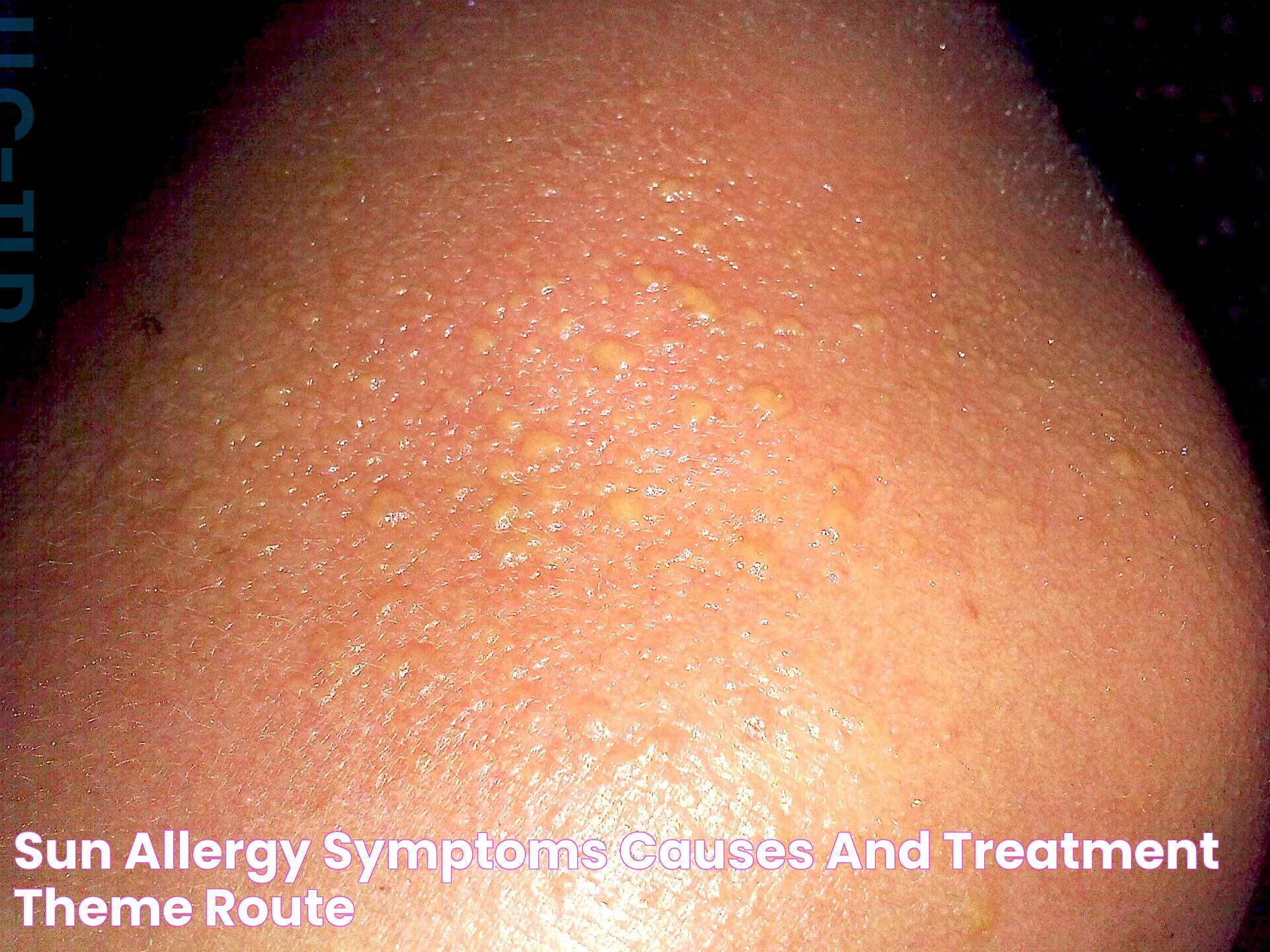
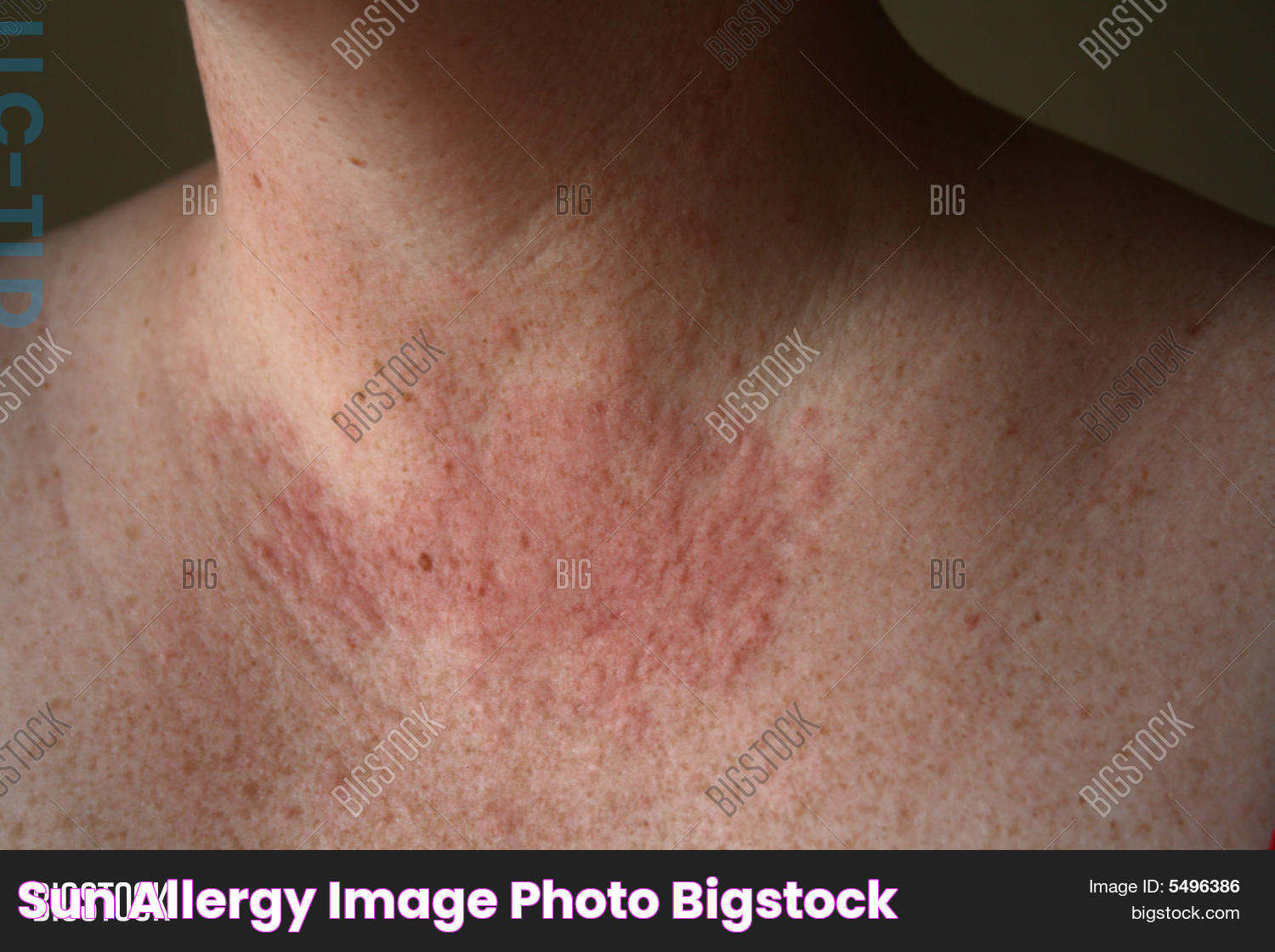
Experiencing an unexpected rash or itchiness after being in the sun can be quite bewildering. Sun allergy, also known as photosensitivity, is a condition where the skin reacts adversely to sunlight. People who suffer from this condition may notice symptoms such as redness, itching, or even blistering on sun-exposed skin. While anyone can develop a sun allergy, it often affects those with fair skin or those who have certain genetic predispositions. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and preventive measures is crucial in managing the condition effectively.
Sun allergy isn't just a minor inconvenience; it can significantly impact one's lifestyle and outdoor activities. For many, it means missing out on sunny days at the beach or picnics in the park. The fear of developing a rash or more severe symptoms can be daunting. However, with the right knowledge and strategies, individuals can enjoy the outdoors while minimizing the risks associated with sun allergy. From protective clothing to sunscreens and lifestyle adjustments, various methods can help manage the condition.
With the increasing awareness of skin health and sun exposure-related issues, it's essential to address the myths and facts surrounding sun allergy. This comprehensive guide aims to shed light on the various facets of sun allergy, offering insight into its causes, symptoms, and practical solutions for those affected. By understanding the condition and implementing effective management strategies, individuals can lead a comfortable life, even under the sun's rays.
Read also:Timeless Scents The Allure Of Perfume In The 80s
Table of Contents
- What is Sun Allergy?
- Symptoms of Sun Allergy
- Causes of Sun Allergy
- Types of Sun Allergy
- How is Sun Allergy Diagnosed?
- Treatment Options for Sun Allergy
- Can Sun Allergy be Prevented?
- Best Practices for Managing Sun Allergy
- Impact of Sun Allergy on Daily Life
- Lifestyle Changes to Cope with Sun Allergy
- Myths and Facts About Sun Allergy
- Is Sun Allergy Hereditary?
- Role of Sunscreen in Sun Allergy Management
- Are There Any Home Remedies for Sun Allergy?
- FAQs About Sun Allergy
- Conclusion
What is Sun Allergy?
Sun allergy is a hypersensitive reaction of the immune system to sunlight, particularly ultraviolet (UV) rays. The condition can manifest in various forms, ranging from mild redness and itching to severe blistering and swelling. Unlike sunburn, which is a direct result of UV damage, sun allergy is an immune response that occurs when the skin is exposed to sunlight.
Understanding the nature of sun allergy is essential for those affected, as it helps in recognizing symptoms early and seeking appropriate treatment. The condition can be challenging because it varies greatly from person to person. Some individuals may experience mild reactions, while others suffer from severe symptoms that require medical attention.
Symptoms of Sun Allergy
Sun allergy symptoms can vary depending on the type of allergy and the individual's sensitivity. Common symptoms include:
- Redness and inflammation on exposed skin
- Itching or a burning sensation
- Small bumps or hives
- Blistering or peeling skin
- Swelling in severe cases
These symptoms typically appear within minutes to hours after sun exposure and can last for several days. It is crucial to differentiate sun allergy from sunburn, as the former involves an immune response, while the latter is a direct effect of UV radiation.
Causes of Sun Allergy
The exact cause of sun allergy isn't fully understood, but several factors contribute to its development. These include:
- Genetic predisposition: A family history of sun allergy increases the risk.
- Certain medications: Some drugs can increase photosensitivity.
- Underlying skin conditions: Conditions like eczema or lupus can exacerbate sun allergy symptoms.
- UV exposure: Both UVA and UVB rays can trigger reactions.
Identifying triggers is an important step in managing sun allergy. Keeping a record of sun exposure and symptoms can help pinpoint specific causes and inform treatment plans.
Read also:Salon Perfect Press On Nails Your Guide To Flawless And Effortless Beauty
Types of Sun Allergy
Sun allergy encompasses several types, each with distinct characteristics:
Polymorphous Light Eruption (PMLE)
PMLE is the most common form of sun allergy. It typically appears as a rash with small red bumps or blisters, usually on the neck, chest, or arms. Symptoms often occur in spring or early summer when sun exposure increases.
Actinic Prurigo (Hereditary PMLE)
This type is similar to PMLE but has a hereditary component. It often affects individuals of Native American descent and presents with more severe symptoms.
Solar Urticaria
Solar urticaria is characterized by hives or large welts that appear on sun-exposed skin. This condition can be severe and requires medical intervention to manage symptoms effectively.
How is Sun Allergy Diagnosed?
Diagnosing sun allergy involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and possibly diagnostic tests:
- Medical History: A detailed history can reveal patterns of sun exposure and symptom onset.
- Physical Examination: A dermatologist examines the rash's characteristics and distribution.
- Phototesting: This test exposes small skin areas to UV light to assess the reaction.
- Blood Tests: These may rule out other conditions with similar symptoms.
Early diagnosis is crucial for implementing effective management strategies and preventing complications from prolonged sun exposure.
Treatment Options for Sun Allergy
Treatment for sun allergy focuses on relieving symptoms and preventing future reactions. Options include:
Topical Treatments
Corticosteroid creams can reduce inflammation and itching. These are commonly prescribed for mild to moderate sun allergy symptoms.
Oral Medications
Antihistamines may relieve itching and reduce hives. In severe cases, oral corticosteroids might be necessary to control the immune response.
Phototherapy
Gradual exposure to ultraviolet light under medical supervision can help desensitize the skin, reducing the severity of reactions over time.
Consulting a dermatologist is recommended to tailor treatment plans based on the severity of symptoms and individual needs.
Can Sun Allergy be Prevented?
While it may not be possible to completely prevent sun allergy, certain measures can significantly reduce the risk of reactions:
- Sun Avoidance: Limiting sun exposure during peak hours (10 am to 4 pm) can minimize symptoms.
- Protective Clothing: Wearing long sleeves, hats, and sunglasses can shield the skin from UV rays.
- Sunscreen Use: Broad-spectrum sunscreens with high SPF can protect against UVA and UVB rays.
- Gradual Exposure: Slowly increasing sun exposure can help build tolerance over time.
Implementing these strategies can help individuals enjoy outdoor activities with reduced risk of sun allergy symptoms.
Best Practices for Managing Sun Allergy
Effectively managing sun allergy involves a combination of preventive and reactive measures:
- Stay Informed: Keep track of local UV indexes and plan outdoor activities accordingly.
- Regular Skin Checks: Monitor skin for any changes or new symptoms and consult a dermatologist if needed.
- Hydration: Staying hydrated can aid in skin health and recovery from sun exposure.
- Avoid Triggers: Identify and avoid known triggers such as specific medications or skincare products.
By adopting these practices, individuals can manage their condition effectively and reduce the impact of sun allergy on their daily lives.
Impact of Sun Allergy on Daily Life
Sun allergy can have a profound impact on daily life, affecting both physical health and emotional well-being. Symptoms can be uncomfortable and may limit outdoor activities. Additionally, the condition may lead to self-consciousness or anxiety about sun exposure.
Social and recreational activities might require careful planning to avoid excessive sun exposure. This can lead to feelings of isolation or missing out on enjoyable experiences. However, with the right coping strategies and support, individuals can lead fulfilling lives while managing their condition.
Lifestyle Changes to Cope with Sun Allergy
Making certain lifestyle changes can help individuals cope with sun allergy and maintain a good quality of life:
- Adopt a Sun-Safe Routine: Incorporate sun protection into daily habits, such as applying sunscreen before leaving the house.
- Support Networks: Engage with support groups or online communities to share experiences and tips.
- Mindfulness and Relaxation: Practices like yoga or meditation can alleviate stress and improve overall well-being.
- Educate Others: Inform friends and family about sun allergy to foster understanding and support.
These changes can empower individuals to manage their condition effectively and enjoy life to the fullest.
Myths and Facts About Sun Allergy
Several myths surround sun allergy, often leading to misconceptions. Here are some common myths and the facts:
- Myth: Only fair-skinned people can have sun allergies.
- Fact: While fair skin is a risk factor, anyone can develop a sun allergy.
- Myth: Sun allergy is the same as sunburn.
- Fact: Sunburn is a result of UV damage, while sun allergy is an immune reaction to sunlight.
- Myth: Sunscreen can completely prevent sun allergy.
- Fact: Sunscreen can reduce the risk but may not prevent all reactions in sensitive individuals.
Understanding these myths and facts can help individuals make informed decisions about managing their condition.
Is Sun Allergy Hereditary?
The hereditary nature of sun allergy varies depending on the type. While some forms like actinic prurigo have a genetic component, others do not have a clear hereditary pattern. Research suggests that a family history of sun allergy or related conditions may increase susceptibility, but environmental factors also play a significant role.
Understanding the hereditary aspects can help individuals assess their risk and take preventive measures if necessary.
Role of Sunscreen in Sun Allergy Management
Sunscreen is a critical component in managing sun allergy. It provides a protective barrier that reduces UV exposure, thereby minimizing the risk of triggering allergic reactions. When choosing a sunscreen, consider the following:
- Broad-Spectrum Protection: Ensure the sunscreen protects against both UVA and UVB rays.
- High SPF: Opt for a sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher for optimal protection.
- Water Resistance: Choose water-resistant formulas for activities involving water or sweating.
- Hypoallergenic Formulas: Select products designed for sensitive skin to reduce irritation.
Regular and proper application of sunscreen can significantly aid in managing sun allergy symptoms and allowing safe outdoor activities.
Are There Any Home Remedies for Sun Allergy?
While home remedies cannot replace medical treatment, they can provide supplemental relief for sun allergy symptoms. Some effective remedies include:
- Aloe Vera Gel: Apply aloe vera to soothe irritated skin and reduce inflammation.
- Cold Compress: Use a cold compress to alleviate itching and swelling.
- Oatmeal Baths: Soak in an oatmeal bath to calm irritated skin.
- Coconut Oil: Moisturize skin with coconut oil to prevent dryness and promote healing.
These remedies can provide comfort and aid in the recovery process, but consulting a healthcare professional for persistent or severe symptoms is recommended.
FAQs About Sun Allergy
1. Can sun allergy develop suddenly?
Yes, sun allergy can develop suddenly, even if you've never experienced symptoms before. It may be triggered by changes in medication, lifestyle, or health conditions.
2. Are there specific foods that can exacerbate sun allergy?
Some foods, like citrus fruits, can increase photosensitivity. However, they generally do not cause sun allergy on their own.
3. Is sun allergy a permanent condition?
Sun allergy can be a chronic condition, but symptoms and severity can vary over time. Some individuals may find their symptoms improve with age or proper management.
4. Can sun allergy affect mental health?
Yes, the impact on lifestyle and self-image can affect mental health, leading to anxiety or depression in some cases.
5. Is it safe to use tanning beds if I have a sun allergy?
No, tanning beds can exacerbate sun allergy symptoms and should be avoided.
6. Can sun allergy lead to skin cancer?
While sun allergy itself does not cause cancer, excessive UV exposure increases the risk of skin cancer. Proper sun protection is essential.
Conclusion
Sun allergy is a challenging yet manageable condition. With the right knowledge and strategies, individuals can control their symptoms and enjoy outdoor activities. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and preventive measures, one can lead a fulfilling life without fear of sun exposure. Emphasizing protective measures and lifestyle adjustments will ensure that those affected by sun allergy can maintain their quality of life and continue to enjoy the sun safely.