Pheromones are invisible chemical messengers that play a crucial role in communication among members of the same species. These naturally occurring substances are emitted by animals and humans alike, influencing a wide range of behaviors such as mating, territorial marking, and social interactions. Despite their pivotal role in the natural world, pheromones remain an enigma, often misunderstood or overlooked by those unfamiliar with their significance.
For centuries, scientists have been fascinated by the power of pheromones, exploring their role in the animal kingdom and, more recently, in human interactions. The term "pheromone" was first coined in the 1950s, derived from the Greek words "pherein" (to transport) and "hormone" (to stimulate). These compelling compounds have since become a subject of extensive research, revealing their diverse applications in nature and potential uses in various industries, including agriculture, pest control, and even personal care products.
In this article, we'll delve into the intricate world of pheromones, providing a comprehensive pheromones definition and exploring their fascinating functions. From their discovery and classification to their impact on behavior and potential applications, we aim to shed light on the complex yet captivating language of scent that influences life on Earth.
Read also:Ogee Makeup Transform Your Look With Timeless Elegance
Table of Contents
- What are Pheromones?
- History and Discovery of Pheromones
- Classification of Pheromones
- How Do Pheromones Work?
- Pheromones in the Animal Kingdom
- Pheromones and Human Interactions
- The Role of Pheromones in Mating
- Social Pheromones and Group Dynamics
- Pheromones in Agriculture
- Pheromones and Pest Control
- Pheromones in Personal Care Products
- Are Pheromones Effective?
- Ethical Considerations and Pheromone Use
- Future Research and Innovations in Pheromone Science
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
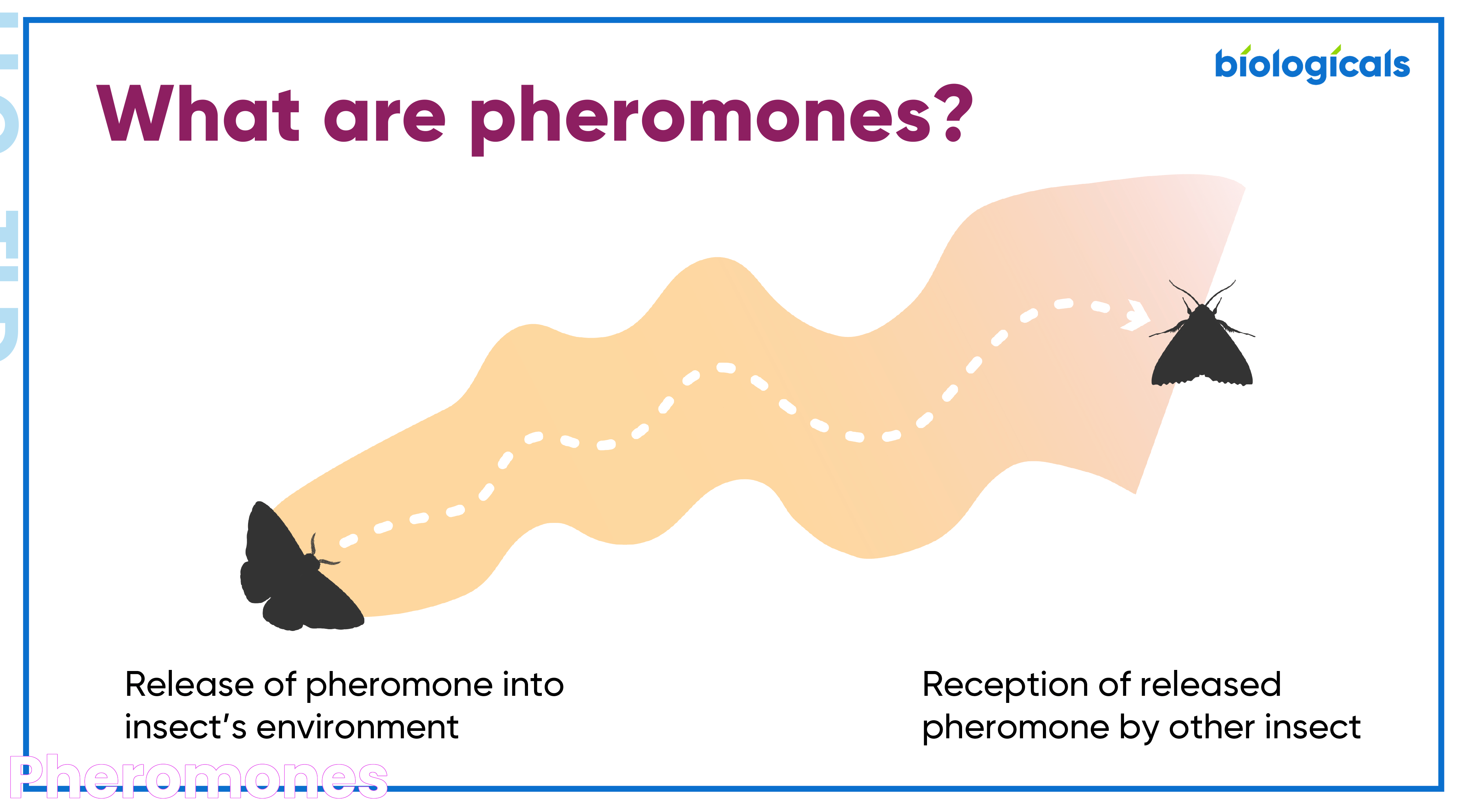
What are Pheromones?
Pheromones are part of a sophisticated communication system used by living organisms to convey messages and trigger specific responses from others of the same species. These chemical substances are secreted externally and can influence a variety of behaviors, including reproductive cycles, social bonding, and territorial behaviors. Their impact can be subtle or profound, often operating below the threshold of conscious awareness.
Unlike hormones, which act within the body to regulate physiological functions, pheromones are emitted into the environment to affect the behavior or physiology of other individuals. This distinction highlights the unique role that pheromones play in inter-organismal communication, acting as a bridge between individual members of a species and their collective behavioral responses.
Understanding the pheromones definition is crucial for appreciating their significance in nature. These compounds serve as an invisible, yet incredibly influential language that guides interactions and behaviors across a wide array of species. From the simplest insects to complex mammals, pheromones facilitate communication and coordination, underscoring their essential role in the natural world.
History and Discovery of Pheromones
The concept of pheromones has its roots in the early 20th century, when scientists began to explore the chemical basis of animal behavior. The discovery of pheromones was a groundbreaking development in biology, providing insights into the complex interactions that govern life on Earth. In 1959, the term "pheromone" was officially introduced by German researchers Peter Karlson and Martin Lüscher, marking a significant milestone in the study of chemical communication.
One of the earliest and most famous discoveries involved the silkworm moth, Bombyx mori, whose females were found to release a potent chemical attractant that could be detected by males from great distances. This finding sparked a wave of research into pheromones, leading to the identification of these compounds in a wide range of species, from ants to elephants.
Over the decades, advancements in analytical techniques have enabled scientists to isolate and identify pheromones with increasing precision. The study of pheromones has since expanded beyond the animal kingdom to encompass plants and even fungi, illustrating the widespread prevalence and importance of these chemical messengers in nature.
Read also:All You Need To Know About Black Mascara A Beauty Staple
Classification of Pheromones
Pheromones can be broadly classified into several categories based on their function and mode of action. Understanding these classifications helps to elucidate the diverse roles that pheromones play in the lives of organisms.
- Releaser Pheromones: These pheromones trigger immediate, specific behavioral responses in the recipient. They are often involved in mating and territorial behaviors, such as attracting mates or repelling rivals.
- Primer Pheromones: Unlike releaser pheromones, primer pheromones induce long-term physiological changes in the recipient. They can influence reproductive cycles, development, and social hierarchies.
- Signal Pheromones: These pheromones convey information about the identity or status of the emitter, such as marking territory or signaling danger.
- Modulator Pheromones: Modulator pheromones affect the mood or emotional state of the recipient, potentially altering their responses to other stimuli.
Each type of pheromone serves a distinct purpose, reflecting the complexity and adaptability of chemical communication in nature. By categorizing pheromones based on their function, researchers can better understand how these compounds contribute to the survival and reproduction of species.
How Do Pheromones Work?
The mechanism of action for pheromones involves the release and detection of chemical signals, which are processed by specialized sensory systems. In many animals, pheromones are detected by the vomeronasal organ (VNO), a chemosensory structure located in the nasal cavity. This organ is specifically adapted to perceive pheromonal cues, sending signals to the brain to elicit appropriate behavioral or physiological responses.
When a pheromone molecule binds to receptors in the VNO, it triggers a cascade of neural events that ultimately influence the behavior or physiology of the recipient. This process is highly specific, with different pheromones targeting distinct receptors and pathways. The precision of this system ensures that organisms can respond appropriately to a wide range of environmental and social cues.
While the VNO is a key player in pheromone detection for many species, humans rely more heavily on the olfactory system to process these chemical signals. Although the human VNO is considered vestigial and non-functional, research suggests that humans can still perceive and respond to pheromones through their sense of smell.
Pheromones in the Animal Kingdom
Pheromones play a vital role in the animal kingdom, facilitating communication and coordination among individuals. These chemical signals are involved in a wide range of behaviors, including mating, foraging, and social interactions.
In insects, pheromones are crucial for coordinating complex social behaviors, such as those seen in ant and bee colonies. Worker ants use trail pheromones to guide their nestmates to food sources, while queen bees release pheromones to regulate the reproductive status of the colony.
Among mammals, pheromones are often used to signal reproductive readiness and establish social hierarchies. For example, male deer release scent marks to advertise their presence and attract females, while female rodents emit pheromones to indicate their fertility to potential mates.
Pheromones also play a role in predator-prey interactions, with some species using chemical signals to warn conspecifics of danger or to mask their scent from predators. This diverse array of functions highlights the importance of pheromones in maintaining the balance and stability of ecosystems.
Pheromones and Human Interactions
While the role of pheromones in human interactions is less understood than in other species, evidence suggests that these chemical signals may still influence our behavior and social dynamics. Studies have shown that humans can detect pheromones through their sense of smell, with potential effects on mood, attraction, and interpersonal relationships.
One area of research focuses on the role of pheromones in human attraction and mate selection. Some studies suggest that pheromones may play a role in subconscious attraction, influencing preferences for potential partners based on genetic compatibility and immune system compatibility.
Additionally, pheromones may impact social interactions by modulating mood and emotional responses. Certain pheromones have been linked to feelings of relaxation or arousal, potentially affecting how individuals perceive and respond to others in social settings.
Despite these findings, the study of human pheromones remains a complex and evolving field, with much still to be discovered about the extent and mechanisms of their influence on our behavior.
The Role of Pheromones in Mating
Pheromones are integral to the mating behaviors of many species, acting as powerful attractants that facilitate reproduction. These chemical signals can convey information about an individual's reproductive status, genetic quality, and overall health, helping to ensure successful mating encounters.
In many animals, pheromones are released by females to signal their fertility and readiness to mate. Male moths, for example, can detect the pheromones of receptive females from great distances, using these cues to locate potential mates.
For males, pheromones can serve as indicators of dominance or territoriality, deterring rivals and attracting females. In some species, males produce complex pheromone blends that reflect their genetic fitness, allowing females to choose mates based on these chemical cues.
The role of pheromones in human mating is less clear, but research suggests that these signals may still play a role in attraction and mate selection. Studies have found that individuals may subconsciously prefer the scent of potential partners with dissimilar immune system genes, potentially enhancing offspring survival.
Social Pheromones and Group Dynamics
Social pheromones are crucial for maintaining group dynamics and cohesion within social species. These chemical signals facilitate communication and coordination among individuals, helping to regulate behaviors such as foraging, defense, and reproduction.
In social insects like ants and bees, pheromones are used to coordinate complex group activities, such as foraging and nest building. Worker ants release trail pheromones to guide their nestmates to food sources, while queen bees emit pheromones to suppress the reproductive abilities of other females in the colony.
Mammalian social structures also rely on pheromones to maintain group cohesion and establish social hierarchies. In some primate species, pheromones are used to signal social status and mediate interactions between individuals.
The role of pheromones in human social interactions is less well understood, but research suggests that these signals may influence mood and emotional responses, potentially affecting how individuals perceive and respond to others in social settings.
Pheromones in Agriculture
Pheromones have found valuable applications in agriculture, where they are used to enhance crop production and protect plants from pests. By utilizing the natural communication systems of insects, farmers can manage pest populations more effectively and reduce the need for chemical pesticides.
One common application of pheromones in agriculture is the use of pheromone traps to monitor and control pest populations. These traps release synthetic pheromones that mimic the natural attractants of target pests, luring them into traps where they can be monitored or eliminated.
Pheromones are also used in mating disruption strategies, where synthetic pheromones are released in large quantities to confuse male insects and prevent them from locating females. This approach can significantly reduce pest populations and minimize damage to crops.
By harnessing the power of pheromones, farmers can adopt more sustainable and environmentally friendly pest management practices, reducing reliance on chemical pesticides and promoting the health of ecosystems.
Pheromones and Pest Control
Pheromones play a crucial role in pest control, offering a targeted and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional chemical pesticides. By exploiting the natural communication systems of pests, pheromones can be used to monitor, manage, and reduce pest populations.
Pheromone traps are a widely used tool in pest control, attracting pests with synthetic pheromones and capturing them for monitoring or removal. These traps can be used to track pest populations and identify when intervention is needed, allowing for more precise and effective pest management.
Mating disruption is another pheromone-based pest control strategy, where synthetic pheromones are released in large quantities to confuse male insects and prevent them from locating females. This approach can significantly reduce pest populations and minimize damage to crops.
Pheromone-based pest control methods offer several advantages over traditional pesticides, including reduced environmental impact, increased specificity, and decreased risk of resistance development. By leveraging the power of pheromones, pest management can become more sustainable and effective.
Pheromones in Personal Care Products
The allure of pheromones has extended into the realm of personal care products, where these chemical signals are marketed as tools for enhancing attraction and social interactions. From perfumes to body sprays, pheromone-infused products promise to boost confidence and allure by harnessing the subtle power of scent.
While the efficacy of pheromone-based products is still debated, their popularity reflects a growing interest in the potential of these chemical signals to influence human behavior. Some studies suggest that certain pheromones may enhance mood and social interactions, although the mechanisms and effects remain poorly understood.
As research into human pheromones continues, the development of personal care products that leverage these chemical signals may offer new opportunities for enhancing well-being and social interactions. However, consumers should approach these products with a critical eye, recognizing the current limitations of scientific understanding in this field.
Are Pheromones Effective?
The effectiveness of pheromones in influencing behavior and communication is well-documented in many animal species, where these chemical signals play a crucial role in mating, social interactions, and territorial behaviors. However, the extent to which pheromones affect human behavior remains a topic of ongoing research and debate.
Some studies suggest that human pheromones may influence mood, attraction, and social interactions, although the mechanisms and effects are less clear than in other species. The human sense of smell is complex and influenced by a variety of factors, making it challenging to isolate the specific impact of pheromones.
Despite these challenges, the potential of pheromones to influence human behavior continues to captivate researchers and consumers alike. As scientific understanding of pheromones advances, new insights may emerge regarding their role in human interactions and their potential applications in various fields.
Ethical Considerations and Pheromone Use
The use of pheromones in various industries raises important ethical considerations, particularly regarding their potential to influence behavior and social interactions. As research into pheromones advances, questions about consent, manipulation, and privacy become increasingly relevant.
In the context of pheromone-based personal care products, ethical concerns may arise regarding the marketing and use of these products to influence attraction and social interactions. Consumers should be informed about the limitations and potential effects of pheromone-based products, allowing them to make informed decisions about their use.
In agriculture and pest control, the use of pheromones offers an opportunity for more sustainable and environmentally friendly practices. However, ethical considerations regarding the impact on ecosystems and non-target species remain important to ensure responsible and effective implementation.
As the field of pheromone research continues to evolve, addressing ethical considerations will be crucial for ensuring the responsible and beneficial use of these powerful chemical signals.
Future Research and Innovations in Pheromone Science
The field of pheromone research is rapidly evolving, with new discoveries and innovations continually expanding our understanding of these chemical signals. Future research holds the potential to unlock new applications and insights into the role of pheromones in communication, behavior, and ecology.
One area of interest is the development of more effective and sustainable pheromone-based pest control methods, offering alternatives to traditional chemical pesticides. Advances in synthetic pheromone production and delivery systems may enhance the efficacy and accessibility of these approaches.
In the realm of human interactions, ongoing research aims to elucidate the mechanisms and effects of human pheromones, potentially leading to new applications in personal care, healthcare, and social dynamics. Understanding the role of pheromones in mood, attraction, and social interactions may offer new opportunities for enhancing well-being and relationships.
As scientific understanding of pheromones continues to grow, interdisciplinary collaborations and innovative technologies will play a crucial role in advancing research and unlocking the potential of these fascinating chemical signals.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are pheromones and how do they work?
Pheromones are chemical signals released by organisms to communicate with others of the same species, influencing behaviors such as mating, social interactions, and territorial marking. They work by being detected by specific sensory systems, such as the vomeronasal organ, which sends signals to the brain to elicit appropriate responses.
Do humans produce and respond to pheromones?
Yes, humans produce and can respond to pheromones, although the extent and mechanisms of their influence are less understood than in other species. Research suggests that human pheromones may impact mood, attraction, and social interactions, but further studies are needed to fully elucidate their effects.
Can pheromones be used in pest control?
Yes, pheromones are widely used in pest control to monitor and manage pest populations. Pheromone traps and mating disruption strategies are common methods that utilize synthetic pheromones to attract, capture, or confuse pests, offering a more sustainable and targeted alternative to chemical pesticides.
Are pheromone-based personal care products effective?
The effectiveness of pheromone-based personal care products remains a topic of debate. While some studies suggest that certain pheromones may enhance mood and social interactions, the scientific understanding of their mechanisms and effects is still limited, and consumers should approach these products with caution.
What ethical considerations are associated with pheromone use?
Ethical considerations related to pheromone use include concerns about consent, manipulation, and privacy, particularly in the context of influencing behavior and social interactions. Responsible use and informed decision-making are crucial for ensuring the ethical application of pheromones in various industries.
What is the future of pheromone research?
The future of pheromone research holds the potential for new discoveries and applications in areas such as pest control, personal care, and human interactions. Advances in technology and interdisciplinary collaborations will play a key role in expanding our understanding of pheromones and unlocking their potential benefits.
Conclusion
Pheromones are powerful chemical signals that facilitate communication and coordination among organisms, influencing a wide range of behaviors and interactions. From their discovery and classification to their diverse applications in nature and industry, pheromones represent a fascinating and essential component of life on Earth.
While research into pheromones continues to unveil their complexity and potential, ethical considerations and responsible use remain crucial for ensuring their beneficial application. As scientific understanding advances, the future of pheromone research holds promise for new insights and innovations that can enhance well-being, sustainability, and our understanding of the natural world.
By exploring the intricate world of pheromones, we gain a deeper appreciation for the subtle yet profound language of scent that shapes the lives of countless species, including our own.