Skin cancer is a crucial concern for many, as it affects millions of people worldwide. Understanding what it looks like is essential for early detection and successful treatment. This type of cancer can manifest in various forms, making it vital for individuals to be aware of the visual indicators that may suggest its presence. By recognizing these signs, one can seek medical attention promptly, potentially improving outcomes and reducing risks. Skin cancer can appear in several ways, such as new growths, changes in existing moles, or lumps on the skin. These can vary in color, size, and shape, often appearing as irregularly shaped spots that are either flesh-colored, red, black, or brown. It's important to note that not all skin irregularities are cancerous, but it's better to be cautious and consult a healthcare professional if there are any concerns.
Being informed about skin cancer's appearance is crucial not only for individuals but also for caregivers and health practitioners. With various types of skin cancer, each with distinct characteristics, recognizing the signs can be challenging. However, with knowledge and vigilance, many cases of skin cancer can be identified early, leading to better management and treatment options. By being proactive and attentive, one can contribute to their own health and well-being.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the visual aspects of skin cancer, exploring different forms and their appearances. We'll also discuss the importance of regular skin checks and provide tips on how to perform self-examinations. Whether you're looking to educate yourself or help a loved one, this article aims to empower you with the knowledge needed to identify and address potential skin cancer concerns effectively.
Read also:Mastering The Art Of Bow Tying A Comprehensive Guide
Table of Contents
- Types of Skin Cancer
- The Visual Signs of Melanoma
- Identifying Basal Cell Carcinoma
- Spotting Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- What does skin cancer look like on different skin tones?
- How to Perform a Self-Examination
- The Role of Dermatologists in Skin Cancer Detection
- Are there risk factors for skin cancer?
- How do environmental factors affect skin cancer appearance?
- Prevention Strategies for Skin Cancer
- Importance of Sunscreen in Preventing Skin Cancer
- What does skin cancer look like after treatment?
- FAQs
- Conclusion
Types of Skin Cancer
Understanding the various types of skin cancer is fundamental for recognizing their distinct appearances. The primary types of skin cancer include melanoma, basal cell carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma. Each type has unique characteristics that differentiate it from the others.
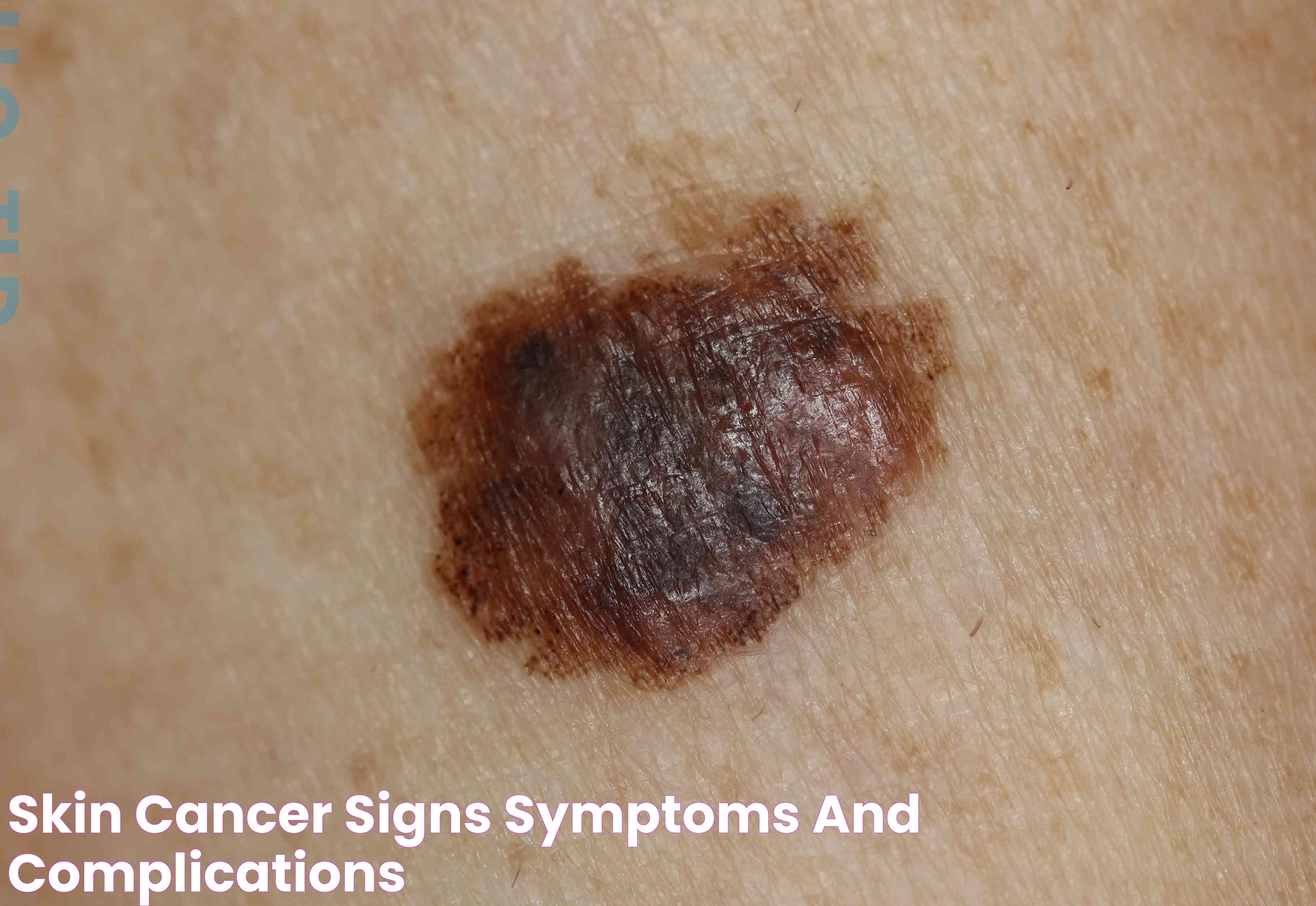
Melanoma is one of the most severe forms of skin cancer, known for its rapid spread if not detected early. It often appears as a new mole or changes an existing mole's appearance. The ABCDE rule is commonly used to identify melanoma: Asymmetry, Border irregularity, Color variation, Diameter over 6mm, and Evolving over time.
Basal cell carcinoma is the most common form of skin cancer, usually occurring in sun-exposed areas such as the face and neck. It appears as a waxy bump or a flat, flesh-colored lesion. Although it grows slowly, it can cause significant damage if left untreated.
Squamous cell carcinoma is another prevalent type that often develops on sun-exposed parts of the body. It may present as a firm, red nodule or a flat sore with a scaly crust. This type of cancer can also spread to other parts of the body, making early detection crucial.
The Visual Signs of Melanoma
Melanoma presents some of the most distinct visual signs compared to other types of skin cancer. It is crucial to recognize these signs early, as melanoma can be life-threatening if not treated promptly. Here's how you can identify melanoma:
- Asymmetry: One half of the mole doesn't match the other half, which is a key indicator of melanoma.
- Border: Look for borders that are irregular, ragged, or blurred. This is a common trait of melanoma lesions.
- Color: Melanomas often contain multiple colors, such as shades of brown, black, or even patches of red, white, or blue.
- Diameter: Melanomas are typically larger than 6mm, about the size of a pencil eraser.
- Evolving: Watch for any changes in size, shape, or color over time, as these could indicate melanoma.
It is important to note that some melanomas may not follow all of these criteria, but if you notice any changes or new growths on your skin, it's imperative to consult a healthcare professional for further evaluation.
Read also:Jennifer Garner Daughter A Unique Insight Into Her Life
Identifying Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is the most frequently occurring type of skin cancer. Although it is less likely to spread to other parts of the body, understanding its appearance is essential for early intervention. Here's how you can identify basal cell carcinoma:
Appearance: BCC often appears as a small, shiny or pearly bump on the skin, particularly on sun-exposed areas like the face, ears, or neck. It can also appear as a flat, flesh-colored or brown scar-like lesion.
Texture: The texture of BCC lesions can vary. They may be smooth or have a slightly raised edge. Some lesions might even appear crusty or bleed easily.
Growth Pattern: BCC tends to grow slowly over time. It might start as a small lesion and gradually increase in size. Despite its slow growth, it can cause significant damage if left untreated, as it can penetrate deeper layers of the skin.
While BCC is less aggressive than melanoma, early detection and treatment are crucial to prevent potential complications. If you notice any new or unusual growths on your skin, it's advisable to seek medical advice promptly.
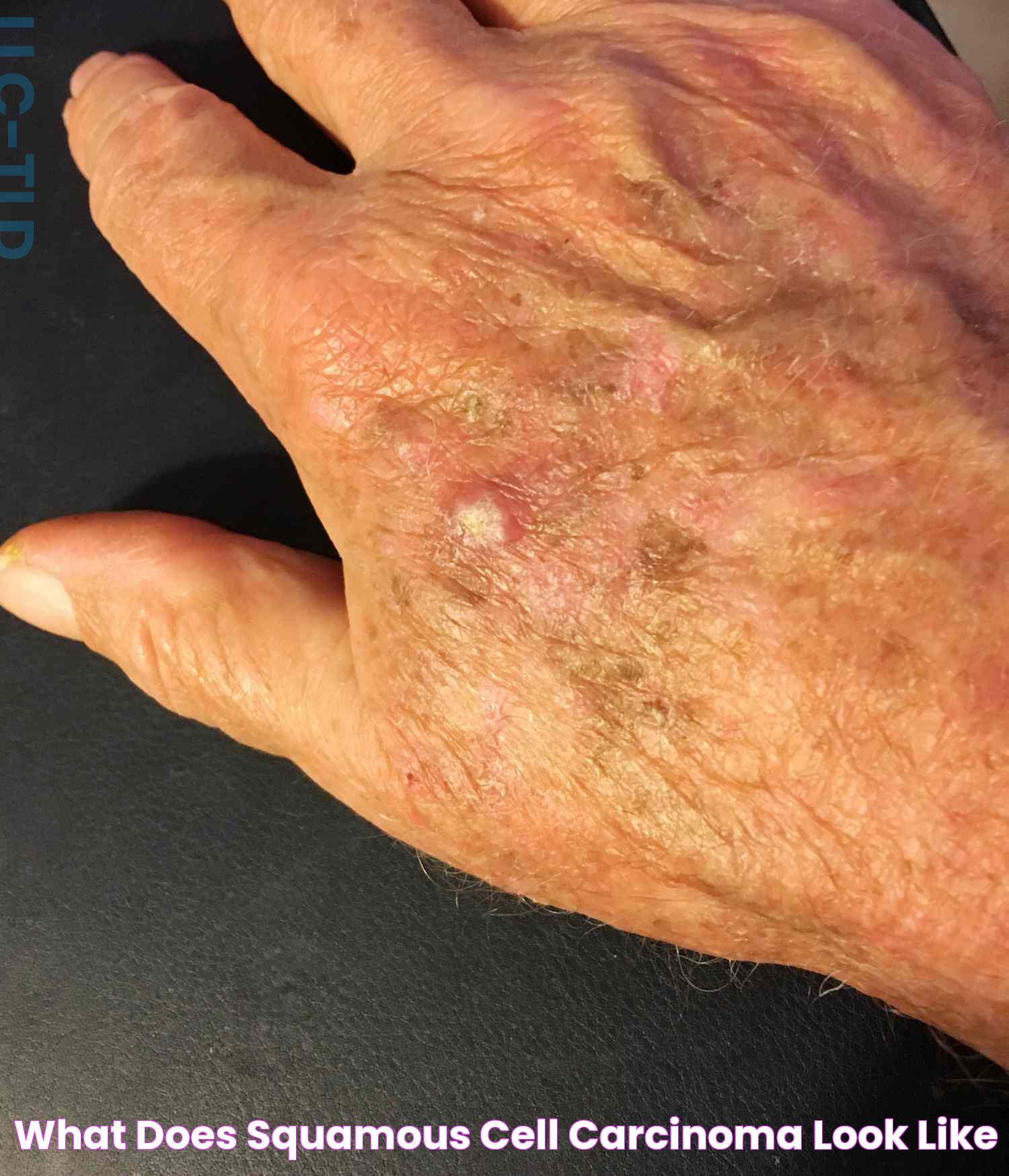
Spotting Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) is another common form of skin cancer, characterized by its potential to spread to other parts of the body if not treated early. Recognizing its appearance is vital for timely intervention. Here's how you can spot squamous cell carcinoma:
Appearance: SCC often appears as a firm, red nodule or a flat sore with a scaly crust. It can also manifest as a rough, scaly patch that may bleed or become crusty.
Location: This type of cancer frequently occurs in sun-exposed areas, such as the face, ears, neck, lips, and backs of the hands. However, it can also develop on other parts of the body that are less exposed to the sun.
Growth Pattern: SCC lesions can grow rapidly, making early detection essential. They may start as small, rough patches and evolve into larger, more pronounced lesions.
Due to its potential to spread, early diagnosis and treatment of SCC are crucial. Regular skin checks and awareness of any changes in your skin can aid in early detection and improve treatment outcomes.
What does skin cancer look like on different skin tones?
Skin cancer can manifest differently across various skin tones, making it essential to understand these variations for accurate identification and diagnosis. Here's how skin cancer may appear on different skin tones:
Light Skin Tones: On lighter skin tones, skin cancer lesions are often more noticeable due to the contrast between the lesion and the surrounding skin. Melanomas, for instance, may appear as dark spots or moles against light skin.
Medium Skin Tones: For individuals with medium skin tones, skin cancer may present as dark or discolored patches that are distinct from the natural skin color. These lesions might be less noticeable compared to lighter skin tones, necessitating careful observation.
Dark Skin Tones: On darker skin tones, skin cancer lesions can be more challenging to detect. Melanomas may appear as dark brown or black spots, while other types of skin cancer might manifest as lighter patches or changes in skin texture.
Regardless of skin tone, it is important to be vigilant about any new or changing lesions. Regular skin checks and consultations with a dermatologist can aid in early detection and improve treatment outcomes for all skin types.
How to Perform a Self-Examination
Regular self-examinations are a crucial aspect of detecting skin cancer early. By conducting thorough checks, you can identify any unusual changes or growths and seek medical advice promptly. Here's how to perform a self-examination:
- Choose a Well-Lit Area: Perform the examination in a well-lit room with a full-length mirror and a hand-held mirror for better visibility.
- Examine Your Entire Body: Start from your head and work your way down to your toes. Pay attention to all areas, including your scalp, between your fingers and toes, and the soles of your feet.
- Check for New or Changing Lesions: Look for any new growths, moles, or changes in existing moles. Note any spots that are asymmetrical, have irregular borders, or exhibit multiple colors.
- Use the ABCDE Rule: Apply the ABCDE rule to evaluate moles or lesions for asymmetry, border irregularity, color variation, diameter over 6mm, and evolution over time.
- Document Your Findings: Keep a record of any changes you observe during the examination. Take photographs if necessary to track changes over time.
If you notice any changes or unusual growths, consult a healthcare professional for further evaluation. Regular self-examinations, combined with professional skin checks, can aid in early detection and improve treatment outcomes.
The Role of Dermatologists in Skin Cancer Detection
Dermatologists play a vital role in the early detection and treatment of skin cancer. Their expertise and specialized training enable them to identify suspicious lesions and recommend appropriate interventions. Here's how dermatologists contribute to skin cancer detection:
Comprehensive Skin Examinations: Dermatologists perform thorough skin examinations to assess any unusual growths or changes. They use specialized tools, such as dermatoscopes, to examine lesions more closely and determine if further testing is necessary.
Biopsy and Diagnosis: If a suspicious lesion is identified, dermatologists may perform a biopsy to obtain a tissue sample for laboratory analysis. This helps confirm the presence of skin cancer and determines its type and stage.
Treatment Recommendations: Based on the diagnosis, dermatologists develop personalized treatment plans tailored to the patient's needs. These plans may include surgical removal, topical treatments, radiation therapy, or other interventions.
Regular visits to a dermatologist are essential for individuals at higher risk of skin cancer, such as those with a history of excessive sun exposure or a family history of skin cancer. By partnering with a dermatologist, individuals can receive expert guidance and proactive care for their skin health.
Are there risk factors for skin cancer?
Several risk factors can increase an individual's likelihood of developing skin cancer. Understanding these factors can help individuals take preventive measures and reduce their risk. Here are some common risk factors:
- Excessive Sun Exposure: Prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or tanning beds is a significant risk factor for skin cancer. UV rays can damage the DNA in skin cells, leading to cancerous changes over time.
- Fair Skin: Individuals with fair skin, light hair, and light-colored eyes are more susceptible to skin cancer, as they have less melanin to protect against UV radiation.
- Family History: A family history of skin cancer can increase the risk of developing the disease, as certain genetic factors may be inherited.
- Previous Skin Cancer: Individuals who have previously had skin cancer are at higher risk of developing it again.
- Age: The risk of skin cancer increases with age, as cumulative sun exposure and DNA damage accumulate over time.
While some risk factors, such as genetics and skin type, cannot be changed, individuals can take proactive steps to minimize their risk, such as practicing sun safety and performing regular skin checks.
How do environmental factors affect skin cancer appearance?
Environmental factors play a significant role in influencing the appearance and development of skin cancer. Understanding these factors can aid in identifying potential risks and taking preventive measures. Here's how environmental factors affect skin cancer appearance:
Sun Exposure: Prolonged exposure to UV radiation from the sun is a primary environmental factor contributing to skin cancer development. UV rays can cause DNA damage, leading to the formation of cancerous lesions.
Altitude: Higher altitudes have increased UV radiation levels, which can increase the risk of skin cancer. Individuals living or spending time at higher altitudes should take extra precautions to protect their skin.
Geographic Location: Regions closer to the equator receive more intense UV radiation, increasing the risk of skin cancer. Individuals in these areas should be particularly vigilant about sun protection.
Pollution: Environmental pollutants can contribute to skin damage and increase the risk of skin cancer. Pollutants may interact with UV radiation to enhance its harmful effects.
By understanding the impact of environmental factors, individuals can take necessary precautions to minimize their risk of skin cancer. This includes using sunscreen, wearing protective clothing, and avoiding excessive sun exposure, especially during peak hours.
Prevention Strategies for Skin Cancer
Preventing skin cancer involves adopting a proactive approach to protect the skin from harmful UV rays and other risk factors. Here are some effective prevention strategies:
- Use Sunscreen: Apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30 to all exposed skin, even on cloudy days. Reapply every two hours or after swimming or sweating.
- Seek Shade: Whenever possible, stay in the shade, especially during peak sun hours between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m.
- Wear Protective Clothing: Wear long-sleeved shirts, wide-brimmed hats, and sunglasses to shield your skin from UV rays.
- Avoid Tanning Beds: Tanning beds emit UV radiation that can damage the skin and increase the risk of skin cancer.
- Perform Regular Skin Checks: Conduct self-examinations and schedule regular skin checks with a dermatologist to detect any changes early.
By incorporating these prevention strategies into your daily routine, you can significantly reduce your risk of developing skin cancer and protect your skin's health.
Importance of Sunscreen in Preventing Skin Cancer
Sunscreen is a crucial component of any skin cancer prevention strategy. It provides a protective barrier against harmful UV rays and helps reduce the risk of skin damage. Here's why sunscreen is important in preventing skin cancer:
Protection Against UV Rays: Sunscreen shields the skin from both UVA and UVB rays, which can cause sunburn, premature aging, and DNA damage that leads to skin cancer.
Prevention of Sunburn: Sunburn is a clear sign of skin damage from UV exposure. Using sunscreen can prevent sunburn and reduce the risk of developing skin cancer.
Daily Use Benefits: Applying sunscreen daily, even on cloudy days or during winter, provides consistent protection against UV rays and reduces the cumulative damage to the skin.
Complementary to Other Measures: Sunscreen should be used alongside other protective measures, such as wearing protective clothing and seeking shade, for comprehensive sun protection.
By making sunscreen a part of your daily skincare routine, you can safeguard your skin's health and reduce the risk of skin cancer.
What does skin cancer look like after treatment?
After treatment, the appearance of skin cancer-affected areas can vary depending on the type of treatment received and the extent of the cancer. Here's what skin cancer may look like after treatment:
Surgical Removal: Surgical treatment may leave scars or changes in skin texture at the site of the removed cancerous lesion. Over time, these scars may fade and become less noticeable.
Topical Treatments: Topical treatments, such as creams or ointments, may cause temporary redness, peeling, or scabbing at the treatment site. These effects usually resolve as the skin heals.
Radiation Therapy: Radiation therapy may lead to skin changes, such as redness, dryness, or darkening of the treated area. These effects may persist for some time but often improve with proper skincare.
It's important to follow post-treatment care instructions provided by healthcare professionals to promote healing and minimize potential side effects. Regular follow-up appointments with a dermatologist are also essential to monitor the treated area and detect any recurrence.
FAQs
1. Can skin cancer appear suddenly?
Yes, skin cancer can appear suddenly as a new growth or change in an existing mole. It's important to monitor your skin regularly and seek medical advice if you notice any sudden changes.
2. Is skin cancer always visible on the skin's surface?
Not always. Some skin cancers may develop beneath the skin's surface and become visible as they grow. Regular skin checks can help detect such hidden cancers early.
3. Can skin cancer be itchy or painful?
Yes, some skin cancers may cause itching, tenderness, or pain. If you experience any unusual sensations in a skin lesion, it's advisable to consult a dermatologist.
4. Are all moles with irregular shapes cancerous?
Not all irregularly shaped moles are cancerous. However, it's important to monitor them for any changes and consult a healthcare professional if you have concerns.
5. Can skin cancer develop in areas not exposed to the sun?
Yes, skin cancer can develop in areas not typically exposed to the sun, such as the soles of the feet or under fingernails. Regular self-examinations can help detect such cases.
6. Is skin cancer preventable?
While not all cases are preventable, taking proactive measures such as using sunscreen, wearing protective clothing, and avoiding tanning beds can significantly reduce the risk of skin cancer.
Conclusion
Understanding what skin cancer looks like is a vital step in early detection and treatment. By recognizing the visual signs associated with different types of skin cancer, individuals can take proactive measures to seek medical attention promptly. Regular self-examinations, combined with professional skin checks, play a crucial role in identifying potential concerns and improving treatment outcomes.
By adopting preventive strategies, such as using sunscreen, wearing protective clothing, and minimizing sun exposure, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing skin cancer. Remember, early detection is key to successful treatment, so stay vigilant and prioritize your skin health. If you have any concerns or notice unusual changes in your skin, consult a healthcare professional for further evaluation and guidance.
For more information and resources on skin cancer, visit the American Cancer Society's Skin Cancer Page.