress and Triggers
- Identify and avoid triggers that exacerbate symptoms.
- Develop healthy coping mechanisms, such as journaling or art therapy, to process emotions.
- Practice mindfulness or meditation to stay grounded in the present moment.
Setting Realistic Goals
- Break down larger tasks into smaller, manageable steps.
- Celebrate achievements and progress, no matter how small.
- Be patient with yourself and recognize that recovery is a gradual process.
Incorporating these coping strategies into daily life can empower individuals with PTSD to regain control over their lives and work towards recovery.
Impact of PTSD on Daily Life
PTSD means experiencing challenges that affect various aspects of daily life, including personal relationships, work, and overall well-being. Understanding the impact of PTSD on daily life is crucial for developing effective coping strategies and seeking appropriate support.
Relationships and Social Life
PTSD can strain personal relationships, leading to feelings of isolation and detachment. Individuals with PTSD may have difficulty maintaining close connections with family and friends, leading to further emotional distress. Understanding and communication from loved ones can help mitigate these challenges, fostering a supportive environment for healing.
Work and Productivity
PTSD symptoms, such as concentration difficulties and emotional distress, can impact work performance and productivity. Individuals with PTSD may find it challenging to meet job demands or maintain employment. Employers and colleagues should be aware of these challenges and provide accommodations, such as flexible schedules or support resources, to help individuals succeed in the workplace.
Physical Health
PTSD can also affect physical health, contributing to issues such as sleep disturbances, chronic pain, and increased risk of substance abuse. Addressing these physical health concerns through medical intervention and self-care strategies can enhance overall well-being and support recovery.
Recognizing the impact of PTSD on daily life is essential for implementing effective strategies to manage symptoms and improve quality of life. With appropriate support and treatment, individuals with PTSD can work towards regaining a sense of normalcy and achieving personal goals.
PTSD in Children and Adolescents
PTSD means understanding that this disorder can affect individuals of all ages, including children and adolescents. The symptoms and impact of PTSD in younger populations can differ from those in adults, requiring age-appropriate interventions and support.
Symptoms in Children
- Bedwetting or loss of previously acquired skills
- Clinginess or fear of being separated from caregivers
- Reenacting the traumatic event through play or drawings
- Physical symptoms, such as headaches or stomachaches
Symptoms in Adolescents
- Withdrawal from friends and activities
- Changes in mood or behavior, such as increased irritability or aggression
- Difficulty concentrating or academic decline
- Substance use or risky behaviors
Early intervention is crucial for children and adolescents with PTSD, as untreated symptoms can affect development and lead to long-term challenges. Age-appropriate therapies, such as play therapy or family therapy, can help young individuals process their experiences and develop healthy coping mechanisms.
Parents and caregivers play a vital role in supporting children with PTSD by providing a stable and nurturing environment. Open communication, patience, and understanding can help children feel safe and supported as they navigate their recovery journey.
Importance of Support Systems
PTSD means recognizing the vital role that support systems play in the recovery process. A strong support network can provide emotional, practical, and social resources that contribute to improved outcomes for individuals with PTSD.
Family and Friends
Family members and friends can offer essential emotional support by being present, listening without judgment, and providing reassurance. Involving loved ones in the treatment process can also enhance understanding and communication, strengthening relationships and promoting healing.
Support Groups
Joining support groups can provide a sense of community and validation, as individuals share experiences and learn from others facing similar challenges. Support groups can be a valuable resource for gaining insights, developing coping strategies, and reducing feelings of isolation.
Professional Support
Mental health professionals, such as therapists and counselors, offer specialized support and guidance throughout the recovery process. Building a strong therapeutic alliance with a professional can empower individuals with PTSD to explore their experiences, develop coping mechanisms, and work towards recovery.
Support systems are crucial for fostering resilience and promoting recovery in individuals with PTSD. Encouraging open communication, empathy, and understanding within these support networks can create a nurturing environment that facilitates healing and growth.
PTSD and Co-occurring Disorders
PTSD means acknowledging that this disorder often co-occurs with other mental health conditions, complicating diagnosis and treatment. Co-occurring disorders can exacerbate symptoms and impact overall well-being, making comprehensive care essential for effective management.
Common Co-occurring Disorders
- Depression: Individuals with PTSD may experience persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and lack of interest in activities, which can compound the emotional distress of PTSD.
- Anxiety Disorders: Generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, or social anxiety disorder may coexist with PTSD, intensifying symptoms and impacting daily life.
- Substance Use Disorders: Some individuals with PTSD may turn to alcohol or drugs as a coping mechanism, leading to substance use disorders that further complicate recovery.
- Chronic Pain: PTSD can contribute to or exacerbate chronic pain conditions, creating a cycle of physical and emotional distress.
Treatment for co-occurring disorders requires an integrated approach that addresses both PTSD and the accompanying conditions. A combination of therapy, medication, and lifestyle changes can provide comprehensive care to manage symptoms and improve overall well-being.
Future Research and Developments in PTSD
PTSD means exploring new avenues for understanding and treating the disorder, as ongoing research continues to shed light on the complexities of PTSD. Advances in neuroscience, psychology, and pharmacology are contributing to a deeper understanding of the disorder and the development of innovative treatment approaches.
Neuroscience and Brain Research
Research into the neurobiological mechanisms of PTSD is uncovering insights into how the brain processes trauma and stress. Advances in brain imaging and neuroimaging technologies are helping scientists identify specific brain regions and pathways involved in PTSD, potentially leading to targeted interventions and therapies.
Pharmacological Advances
Emerging research into new medications and treatment modalities is offering hope for more effective management of PTSD symptoms. Innovative approaches, such as the use of psychedelic-assisted therapy and novel pharmacological agents, are being explored to enhance treatment outcomes.
Innovative Therapeutic Approaches
Therapeutic approaches are evolving to incorporate cutting-edge techniques and technologies. Virtual reality therapy, for example, is being used to create controlled environments for exposure therapy, allowing individuals to confront traumatic memories in a safe and supportive setting.
Ongoing research and advancements in PTSD treatment hold promise for improving the lives of individuals affected by the disorder. By staying informed about these developments, individuals and healthcare providers can make informed decisions about treatment options and support strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does PTSD mean?
PTSD means Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder, a mental health condition triggered by experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event. It involves symptoms such as intrusive memories, avoidance, negative changes in thinking and mood, and changes in physical and emotional reactions.
Can PTSD affect anyone?
Yes, PTSD can affect anyone who has experienced or witnessed a traumatic event. It is not limited to military personnel; it can impact individuals from all backgrounds, including survivors of accidents, natural disasters, assault, and other traumatic experiences.
How is PTSD treated?
PTSD is typically treated through a combination of psychotherapy, medication, and alternative therapies. Common therapeutic approaches include Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR), and group therapy.
Is it possible to recover from PTSD?
Yes, with appropriate treatment and support, many individuals with PTSD can find relief from their symptoms and regain control over their lives. Recovery is a gradual process that involves understanding the disorder, developing coping strategies, and accessing appropriate care.
What are the risk factors for developing PTSD?
Risk factors for PTSD include genetic predisposition, previous traumatic experiences, lack of social support, and existing mental health conditions. These factors can interact in complex ways, increasing an individual's vulnerability to developing PTSD.
Can children develop PTSD?
Yes, children and adolescents can develop PTSD after experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event. Symptoms in younger individuals may differ from those in adults, requiring age-appropriate interventions and support.
Conclusion
PTSD means acknowledging the profound impact this disorder can have on individuals and their loved ones. Understanding PTSD involves recognizing its symptoms, causes, and treatment options, as well as the importance of support systems and coping strategies. With ongoing research and advancements in treatment approaches, there is hope for improving the lives of those affected by PTSD. By fostering empathy, understanding, and support, we can create a more compassionate and inclusive environment for individuals navigating the challenges of PTSD.
For more information and resources on PTSD, visit the National Institute of Mental Health website.