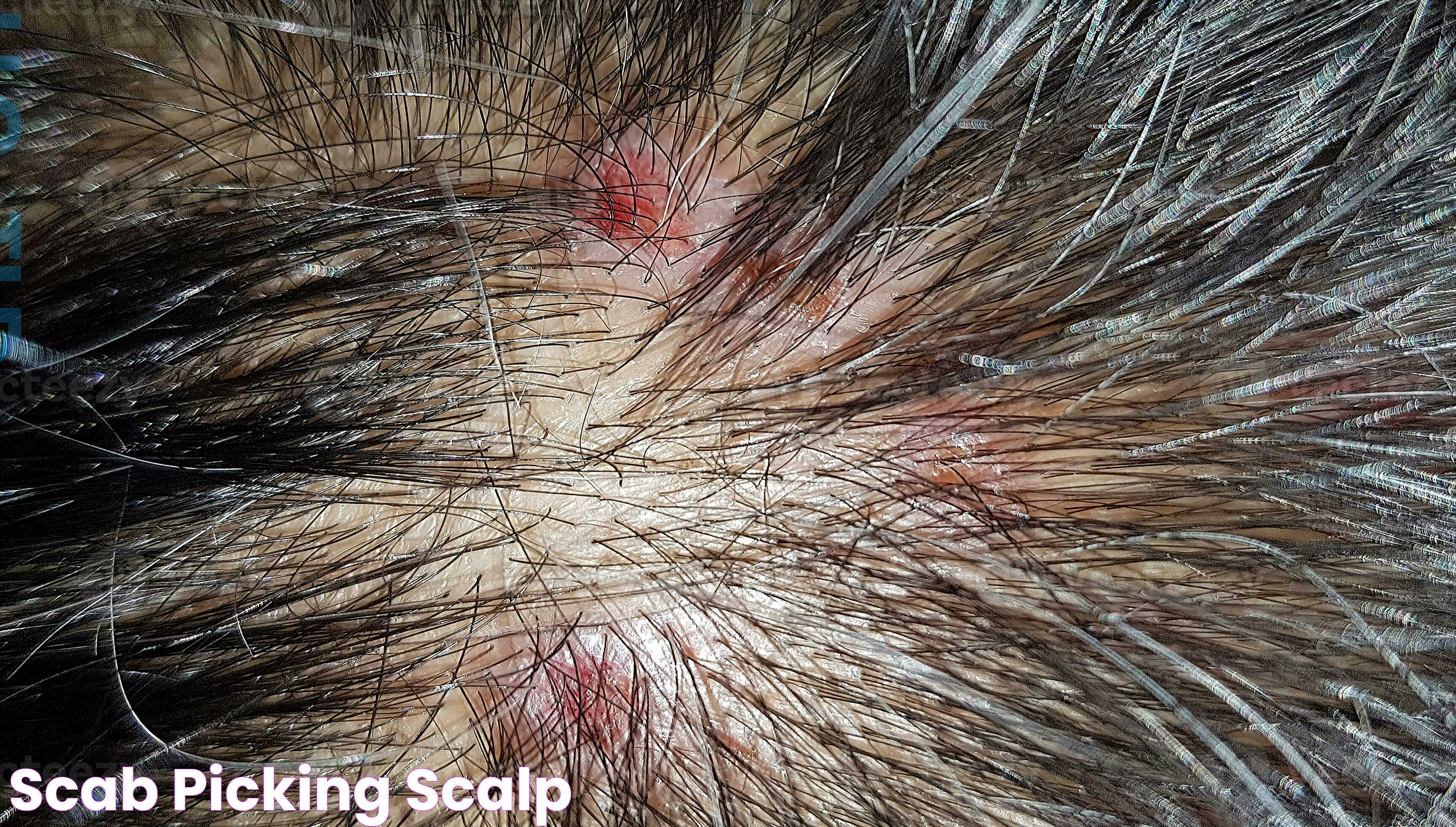
Scalp scab picking can be a perplexing and frustrating behavior for those who experience it. It's a habit that often goes unnoticed until it becomes a significant concern. Many individuals wonder whether this behavior is merely a bad habit or if it points to a deeper psychological issue, such as Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD). Understanding the psychology behind scalp scab picking is crucial to determine whether it falls under the spectrum of OCD and to find effective solutions for those affected.
For some, scalp scab picking is a repetitive action that provides a momentary sense of relief or satisfaction. However, it can lead to physical damage and emotional distress over time. The behavior might seem harmless at first, but as it progresses, it can become a compulsive act that interferes with daily life. By exploring the underlying causes and effects, we can gain insight into why individuals engage in this behavior and how it relates to OCD.
Addressing scalp scab picking as a potential form of OCD requires a comprehensive approach. It's essential to recognize the signs, understand the triggers, and explore treatment options. With the right resources and support, individuals struggling with this behavior can find effective ways to manage and overcome it. This article delves into the complexities of scalp scab picking, offering insights into its connection with OCD, and providing strategies for healing and recovery.
Read also:Julianne Fashion Timeless Elegance In Modern Style
Table of Contents
- What is Scalp Scab Picking?
- Is Scalp Scab Picking OCD?
- Causes of Scalp Scab Picking
- Psychological Effects of Scalp Scab Picking
- Physical Consequences of Scalp Scab Picking
- How to Identify Scalp Scab Picking as OCD?
- Treatment Options for Scalp Scab Picking OCD
- Behavioral Therapy for Scalp Scab Picking
- Medications for Scalp Scab Picking OCD
- Self-Help Strategies for Scalp Scab Picking
- Support Groups and Communities
- How to Prevent Scalp Scab Picking?
- FAQ
- Conclusion
What is Scalp Scab Picking?
Scalp scab picking refers to the repetitive action of picking at scabs or skin on the scalp. This behavior can be associated with a variety of factors, including stress, anxiety, or dermatological conditions. For some individuals, this act may provide a temporary sense of relief or satisfaction, while for others, it can be an unconscious habit that occurs during times of distress or boredom.
This behavior is not just limited to the scalp; it can also manifest in other areas of the body. However, the scalp is a common site due to its accessibility and the tactile sensation that picking can provide. While occasional picking might seem innocuous, when it becomes frequent and causes harm or distress, it may be indicative of a more serious underlying issue.
Is Scalp Scab Picking OCD?
The question of whether scalp scab picking falls under Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) is complex. OCD is a mental health disorder characterized by unwanted, intrusive thoughts (obsessions) and repetitive behaviors or mental acts (compulsions) that individuals feel driven to perform. Scalp scab picking can be considered a type of Body-Focused Repetitive Behavior (BFRB), which is often associated with OCD.
In some cases, scalp scab picking may be a compulsion driven by obsessive thoughts about the appearance or texture of the scalp. For these individuals, the act of picking is a way to alleviate the anxiety or discomfort caused by these obsessions. However, not everyone who picks at their scalp has OCD. It's important to differentiate between a habitual behavior and a compulsive disorder by examining the frequency, intensity, and reasons behind the picking.
Causes of Scalp Scab Picking
Several factors can contribute to the development of scalp scab picking. Understanding these causes is crucial for identifying the appropriate treatment and management strategies. Some common causes include:
- Psychological Factors: Stress, anxiety, and depression can increase the likelihood of engaging in repetitive behaviors like scab picking. These emotions may trigger the behavior as a coping mechanism.
- Dermatological Conditions: Conditions such as psoriasis, eczema, or dandruff can cause itchiness and discomfort, leading individuals to pick at their scalp.
- Habitual Behavior: For some, scalp scab picking is a habit that develops over time, often starting as a way to relieve boredom or stress.
- Genetic Predisposition: There may be a genetic component to BFRBs, as they can run in families.
- Neurological Factors: Imbalances in brain chemistry can contribute to the development of compulsive behaviors.
Psychological Effects of Scalp Scab Picking
Engaging in scalp scab picking can have significant psychological effects. Individuals may experience feelings of shame, guilt, or embarrassment, particularly if the behavior leads to visible damage or scarring. This can result in social withdrawal and a decrease in self-esteem.
Read also:Unraveling The Wore Meaning A Deep Dive Into Historical And Cultural Significance
In addition, the compulsive nature of the behavior can lead to increased anxiety and stress. The cycle of picking, feeling relief, and then experiencing guilt can be emotionally exhausting. Recognizing these psychological effects is an important step in addressing the behavior and seeking help.
Physical Consequences of Scalp Scab Picking
Beyond the psychological impact, scalp scab picking can lead to various physical consequences. Persistent picking can cause:
- Scarring and Infection: Open wounds from picking are susceptible to infection, which can result in scarring.
- Hair Loss: Damage to hair follicles through repeated picking can lead to hair loss in affected areas.
- Skin Damage: The integrity of the scalp skin can be compromised, leading to further dermatological issues.
Understanding these physical consequences underscores the importance of addressing the behavior and seeking appropriate treatment.
How to Identify Scalp Scab Picking as OCD?
Identifying scalp scab picking as part of OCD involves recognizing several key characteristics. Firstly, the behavior is often driven by intrusive thoughts or obsessions about the scalp. Secondly, the act of picking is performed as a compulsion to alleviate anxiety or discomfort associated with these obsessions.
Individuals with OCD-related scalp scab picking may experience significant distress or impairment in daily functioning due to the behavior. The picking is not merely a habit but a compulsion that feels necessary to perform. If these criteria are met, seeking a professional evaluation is recommended to determine if OCD is present.
Treatment Options for Scalp Scab Picking OCD
Treating scalp scab picking OCD involves a multifaceted approach that addresses both the psychological and physical aspects of the behavior. Treatment options may include:
- Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT focuses on changing negative thought patterns and behaviors associated with scalp scab picking. It can help individuals develop healthier coping mechanisms.
- Habit Reversal Training (HRT): HRT is a type of behavioral therapy specifically designed to address BFRBs. It involves identifying triggers and replacing the picking behavior with alternative actions.
- Medication: In some cases, medications such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) may be prescribed to help manage OCD symptoms.
Behavioral Therapy for Scalp Scab Picking
Behavioral therapy is a cornerstone of treatment for scalp scab picking. Techniques such as exposure and response prevention (ERP) can be effective in reducing compulsive behaviors. ERP involves gradually exposing individuals to situations that trigger the urge to pick, while preventing the actual behavior.
This form of therapy helps individuals build tolerance to distressing thoughts and feelings, reducing the compulsion to engage in scalp scab picking. Working with a trained therapist is essential to tailor the therapy to the individual's specific needs.
Medications for Scalp Scab Picking OCD
Medications can play a role in managing scalp scab picking OCD, particularly when combined with therapy. SSRIs are commonly prescribed to help regulate serotonin levels in the brain, which can reduce OCD symptoms.
It's important to work closely with a healthcare provider to determine the appropriate medication and dosage. Medications can take time to show effects, and monitoring by a professional is crucial to ensure their effectiveness and manage any side effects.
Self-Help Strategies for Scalp Scab Picking
In addition to professional treatment, self-help strategies can be beneficial in managing scalp scab picking. Some effective strategies include:
- Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques: Practices such as meditation, deep breathing, and yoga can help reduce stress and anxiety, which may decrease the urge to pick.
- Keeping Hands Occupied: Engaging in activities that keep hands busy, such as drawing, knitting, or using stress balls, can help redirect the urge to pick.
- Creating a Healthy Scalp Care Routine: Regularly cleansing and moisturizing the scalp can reduce itchiness and discomfort, minimizing triggers for picking.
Implementing these strategies can empower individuals to take an active role in managing their behavior and improving their well-being.
Support Groups and Communities
Connecting with others who experience similar challenges can provide valuable support and encouragement. Support groups, both in-person and online, offer a safe space to share experiences, exchange coping strategies, and receive emotional support.
Organizations such as the Trichotillomania Learning Center (TLC) provide resources and support for individuals with BFRBs, including scalp scab picking. Joining a community can help reduce feelings of isolation and foster a sense of belonging and understanding.
How to Prevent Scalp Scab Picking?
Preventing scalp scab picking involves addressing both the triggers and the behavior itself. Strategies for prevention include:
- Identifying Triggers: Keeping a journal to track situations, emotions, or environments that trigger the urge to pick can help identify patterns and develop targeted interventions.
- Developing Coping Mechanisms: Learning and practicing alternative coping strategies, such as stress management techniques, can reduce reliance on picking as a coping mechanism.
- Seeking Professional Help: Early intervention from mental health professionals can prevent the behavior from escalating and provide effective strategies for management.
By implementing these prevention strategies, individuals can take proactive steps to reduce the occurrence of scalp scab picking and improve their overall quality of life.
FAQ
1. Can scalp scab picking be a sign of a dermatological condition?
Yes, scalp scab picking can be associated with dermatological conditions like psoriasis, eczema, or dandruff that cause itchiness.
2. Is scalp scab picking similar to trichotillomania?
While both are Body-Focused Repetitive Behaviors, scalp scab picking involves picking at the skin, whereas trichotillomania involves pulling out hair.
3. Can medication alone cure scalp scab picking OCD?
Medication can help manage symptoms, but it is often most effective when combined with behavioral therapies and self-help strategies.
4. How can I support a loved one struggling with scalp scab picking?
Offer understanding and encourage them to seek professional help. Avoid judgment and provide a supportive environment.
5. Is it possible for children to develop scalp scab picking OCD?
Yes, children can develop this behavior. Early intervention and support can help manage it effectively.
6. Are there any long-term effects of untreated scalp scab picking?
Untreated scalp scab picking can lead to chronic skin damage, infections, and psychological distress, impacting quality of life.
Conclusion
Scalp scab picking is a behavior that can have significant physical and psychological effects. Understanding its connection to OCD and recognizing the underlying causes is essential for effective treatment and management. Through a combination of therapy, medication, and self-help strategies, individuals can overcome this behavior and improve their quality of life. By seeking support from professionals and connecting with supportive communities, those affected by scalp scab picking can find healing and regain control over their lives.