As technology advances, the significance of radio frequency continues to grow. Radio frequency waves are the backbone of wireless communication systems that keep us connected globally. They enable us to send and receive information over long distances without the need for physical connections. From Wi-Fi networks to Bluetooth devices, RF technology is essential for the seamless operation of the gadgets we use every day.
Moreover, radio frequency has made remarkable contributions to various scientific and medical fields. In medicine, RF energy is used in MRI machines for imaging the human body and for treatments such as radiofrequency ablation to manage pain or tumors. In scientific research, RF technologies help in exploring space and understanding the universe. Indeed, radio frequency is an omnipresent force that influences numerous aspects of life, making its understanding indispensable for navigating the modern world.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Frequency Range | 3 kHz to 300 GHz |
| Common Applications | Communication, Medical, Industrial |
| Discovery | 19th Century |
| Key Technologies | Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, MRI, Microwave Ovens |
Table of Contents
- What is Radio Frequency?
- The History of Radio Frequency
- How Does Radio Frequency Work?
- Applications of Radio Frequency
- Radio Frequency in Communications
- Medical Applications of Radio Frequency
- Industrial Uses of Radio Frequency
- Radio Frequency Safety Considerations
- What are the Benefits of Radio Frequency?
- Challenges in Radio Frequency Technology
- The Future of Radio Frequency
- How is Radio Frequency Measured?
- Radio Frequency and Environmental Impact
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
What is Radio Frequency?
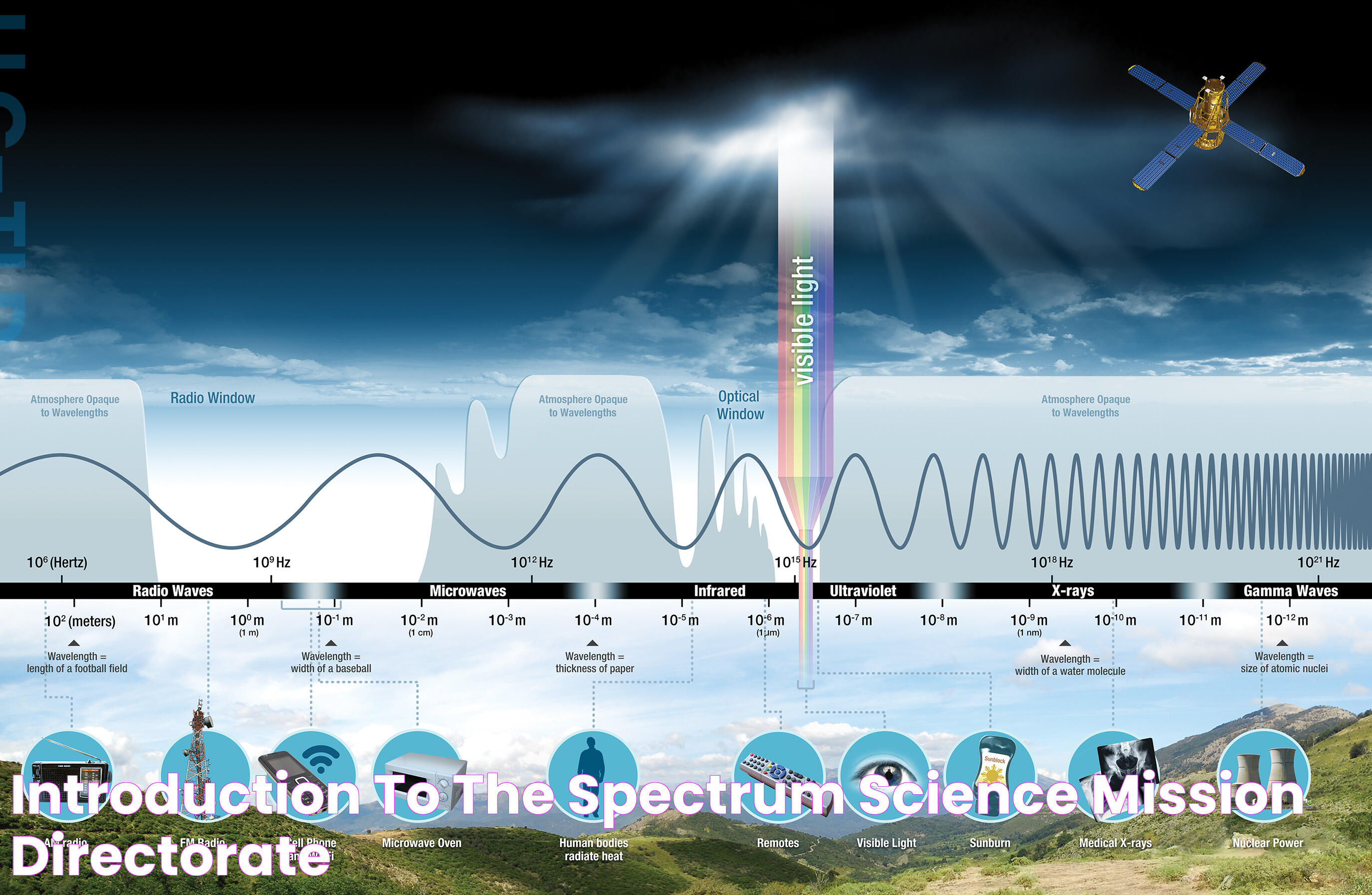
Radio frequency refers to the oscillation rate of electromagnetic radio waves in the range of 3 kHz to 300 GHz. These waves are a part of the electromagnetic spectrum that facilitates wireless transmission of signals. The concept of radio frequency is fundamental to modern communication systems, enabling data to be sent across vast distances without the need for a physical medium.
Read also:Alluring Shades Of Teal Nail Polish A Colorful Guide
The RF spectrum is divided into different ranges, each serving various applications. For instance, the lower frequency bands are typically used in AM radio broadcasting, while higher frequencies are utilized in mobile communication and satellite transmissions. The versatility of radio frequency makes it a cornerstone of modern technology, impacting everything from personal gadgets to large-scale communication networks.
Why is Radio Frequency Important?
Radio frequency is vital for the functionality of numerous devices and systems that people depend on daily. It underpins the infrastructure of cellular networks, allowing seamless communication across continents. RF technology is also crucial in broadcasting, enabling the transmission of radio and television signals to millions of homes worldwide.
Moreover, the importance of radio frequency extends to scientific and medical fields. It is used in MRI machines to provide detailed images of the human body and in various treatments that help manage medical conditions. In the scientific community, RF technology is essential for space exploration and the study of astronomical phenomena.
The History of Radio Frequency
The concept of radio frequency dates back to the 19th century with the pioneering work of scientists like Heinrich Hertz and James Clerk Maxwell. Hertz's experiments in the late 1880s demonstrated the existence of electromagnetic waves, confirming Maxwell's earlier theoretical predictions. This discovery laid the groundwork for the development of radio communication.
By the early 20th century, inventors like Guglielmo Marconi and Nikola Tesla made significant advancements in radio technology, leading to the establishment of the first radio stations. These innovations revolutionized communication, allowing information to be transmitted over long distances without the need for physical connections. The radio frequency spectrum has since been harnessed for various applications, from broadcasting to telecommunications and beyond.
Key Milestones in Radio Frequency Development
- 1887: Heinrich Hertz proves the existence of electromagnetic waves.
- 1895: Guglielmo Marconi transmits the first wireless signal.
- 1920: The first commercial radio stations begin broadcasting.
- 1940s: Development of radar technology during World War II.
- 1980s: Introduction of mobile communication technology.
- 2000s: Expansion of wireless internet and smart devices.
How Does Radio Frequency Work?
Radio frequency waves are generated by oscillating electric currents that create alternating electromagnetic fields. These fields radiate outward as waves, which can be modulated to carry information. The process of modulation involves varying the amplitude, frequency, or phase of the waves to encode data, which can then be transmitted over long distances.
Read also:Mercury Retrograde 2024 Dates And Impacts On Your Life
When these modulated RF waves reach a receiver, they are demodulated to extract the original information. This process is fundamental to wireless communication systems, enabling the transmission of voice, data, and video signals without the need for physical connections.
Components of Radio Frequency Systems
Radio frequency systems comprise various components that work together to facilitate wireless communication. These components include:
- Transmitter: Generates and modulates RF signals for transmission.
- Antenna: Converts electrical signals into electromagnetic waves and vice versa.
- Receiver: Captures and demodulates incoming RF signals to retrieve information.
- Amplifier: Boosts the strength of RF signals to ensure clear transmission and reception.
Applications of Radio Frequency
The applications of radio frequency are diverse, spanning numerous industries and impacting various aspects of daily life. From communication to healthcare, RF technology is integral to the functioning of many modern systems.
Radio Frequency in Communications
Radio frequency is the backbone of contemporary communication systems, enabling wireless transmission of data over long distances. It is used in various technologies, including:
- Cellular Networks: RF waves facilitate mobile communication, allowing calls and data to be transmitted between devices and cell towers.
- Broadcasting: Radio and television stations use RF signals to transmit audio and visual content to audiences globally.
- Satellite Communication: Satellites rely on RF technology to relay signals for television, internet, and GPS services.
Medical Applications of Radio Frequency
In the medical field, radio frequency technology is used for both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. Some notable applications include:
- MRI Machines: RF waves are used in magnetic resonance imaging to produce detailed images of organs and tissues.
- Radiofrequency Ablation: A treatment that uses RF energy to destroy abnormal tissue, such as tumors, and relieve pain.
Industrial Uses of Radio Frequency
Radio frequency technology is also employed in various industrial applications, enhancing efficiency and productivity in numerous sectors. Some examples include:
- Manufacturing: RF heating is used in processes such as sealing, welding, and drying, offering precise temperature control and energy efficiency.
- RFID Technology: Radio frequency identification is used for tracking and managing inventory, assets, and supply chains.
How is Radio Frequency Used in Cooking?
One of the most common household applications of radio frequency is in microwave ovens. These appliances use RF waves to heat food by causing water molecules to vibrate, generating heat through friction. This process allows for quick and efficient cooking, making microwave ovens a staple in kitchens worldwide.
Radio Frequency Safety Considerations
While radio frequency technology offers numerous benefits, it is essential to consider safety aspects to minimize potential risks. Prolonged exposure to high levels of RF radiation can have adverse health effects, making it crucial to adhere to safety guidelines and regulations.
What are the Health Risks of Radio Frequency Exposure?
Although RF exposure from common devices is generally considered safe, excessive exposure can lead to health issues. Potential risks include:
- Thermal Effects: High levels of RF radiation can cause tissue heating and burns.
- Non-Thermal Effects: Some studies suggest potential links between RF exposure and long-term health effects, such as cancer, though more research is needed.
What are the Benefits of Radio Frequency?
Radio frequency technology offers numerous advantages, contributing to the advancement of various fields and improving the quality of life. Some benefits include:
- Enhanced Communication: RF technology enables seamless wireless communication, connecting people and businesses worldwide.
- Medical Advancements: RF applications in healthcare provide non-invasive diagnostic and therapeutic options.
- Efficiency in Industries: RF technology enhances industrial processes, improving efficiency and reducing energy consumption.
Challenges in Radio Frequency Technology
Despite its numerous benefits, radio frequency technology faces several challenges that need to be addressed to ensure its continued growth and development. Some of the key challenges include:
- Interference: As RF spectrum usage increases, the potential for interference between signals also grows, affecting communication quality and reliability.
- Spectrum Scarcity: The increasing demand for wireless communication services has led to congestion in the RF spectrum, necessitating efficient spectrum management and allocation.
- Security Concerns: RF communication systems are susceptible to security threats, such as eavesdropping and unauthorized access, requiring robust security measures to protect sensitive data.
The Future of Radio Frequency
The future of radio frequency technology is promising, with ongoing advancements poised to revolutionize various industries. As technology continues to evolve, RF applications are expected to expand and diversify, driving innovation and improving quality of life.
Some emerging trends in radio frequency technology include:
- 5G Networks: The rollout of 5G technology promises faster data speeds, reduced latency, and improved connectivity, enabling new applications and services.
- Internet of Things (IoT): RF technology will play a crucial role in the development of IoT, connecting billions of devices and enabling smart environments.
- Advanced Healthcare Solutions: RF applications in healthcare are expected to grow, offering innovative diagnostic and therapeutic options.
How is Radio Frequency Measured?
Radio frequency is measured in hertz (Hz), representing the number of oscillations or cycles per second. The RF spectrum is divided into various frequency bands, each serving different applications. These bands include:
- Low Frequency (LF): 30 kHz to 300 kHz
- Medium Frequency (MF): 300 kHz to 3 MHz
- High Frequency (HF): 3 MHz to 30 MHz
- Very High Frequency (VHF): 30 MHz to 300 MHz
- Ultra High Frequency (UHF): 300 MHz to 3 GHz
- Super High Frequency (SHF): 3 GHz to 30 GHz
- Extremely High Frequency (EHF): 30 GHz to 300 GHz
Radio Frequency and Environmental Impact
As radio frequency technology continues to proliferate, it is essential to consider its potential impact on the environment. Some concerns include:
- Energy Consumption: The increasing demand for RF technology contributes to higher energy consumption, necessitating the development of energy-efficient solutions.
- Electromagnetic Pollution: The widespread use of RF devices raises concerns about electromagnetic pollution and its effects on ecosystems and wildlife.
Addressing these environmental challenges is crucial for ensuring the sustainable growth of radio frequency technology and minimizing its impact on the planet.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between radio waves and RF waves?
Radio waves are a type of electromagnetic wave, while RF waves refer specifically to the frequency range within the electromagnetic spectrum that encompasses radio waves. Essentially, all radio waves are RF waves, but not all RF waves are confined to traditional radio applications.
Can radio frequency waves be harmful to humans?
Exposure to high levels of radio frequency waves can be harmful, causing tissue heating and potential health effects. However, common RF exposure from devices like cell phones and Wi-Fi is generally considered safe when used within established safety guidelines.
How do radio frequency identification (RFID) systems work?
RFID systems use radio frequency waves to identify and track objects. They consist of tags with embedded chips and antennas that communicate with RFID readers, transmitting information wirelessly to manage inventory and assets efficiently.
What are some common devices that emit radio frequency waves?
Common devices that emit radio frequency waves include mobile phones, Wi-Fi routers, Bluetooth devices, radio and television transmitters, and microwave ovens. These devices use RF waves for communication, broadcasting, and heating applications.
How does radio frequency affect wireless communication?
Radio frequency is essential for wireless communication, enabling the transmission of data over long distances without physical connections. RF waves carry information by modulating their amplitude, frequency, or phase, allowing seamless communication between devices.
Is radio frequency used in space exploration?
Yes, radio frequency technology is integral to space exploration. It is used in communication systems for spacecraft and satellites, allowing data transmission between Earth and space missions. RF technology also aids in studying astronomical phenomena and understanding the universe.
Conclusion
Radio frequency is a powerful and versatile aspect of the electromagnetic spectrum that has transformed modern life. Its applications in communication, healthcare, industry, and beyond showcase its immense potential and significance. As technology continues to advance, radio frequency will undoubtedly play a crucial role in shaping the future, driving innovation, and improving the quality of life for people worldwide.
For more information on radio frequency and its applications, consider exploring resources from reputable organizations such as the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) or academic publications on electromagnetic technology. Understanding radio frequency is essential for anyone looking to navigate the complexities of modern technology and its impact on society.