Women with lupus often experience a wide range of symptoms, which can vary in severity and fluctuate over time. These symptoms can affect different parts of the body, including the skin, joints, kidneys, and even the brain. Due to its unpredictable nature, lupus is often referred to as "the great imitator," as it can mimic other diseases and conditions. This makes it essential for women to be aware of the early signs of lupus and seek medical advice if they suspect they may be affected.
In this article, we will explore the signs of lupus in women, delving into the various symptoms, the process of diagnosis, and the potential impact on daily life. By understanding the intricacies of this autoimmune disease, women can take proactive steps towards managing their health and well-being. Let's delve into the signs of lupus in women and the pathways to a timely diagnosis and effective treatment.
Table of Contents
- What is Lupus?
- Lupus and Its Impact on Women
- Common Signs of Lupus in Women
- How Does Lupus Affect the Skin?
- Joint Pain and Stiffness
- Fatigue and Exhaustion
- Kidney Problems Related to Lupus
- Neurological Symptoms
- Diagnosing Lupus in Women
- Treatment Options for Lupus
- Lifestyle Changes and Management
- How to Prevent Lupus Flare-ups?
- Living with Lupus
- Frequently Asked Questions About Lupus
- Conclusion
What is Lupus?
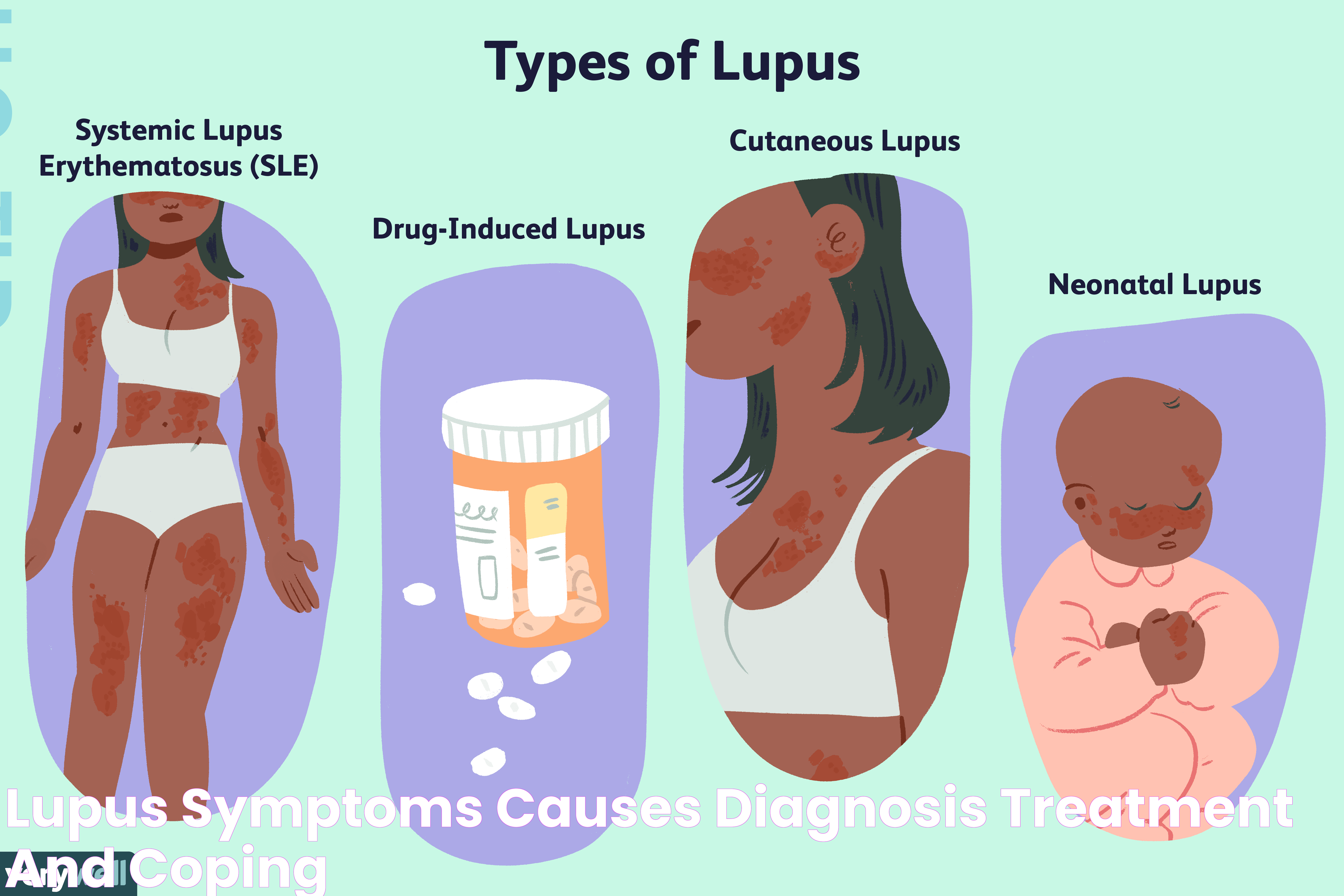
Lupus, or systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), is a chronic autoimmune disease where the body's immune system mistakenly attacks its own tissues and organs. This results in inflammation, pain, and damage to various parts of the body, including the skin, joints, kidneys, heart, lungs, and brain. Lupus is characterized by periods of remission and flare-ups, where symptoms become more severe. It is important to note that lupus can affect anyone, but it occurs more frequently in women, particularly those of African, Hispanic, Asian, and Native American descent.
Read also:Chic Short Hairstyle Ideas To Elevate Your Look
The exact cause of lupus is unknown, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic, environmental, and hormonal factors. Some potential triggers for lupus include infections, certain medications, and exposure to sunlight. Understanding the nature of lupus and its triggers is key to managing the condition effectively.
Lupus and Its Impact on Women
Lupus is more common in women than men, with approximately 90% of lupus patients being female. The disease often presents itself during a woman's reproductive years, between the ages of 15 and 44. The impact of lupus on women can be significant, affecting their physical health, emotional well-being, and quality of life.
Women with lupus may face additional challenges due to hormonal fluctuations, pregnancy, and childbirth. The disease can also increase the risk of complications during pregnancy, such as pre-eclampsia and preterm birth. As such, it is essential for women with lupus to work closely with their healthcare providers to manage their condition and minimize potential risks.
Furthermore, lupus can have a profound effect on a woman's mental health, leading to anxiety, depression, and feelings of isolation. Support from family, friends, and healthcare professionals is crucial in helping women cope with the emotional and psychological challenges posed by lupus.
Common Signs of Lupus in Women
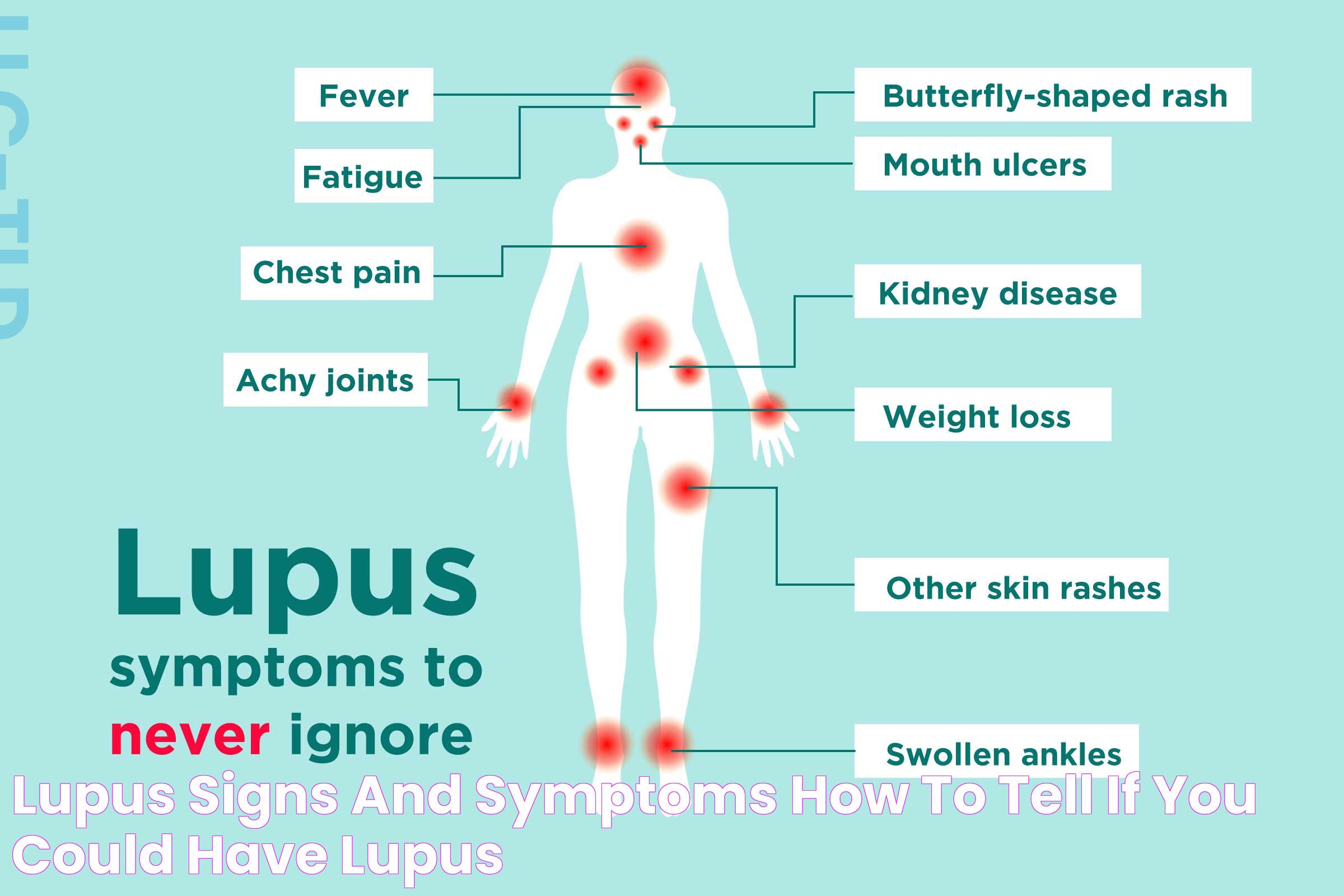
The signs of lupus in women can be diverse and may affect multiple organ systems. Some of the most common symptoms include:
- Fatigue: Feeling extremely tired and lacking energy, even after a good night's sleep.
- Joint pain and stiffness: Swelling, pain, and stiffness in the joints, particularly in the morning.
- Skin rashes: A butterfly-shaped rash across the cheeks and nose, as well as other rashes on the body.
- Hair loss: Thinning or loss of hair, which may be patchy or widespread.
- Fever: Unexplained fevers that may come and go.
- Kidney problems: Inflammation of the kidneys, leading to proteinuria (protein in the urine) and other issues.
- Chest pain: Pain in the chest when taking deep breaths, often due to inflammation of the lining around the lungs or heart.
- Mouth sores: Ulcers or sores in the mouth, which are usually painless.
- Sun sensitivity: Increased sensitivity to sunlight, causing rashes or worsening of other symptoms.
These symptoms can vary greatly from person to person and may change over time. It is essential for women to monitor their symptoms and report any changes to their healthcare provider promptly.
Read also:Nurturing Skin The Ultimate Guide To Body Lotion For Dry Skin
How Does Lupus Affect the Skin?
Lupus can have a significant impact on the skin, with approximately two-thirds of lupus patients experiencing some form of skin involvement. The most recognizable skin manifestation of lupus is the "butterfly rash," a red rash that appears across the cheeks and nose. However, lupus can cause various other skin issues, including:
- Discoid rash: Red, scaly patches that can lead to scarring, commonly found on the face, scalp, and ears.
- Subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus: Red, ring-shaped lesions that may appear on sun-exposed areas of the skin.
- Photosensitivity: Increased sensitivity to sunlight, resulting in rashes or worsening of other symptoms.
- Alopecia: Hair loss due to inflammation of the skin and hair follicles.
These skin issues can be distressing and may impact a woman's self-esteem and confidence. It is essential for women with lupus to protect their skin from sun exposure and seek medical advice for appropriate treatment and management of skin symptoms.
Joint Pain and Stiffness
Joint pain and stiffness are common symptoms of lupus, affecting up to 90% of patients. Women with lupus may experience aching, swelling, and stiffness in their joints, particularly in the hands, wrists, and knees. These symptoms are often worse in the morning and may improve throughout the day.
Lupus-related joint pain can be debilitating and may interfere with daily activities. It is important for women to work with their healthcare providers to develop a treatment plan that addresses joint pain and improves their quality of life. This may include medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications.
Fatigue and Exhaustion
Fatigue is one of the most common and challenging symptoms of lupus, affecting up to 80% of patients. Women with lupus often experience extreme tiredness and a lack of energy, even after a good night's sleep. This fatigue can be overwhelming and may interfere with daily activities, work, and social life.
Managing fatigue requires a comprehensive approach, including medications, lifestyle changes, and stress management techniques. Women with lupus should work closely with their healthcare providers to identify the underlying causes of their fatigue and develop an effective management plan.
Kidney Problems Related to Lupus
Kidney problems are a common complication of lupus, with up to 50% of patients experiencing some form of kidney involvement. Lupus nephritis, or inflammation of the kidneys, can lead to serious complications if left untreated. Symptoms of lupus-related kidney problems may include:
- Swelling: Swelling in the legs, ankles, and feet due to fluid retention.
- Foamy urine: Excessive protein in the urine, leading to foamy or frothy urine.
- High blood pressure: Elevated blood pressure due to kidney damage.
Early detection and treatment of lupus-related kidney problems are crucial to prevent long-term damage. Women with lupus should have regular check-ups and urine tests to monitor their kidney function and detect any changes promptly.
Neurological Symptoms
Lupus can also affect the central nervous system, leading to a range of neurological symptoms. These may include headaches, dizziness, memory problems, and difficulty concentrating. In some cases, lupus may cause more severe neurological issues, such as seizures, strokes, or mood disorders.
Managing neurological symptoms requires a comprehensive approach, including medications, lifestyle changes, and support from healthcare professionals. Women with lupus should work closely with their healthcare providers to address their neurological symptoms and improve their quality of life.
Diagnosing Lupus in Women
Diagnosing lupus can be challenging due to its diverse and fluctuating symptoms. There is no single test for lupus, and diagnosis often involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and laboratory tests. Some common tests used in the diagnosis of lupus include:
- Antinuclear antibody (ANA) test: A blood test that detects antibodies that attack the body's own tissues.
- Complete blood count (CBC): A test that measures the levels of red and white blood cells, hemoglobin, and platelets.
- Urinalysis: A test that examines urine for signs of kidney damage, such as protein or blood.
- Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR): A test that measures inflammation in the body.
In addition to these tests, healthcare providers may use imaging studies, such as X-rays or ultrasounds, to assess organ involvement. A thorough and accurate diagnosis is essential for developing an effective treatment plan and managing the signs of lupus in women.
Treatment Options for Lupus
The treatment of lupus is tailored to the individual's symptoms and the severity of their condition. While there is no cure for lupus, treatments aim to manage symptoms, prevent flare-ups, and minimize organ damage. Common treatment options for lupus include:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): Medications that reduce inflammation and relieve pain.
- Corticosteroids: Medications that suppress the immune system and reduce inflammation.
- Immunosuppressants: Medications that suppress the immune system to prevent it from attacking the body's own tissues.
- Antimalarials: Medications that help control lupus symptoms and prevent flare-ups.
In addition to medications, women with lupus may benefit from lifestyle changes, such as regular exercise, stress management techniques, and a healthy diet. It is essential for women with lupus to work closely with their healthcare providers to develop a comprehensive treatment plan that addresses their unique needs.
Lifestyle Changes and Management
In addition to medical treatment, lifestyle changes can play a crucial role in managing the signs of lupus in women. These changes may include:
- Regular exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity to improve overall health and well-being.
- Stress management: Practicing stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation or yoga, to manage stress and prevent flare-ups.
- Healthy diet: Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains to support overall health.
- Sun protection: Protecting the skin from sun exposure to prevent rashes and other skin symptoms.
By incorporating these lifestyle changes, women with lupus can improve their quality of life and reduce the frequency and severity of flare-ups. It is essential for women with lupus to work closely with their healthcare providers to develop a personalized management plan that addresses their unique needs.
How to Prevent Lupus Flare-ups?
Preventing lupus flare-ups requires a proactive approach to managing the disease and minimizing potential triggers. Some strategies to prevent flare-ups include:
- Adhering to treatment plans: Taking medications as prescribed and attending regular check-ups with healthcare providers.
- Managing stress: Practicing stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation or yoga, to prevent flare-ups.
- Protecting the skin: Wearing sunscreen and protective clothing to prevent sun exposure.
- Monitoring symptoms: Keeping track of symptoms and reporting any changes to healthcare providers promptly.
By following these strategies, women with lupus can reduce the frequency and severity of flare-ups and maintain a better quality of life. It is essential for women with lupus to work closely with their healthcare providers to develop a comprehensive management plan that addresses their unique needs.
Living with Lupus
Living with lupus can be challenging, but with the right support and management strategies, women can lead fulfilling and productive lives. It is essential for women with lupus to build a strong support network, including family, friends, and healthcare professionals, to help them cope with the emotional and physical challenges posed by the disease.
Women with lupus should also prioritize self-care and engage in activities that promote overall health and well-being, such as regular exercise, a healthy diet, and stress management techniques. By taking a proactive approach to managing the disease, women with lupus can improve their quality of life and reduce the impact of the signs of lupus in women.
Frequently Asked Questions About Lupus
- What causes lupus? While the exact cause of lupus is unknown, it is believed to involve a combination of genetic, environmental, and hormonal factors.
- Can lupus be cured? There is currently no cure for lupus, but treatments are available to manage symptoms and prevent flare-ups.
- Is lupus hereditary? Lupus is not directly inherited, but having a family history of the disease may increase the risk of developing it.
- How is lupus diagnosed? Lupus is diagnosed through a combination of medical history, physical examination, and laboratory tests.
- Can lupus affect pregnancy? Yes, lupus can increase the risk of complications during pregnancy, such as pre-eclampsia and preterm birth.
- What lifestyle changes can help manage lupus? Regular exercise, stress management, a healthy diet, and sun protection can help manage lupus symptoms and prevent flare-ups.
Conclusion
Understanding the signs of lupus in women is crucial for early detection and effective management of this complex autoimmune disease. By being aware of the diverse symptoms and working closely with healthcare providers, women with lupus can develop personalized treatment plans that address their unique needs and improve their quality of life. A proactive approach to managing the disease, including lifestyle changes and support from family and friends, can help women with lupus lead fulfilling and productive lives.
For more information on lupus and its management, visit reputable sources such as the Lupus Foundation of America (https://www.lupus.org).