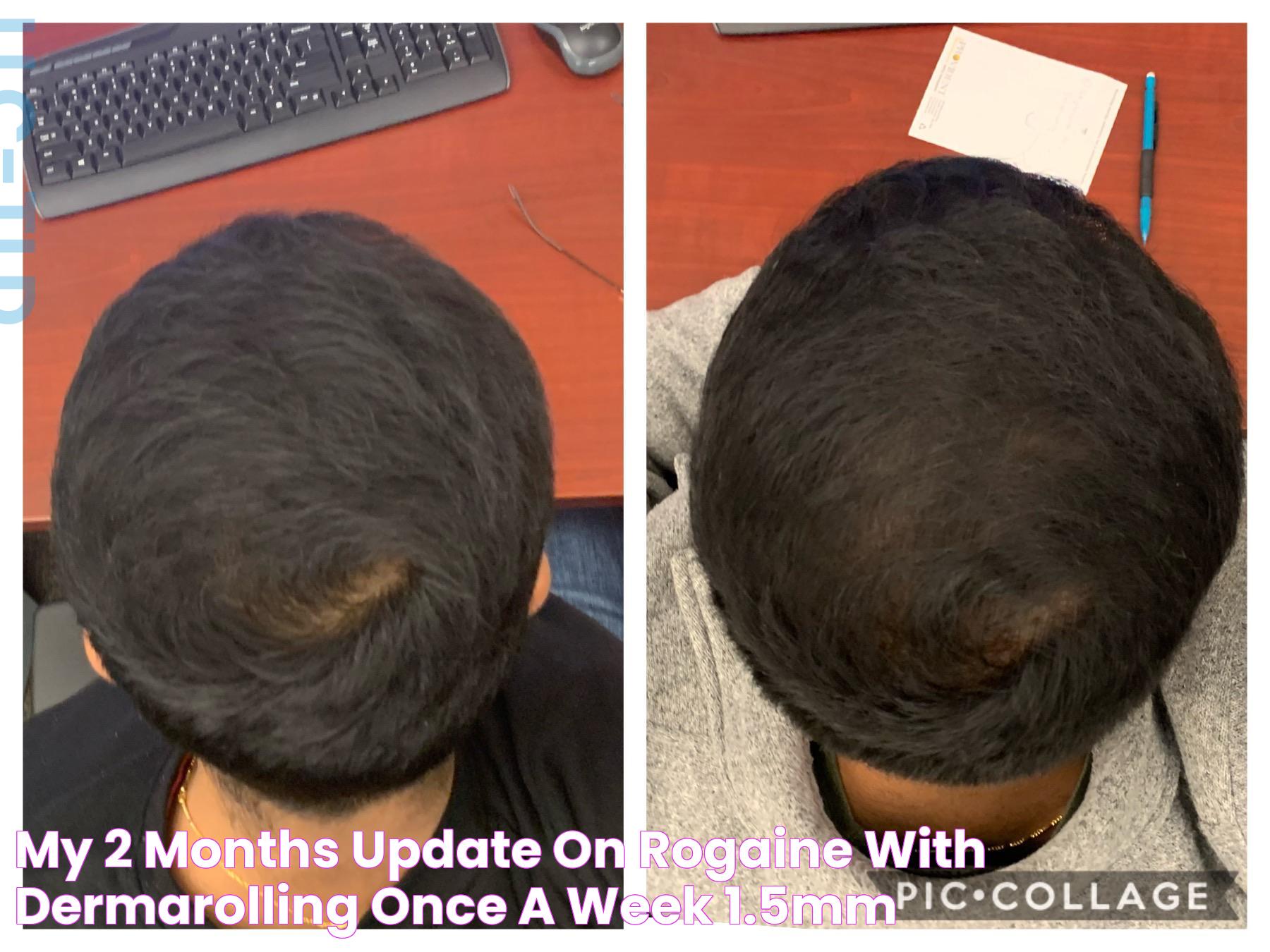
Rogaine is a popular over-the-counter medication used to treat hair loss, particularly in cases of androgenetic alopecia, also known as male or female pattern baldness. While it has proven to be effective for many, some users may notice that their bald spot appears to get worse before it gets better. This phenomenon can be puzzling and concerning, leading to questions about the efficacy of the treatment and whether it should be continued.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the reasons why a bald spot may worsen after starting Rogaine, delve into the science behind this temporary setback, and provide insights into how to manage and mitigate these effects. We'll also discuss potential alternatives and supplementary treatments that can support hair regrowth and address common concerns related to hair loss treatments.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Rogaine and Its Effects
- The Science Behind Rogaine
- Why Does the Bald Spot Get Worse After Rogaine?
- How Long Does It Take to See Results with Rogaine?
- Managing Expectations with Rogaine Treatment
- Common Side Effects of Rogaine
- Other Treatments to Consider
- Does Diet Impact Hair Loss?
- Lifestyle Changes to Promote Hair Growth
- When to Consult a Dermatologist?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
Understanding Rogaine and Its Effects
Rogaine, or minoxidil, is one of the most well-known treatments for hair loss. It was initially developed as a treatment for high blood pressure, but researchers discovered its hair growth-promoting side effects. This led to its approval by the FDA for treating hair loss in both men and women.
Read also:Wrinkle Face A Comprehensive Guide To Understanding And Tackling Aging Skin
Minoxidil is applied topically and works by stimulating hair follicles, extending the growth phase of hair, and improving blood flow to the scalp. This increased nourishment encourages dormant follicles to awaken and produce new hair. Despite its widespread use, not everyone experiences the same results, and some might even notice a temporary increase in hair loss, which can be alarming.
The Science Behind Rogaine
The mechanism by which Rogaine promotes hair growth involves the stimulation of hair follicles and the prolongation of the anagen phase of the hair growth cycle. The anagen phase is the active growth phase, and by extending it, minoxidil allows more time for hair to grow longer and thicker.
Minoxidil's vasodilatory effects also play a crucial role in increasing blood flow to the scalp, providing more oxygen and nutrients to hair follicles. This environment is conducive to hair growth and can result in noticeable improvements over time.
Why Does the Bald Spot Get Worse After Rogaine?
The phenomenon of a bald spot worsening after starting Rogaine is known as "shedding." This temporary increase in hair loss occurs because minoxidil accelerates the hair cycle, pushing older hairs out to make way for new growth. While this can be distressing, it's actually a sign that the treatment is working and that new hair will eventually replace the shed strands.
Shedding typically subsides within a few months as the hair cycle stabilizes and new growth becomes more evident. It's important for users to understand this process and maintain patience with their treatment regimen.
How Long Does It Take to See Results with Rogaine?
Patience is key when using Rogaine, as results can vary widely among individuals. Most users begin to see some improvement within 3 to 6 months, with more significant results appearing after a full year of consistent use. It's crucial to adhere to the recommended dosage and application frequency to maximize the likelihood of success.
Read also:Benefits And Applications Of Cotton Padding In Everyday Life
Consistency is essential, as discontinuing the use of Rogaine will likely result in a return to the baseline level of hair loss. For those experiencing initial shedding, it can be reassuring to know that this phase is temporary and indicative of the treatment's activity.
Managing Expectations with Rogaine Treatment
While Rogaine can be effective in promoting hair growth, it's not a magic bullet. Understanding what to expect can help users maintain a realistic outlook and avoid disappointment. It's important to note that Rogaine is more effective for certain types of hair loss and may not work for everyone.
For those who respond well to treatment, Rogaine can lead to thicker, fuller hair. However, it may not fully restore hair to its previous density, especially in cases of extensive hair loss. Combining Rogaine with other treatments and lifestyle changes can enhance overall results and improve satisfaction.
Common Side Effects of Rogaine
Like any medication, Rogaine can cause side effects, although they are generally mild and manageable. Common side effects include:
- Scalp irritation or itching
- Dryness or flaking of the scalp
- Unwanted facial hair growth (in rare cases)
- Increased hair shedding during initial use
If side effects persist or worsen, it's advisable to consult a healthcare professional for guidance. In some cases, adjusting the application technique or frequency can alleviate discomfort.
Other Treatments to Consider
While Rogaine is a popular choice, there are other treatments available that may be suitable for individuals experiencing hair loss. These include:
- Finasteride: An oral medication that inhibits the hormone responsible for hair loss in men.
- Low-level laser therapy (LLLT): A non-invasive treatment that uses light to stimulate hair follicles.
- Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy: A procedure that involves injecting concentrated platelets into the scalp to promote hair growth.
Each treatment has its own set of benefits and considerations, and consulting with a dermatologist can help determine the best approach for individual needs.
Does Diet Impact Hair Loss?
Diet can play a significant role in hair health, as the nutrients obtained from food are essential for hair growth and maintenance. Key nutrients that support healthy hair include:
- Protein: A crucial building block for hair, found in foods like fish, eggs, and legumes.
- Iron: Important for delivering oxygen to hair follicles, found in red meat, spinach, and lentils.
- Zinc: Supports hair follicle health and repair, found in nuts, seeds, and shellfish.
- Biotin: A B-vitamin that strengthens hair, found in whole grains, nuts, and eggs.
Incorporating a balanced diet rich in these nutrients can support overall hair health and complement hair loss treatments.
Lifestyle Changes to Promote Hair Growth
Beyond diet, certain lifestyle changes can positively impact hair growth and minimize hair loss. These include:
- Reducing stress through activities like yoga, meditation, or regular exercise.
- Avoiding harsh hair treatments or styles that pull on the hair, such as tight ponytails or braids.
- Ensuring adequate sleep to support overall health and hair growth.
- Staying hydrated to maintain a healthy scalp environment.
By adopting these habits, individuals can create an optimal environment for hair growth and enhance the effectiveness of treatments like Rogaine.
When to Consult a Dermatologist?
Consulting a dermatologist can be beneficial for individuals experiencing persistent hair loss or those who are uncertain about the best treatment approach. A dermatologist can provide a thorough evaluation, identify underlying causes of hair loss, and recommend personalized treatment plans.
It's particularly important to seek professional advice if hair loss is accompanied by other symptoms, such as scalp inflammation or changes in hair texture, as these may indicate underlying health issues that require medical attention.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is it normal for hair to shed after starting Rogaine?
Yes, initial shedding is a common experience when starting Rogaine. It indicates that the treatment is working by pushing out older hairs to make way for new growth.
2. How long should I use Rogaine to see results?
Most users see some improvement within 3 to 6 months, with more noticeable results after a year of consistent use.
3. Can Rogaine be used indefinitely?
Yes, Rogaine can be used long-term, but discontinuing use will likely result in a return to the baseline level of hair loss.
4. Are there any natural alternatives to Rogaine?
While Rogaine is a widely used treatment, some natural alternatives include essential oils, scalp massages, and dietary supplements that support hair health.
5. What should I do if I experience side effects from Rogaine?
If side effects persist or worsen, consult a healthcare professional for advice on adjusting the application or exploring alternative treatments.
6. Can Rogaine be used in conjunction with other treatments?
Yes, Rogaine can be combined with other treatments like finasteride or PRP therapy to enhance results, but it's important to consult with a dermatologist before combining treatments.
Conclusion
Dealing with a bald spot that worsens after starting Rogaine can be a challenging experience, but understanding the science behind the treatment and the temporary nature of shedding can provide reassurance. By managing expectations, exploring complementary treatments, and adopting healthy lifestyle habits, individuals can optimize their chances of achieving successful hair regrowth. While Rogaine is not a one-size-fits-all solution, it remains a valuable tool in the battle against hair loss, offering hope and potential for those seeking to restore their hair and confidence.