In an increasingly interconnected world, understanding and connecting with others on a deeper level has never been more important. Empathy, often regarded as the ability to understand and share the feelings of another, plays a crucial role in fostering meaningful relationships and promoting emotional well-being. But what does "empathize meaning" truly entail? In this comprehensive guide, we'll delve into the essence of empathy, exploring its significance, applications, and the ways it shapes our interactions with others.
For many, empathy is a natural and intuitive response, while for others, it requires conscious effort and practice. By examining the various facets of empathy, we aim to provide a clearer understanding of its role in our lives and the impact it can have on our personal and professional relationships. From the neuroscience behind empathy to its cultural implications, this article will equip you with the knowledge to enhance your empathetic skills and create more harmonious connections.
Whether you're looking to improve your communication skills, enhance your leadership abilities, or simply become a more understanding and compassionate individual, understanding the "empathize meaning" is a vital first step. Join us as we uncover the layers of empathy, offering practical insights and strategies to help you cultivate a deeper sense of understanding and connection with those around you.
Read also:Ultimate Guide To Jeniffer Lopez From Biography To Stardom
Table of Contents
- Biography of Empathy
- What is the Empathize Meaning?
- Types of Empathy
- The Neuroscience of Empathy
- Benefits of Empathy
- Empathy in Different Cultures
- How Can We Cultivate Empathy?
- Empathy in Leadership
- Empathy in Healthcare
- Empathy in Education
- Empathy and Technology
- Empathy vs. Sympathy
- Empathy in Conflict Resolution
- Empathy and Emotional Intelligence
- Frequently Asked Questions about Empathy
- Conclusion
Biography of Empathy
Empathy is not a new concept; it has been an integral part of human evolution and social interaction for centuries. The term "empathy" is derived from the Greek word "empatheia," meaning "passion" or "physical affection." It was first introduced into the English language in the early 20th century by psychologist Edward B. Titchener. Titchener used the term to describe the process of "feeling into" someone else's emotions, drawing a distinction between empathy and sympathy.
Historical Perspectives on Empathy
Throughout history, philosophers and psychologists have explored the concept of empathy, emphasizing its importance in understanding human behavior and fostering social connections. In the 18th century, Scottish philosopher David Hume highlighted the role of empathy in moral judgment, while German philosopher Friedrich Nietzsche viewed empathy as a means of overcoming egoism and achieving a higher state of consciousness.
Modern Interpretations of Empathy
In contemporary times, empathy has gained recognition as a valuable skill in various fields, including psychology, education, healthcare, and leadership. Researchers have identified different forms of empathy, such as cognitive empathy (the ability to understand another's perspective) and emotional empathy (the capacity to feel what another person feels). These distinctions have furthered our understanding of how empathy functions and its impact on our interactions.
What is the Empathize Meaning?
At its core, the empathize meaning refers to the ability to understand and share the feelings, thoughts, and experiences of others. It involves putting oneself in another person's shoes, perceiving their emotions, and responding with care and compassion. Empathy is not just about recognizing someone else's emotions; it also requires an active effort to connect with them on a deeper level.
Components of Empathy
- Cognitive Empathy: This involves understanding another person's perspective and recognizing their emotions without necessarily sharing those feelings.
- Emotional Empathy: This entails feeling the emotions that another person is experiencing, allowing for a deeper emotional connection.
- Compassionate Empathy: This goes beyond understanding and feeling; it involves taking action to help or support the person in need.
The Role of Empathy in Human Interaction
Empathy plays a critical role in human interaction, enabling individuals to connect, communicate, and understand each other more effectively. It fosters trust, builds rapport, and creates a supportive environment where individuals feel valued and heard. By incorporating empathy into our interactions, we can improve our relationships and contribute to a more compassionate and understanding society.
Types of Empathy
Empathy is a multifaceted concept that encompasses various types, each contributing to our ability to connect with others. Understanding the different types of empathy can help us develop more nuanced and effective empathetic responses.
Read also:Timeless Charm Of Vintage Pink A Nostalgic And Elegant Hue
Cognitive Empathy
Cognitive empathy, also known as perspective-taking, involves understanding another person's thoughts and emotions. It requires recognizing their perspective and considering their experiences. While cognitive empathy allows us to comprehend someone else's situation, it doesn't necessarily involve sharing their emotions. This form of empathy is crucial in communication, negotiation, and conflict resolution, as it enables us to anticipate others' needs and respond appropriately.
Emotional Empathy
Emotional empathy, often referred to as affective empathy, involves feeling the emotions that another person is experiencing. This type of empathy allows us to share in another's joy, sadness, or pain, creating a deep emotional connection. Emotional empathy is essential for building strong, supportive relationships and fostering a sense of belonging and understanding.
Compassionate Empathy
Compassionate empathy, also known as empathic concern, goes beyond understanding and feeling; it involves taking action to alleviate another person's suffering. This type of empathy is characterized by a desire to help and support those in need, reflecting a commitment to making a positive difference in their lives. Compassionate empathy is vital in caregiving, social work, and volunteerism, where individuals seek to provide comfort and assistance to others.
The Neuroscience of Empathy
The study of empathy has extended beyond psychology and philosophy, reaching into the realm of neuroscience. Advances in brain imaging techniques have enabled researchers to explore the neural mechanisms underlying empathy, shedding light on how our brains process and respond to the emotions of others.
The Brain Regions Involved in Empathy
Empathy involves several interconnected brain regions, including the anterior insula, anterior cingulate cortex, and the mirror neuron system. These areas are responsible for processing emotions, understanding others' perspectives, and facilitating empathetic responses.
The Mirror Neuron System
Mirror neurons, discovered in the 1990s, play a crucial role in empathy. These specialized neurons fire both when we perform an action and when we observe someone else performing the same action. The mirror neuron system allows us to simulate and understand others' actions and emotions, contributing to our ability to empathize and connect with them on a deeper level.
The Role of Oxytocin in Empathy
Oxytocin, often referred to as the "love hormone," has been linked to empathy and social bonding. Studies have shown that higher levels of oxytocin can enhance our ability to understand and share others' emotions, promoting more empathetic and compassionate behavior. This hormone plays a vital role in forming and maintaining social connections, highlighting the biological underpinnings of empathy.
Benefits of Empathy
Empathy offers numerous benefits, both for individuals and society as a whole. By fostering empathy in our interactions, we can improve our relationships, enhance our well-being, and contribute to a more compassionate and understanding world.
Improved Communication and Relationships
Empathy enhances our ability to communicate effectively, allowing us to understand others' perspectives and respond with care and consideration. By fostering empathy in our interactions, we can build stronger, more meaningful relationships based on trust and mutual understanding.
Increased Emotional Well-Being
Empathy allows us to connect with others on a deeper emotional level, promoting a sense of belonging and reducing feelings of isolation. By fostering empathy, we can enhance our emotional well-being, leading to greater happiness and life satisfaction.
Enhanced Conflict Resolution Skills
Empathy plays a crucial role in conflict resolution, enabling us to understand and address the underlying emotions and needs of all parties involved. By fostering empathy, we can facilitate more constructive and compassionate solutions, reducing tension and promoting harmony.
Positive Impact on Society
Empathy promotes prosocial behavior, encouraging individuals to act with kindness and compassion towards others. By fostering empathy in society, we can create a more inclusive and supportive environment where individuals feel valued and heard.
Empathy in Different Cultures
Empathy is a universal human trait, but its expression and significance can vary across cultures. By exploring empathy in different cultural contexts, we can gain a deeper understanding of its role in shaping human interactions and social dynamics.
Western Perspectives on Empathy
In Western cultures, empathy is often viewed as an essential component of emotional intelligence and interpersonal skills. It is emphasized in various fields, including psychology, education, and leadership, as a means of fostering understanding and building strong, supportive relationships.
Eastern Perspectives on Empathy
In Eastern cultures, empathy is often associated with concepts of harmony, balance, and interconnectedness. It is viewed as a fundamental aspect of human relationships, promoting compassion and understanding in social interactions. Empathy is also emphasized in spiritual and philosophical traditions, such as Buddhism and Confucianism, as a means of achieving personal growth and enlightenment.
Cross-Cultural Differences in Empathy
While empathy is a universal trait, its expression and significance can vary across cultures. Cultural norms, values, and social practices can influence how empathy is perceived and expressed, leading to differences in empathetic behavior and responses. By understanding these cross-cultural differences, we can foster more inclusive and empathetic interactions in our increasingly globalized world.
How Can We Cultivate Empathy?
Cultivating empathy is a continuous process that requires conscious effort and practice. By developing our empathetic skills, we can improve our relationships, enhance our well-being, and contribute to a more compassionate and understanding society.
Practicing Active Listening
Active listening involves fully engaging with the speaker, paying attention to their words, emotions, and nonverbal cues. By practicing active listening, we can better understand others' perspectives and respond with care and consideration, fostering empathy in our interactions.
Engaging in Perspective-Taking Exercises
Perspective-taking exercises involve imagining oneself in someone else's situation, considering their thoughts, feelings, and experiences. By engaging in perspective-taking, we can enhance our cognitive empathy and develop a deeper understanding of others' perspectives.
Developing Emotional Awareness
Emotional awareness involves recognizing and understanding our own emotions and the emotions of others. By developing emotional awareness, we can enhance our emotional empathy, allowing us to connect with others on a deeper emotional level.
Practicing Mindfulness
Mindfulness involves being present in the moment, observing our thoughts and emotions without judgment. By practicing mindfulness, we can enhance our self-awareness and empathy, promoting more compassionate and understanding interactions.
Empathy in Leadership
Empathy is a critical leadership skill, enabling leaders to connect with their team, understand their needs, and foster a supportive and inclusive environment. By incorporating empathy into their leadership style, leaders can enhance their effectiveness, build strong relationships, and promote a positive organizational culture.
The Role of Empathy in Effective Leadership
Empathy allows leaders to understand and address the needs and concerns of their team, fostering trust and collaboration. By demonstrating empathy, leaders can create a supportive environment where individuals feel valued and heard, leading to increased engagement and productivity.
Empathy and Emotional Intelligence in Leadership
Emotional intelligence, which encompasses self-awareness, self-regulation, motivation, empathy, and social skills, is a critical component of effective leadership. Empathy is a key aspect of emotional intelligence, enabling leaders to connect with others, understand their emotions, and respond with care and consideration.
Strategies for Enhancing Empathy in Leadership
- Active Listening: Engaging with team members, paying attention to their words and emotions, and responding with empathy and understanding.
- Open Communication: Promoting open and honest communication, encouraging team members to share their thoughts and feelings.
- Building Relationships: Investing time and effort in building strong, supportive relationships with team members, fostering trust and collaboration.
Empathy in Healthcare
Empathy plays a crucial role in healthcare, enhancing patient care, improving communication, and promoting positive health outcomes. By fostering empathy in healthcare settings, providers can build trust, enhance patient satisfaction, and contribute to a more compassionate and supportive healthcare environment.
The Importance of Empathy in Patient Care
Empathy allows healthcare providers to understand and address the emotional and physical needs of their patients, fostering trust and collaboration. By demonstrating empathy, providers can enhance patient satisfaction, improve communication, and promote positive health outcomes.
Empathy and Communication in Healthcare
Effective communication is a critical component of patient care, allowing providers to understand patients' needs, concerns, and preferences. Empathy enhances communication by enabling providers to listen actively, understand patients' perspectives, and respond with care and consideration.
Strategies for Enhancing Empathy in Healthcare
- Active Listening: Engaging with patients, paying attention to their words and emotions, and responding with empathy and understanding.
- Building Rapport: Investing time and effort in building strong, supportive relationships with patients, fostering trust and collaboration.
- Providing Emotional Support: Offering comfort and support to patients, addressing their emotional needs and concerns.
Empathy in Education
Empathy is a vital skill in education, fostering a supportive and inclusive learning environment, enhancing communication, and promoting positive student outcomes. By incorporating empathy into educational practices, educators can enhance their effectiveness, build strong relationships, and contribute to a more compassionate and understanding society.
The Role of Empathy in Effective Teaching
Empathy allows educators to understand and address the needs and concerns of their students, fostering trust and collaboration. By demonstrating empathy, educators can create a supportive environment where students feel valued and heard, leading to increased engagement and academic success.
Empathy and Classroom Management
Empathy plays a crucial role in classroom management, enabling educators to understand and address students' emotional and behavioral needs. By fostering empathy, educators can promote a positive classroom culture, reducing conflict and promoting cooperation.
Strategies for Enhancing Empathy in Education
- Active Listening: Engaging with students, paying attention to their words and emotions, and responding with empathy and understanding.
- Building Relationships: Investing time and effort in building strong, supportive relationships with students, fostering trust and collaboration.
- Promoting Inclusion: Creating an inclusive learning environment that values and respects diversity, fostering empathy and understanding.
Empathy and Technology
In the digital age, technology plays an increasingly important role in shaping our interactions and communication. While technology offers numerous benefits, it also presents challenges in fostering empathy and understanding. By exploring the intersection of empathy and technology, we can gain insights into how to navigate the digital landscape and promote more empathetic and compassionate interactions.
The Impact of Technology on Empathy
Technology has transformed the way we communicate and interact with others, offering new opportunities for connection and collaboration. However, it can also present challenges in fostering empathy, as digital communication often lacks the emotional cues and context that facilitate understanding and connection.
Promoting Empathy in the Digital Age
To foster empathy in the digital age, it is essential to leverage technology in ways that enhance understanding and connection. This includes using digital tools to facilitate meaningful communication, promote inclusivity, and encourage perspective-taking.
Strategies for Enhancing Empathy through Technology
- Digital Storytelling: Using digital platforms to share personal stories and experiences, fostering empathy and understanding.
- Virtual Reality: Leveraging virtual reality technology to create immersive experiences that promote perspective-taking and empathy.
- Online Communities: Building and participating in online communities that promote inclusivity, diversity, and empathy.
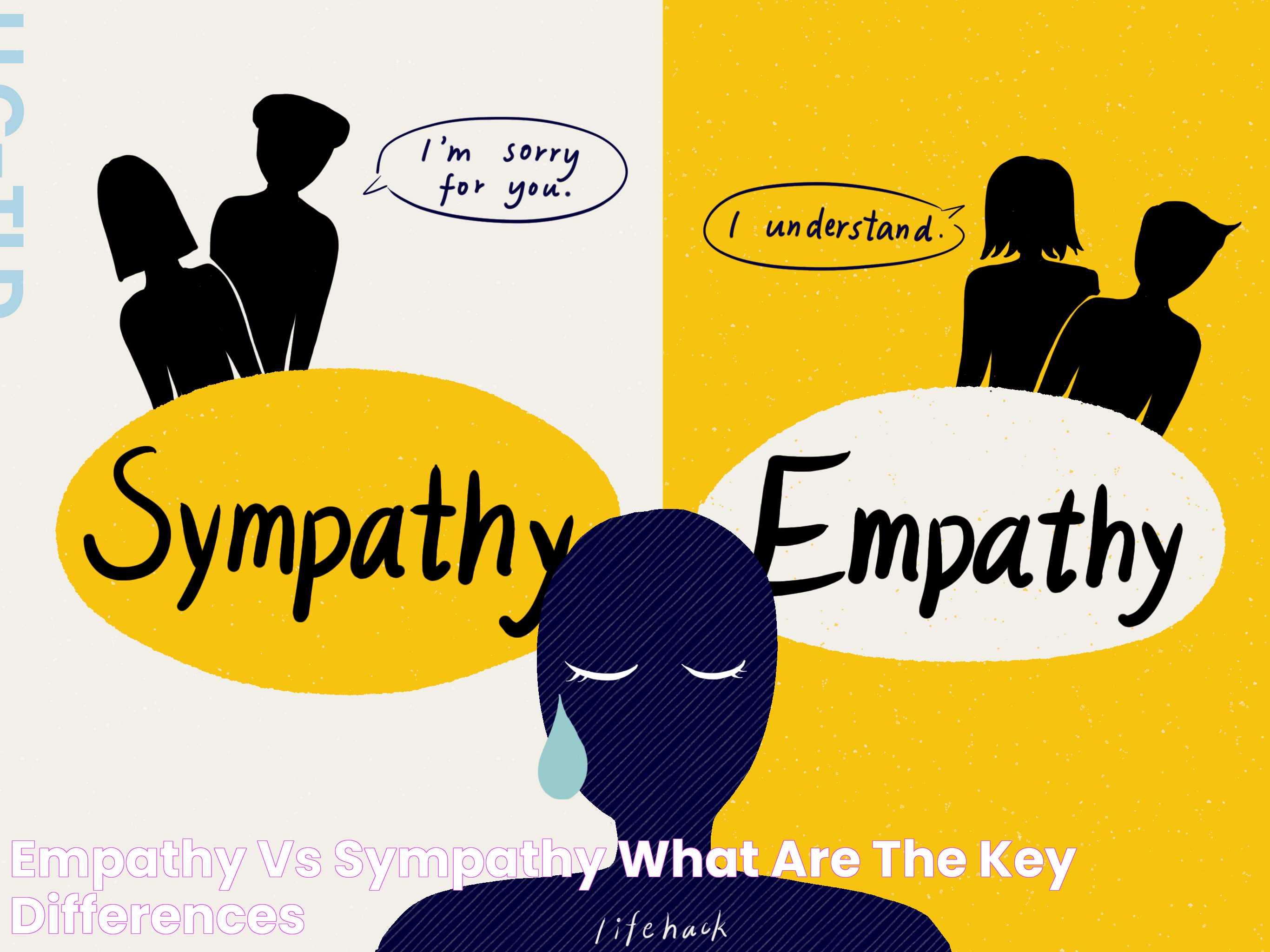
Empathy vs. Sympathy
While empathy and sympathy are often used interchangeably, they represent distinct concepts with different implications for our interactions and relationships. By understanding the differences between empathy and sympathy, we can foster more effective and compassionate connections with others.
Understanding Empathy
Empathy involves understanding and sharing the feelings, thoughts, and experiences of others. It requires putting oneself in another person's shoes, perceiving their emotions, and responding with care and compassion.
Understanding Sympathy
Sympathy involves feeling pity or sorrow for someone else's situation without necessarily understanding or sharing their emotions. While sympathy acknowledges another person's suffering, it often maintains a degree of emotional distance.
The Importance of Empathy over Sympathy
Empathy offers a deeper and more meaningful connection than sympathy, as it involves understanding and sharing another person's emotions. By fostering empathy, we can create more compassionate and supportive interactions, promoting a sense of belonging and understanding.
Empathy in Conflict Resolution
Empathy plays a crucial role in conflict resolution, enabling us to understand and address the underlying emotions and needs of all parties involved. By fostering empathy, we can facilitate more constructive and compassionate solutions, reducing tension and promoting harmony.
The Role of Empathy in Understanding Conflict
Empathy allows us to understand the perspectives and emotions of all parties involved in a conflict, identifying the underlying needs and concerns. By fostering empathy, we can gain insights into the root causes of conflict and develop more effective strategies for resolution.
Empathy and Effective Communication in Conflict Resolution
Effective communication is a critical component of conflict resolution, allowing us to understand and address the needs and concerns of all parties involved. Empathy enhances communication by enabling us to listen actively, understand others' perspectives, and respond with care and consideration.
Strategies for Enhancing Empathy in Conflict Resolution
- Active Listening: Engaging with all parties involved, paying attention to their words and emotions, and responding with empathy and understanding.
- Perspective-Taking: Considering the perspectives and emotions of all parties involved, fostering empathy and understanding.
- Collaborative Problem Solving: Working together to develop mutually beneficial solutions that address the needs and concerns of all parties involved.
Empathy and Emotional Intelligence
Empathy is a key component of emotional intelligence, which encompasses self-awareness, self-regulation, motivation, empathy, and social skills. By enhancing our emotional intelligence, we can improve our relationships, enhance our well-being, and contribute to a more compassionate and understanding society.
The Connection Between Empathy and Emotional Intelligence
Empathy is a critical aspect of emotional intelligence, enabling us to understand and connect with others on a deeper emotional level. By fostering empathy, we can enhance our emotional intelligence, improving our relationships and promoting positive social interactions.
The Role of Empathy in Enhancing Self-Awareness and Self-Regulation
Empathy allows us to understand and manage our own emotions, promoting self-awareness and self-regulation. By fostering empathy, we can enhance our emotional intelligence, leading to greater personal growth and development.
Strategies for Enhancing Empathy and Emotional Intelligence
- Developing Emotional Awareness: Recognizing and understanding our own emotions and the emotions of others.
- Practicing Active Listening: Engaging with others, paying attention to their words and emotions, and responding with empathy and understanding.
- Building Relationships: Investing time and effort in building strong, supportive relationships with others, fostering trust and collaboration.
Frequently Asked Questions about Empathy
Empathy is a complex and multifaceted concept, often raising questions about its nature and application. Here, we address some of the most common questions about empathy to provide clarity and understanding.
What is the difference between empathy and sympathy?
Empathy involves understanding and sharing the feelings, thoughts, and experiences of others, while sympathy involves feeling pity or sorrow for someone else's situation without necessarily understanding or sharing their emotions.
Can empathy be learned or improved?
Yes, empathy is a skill that can be developed and improved through conscious effort and practice. By engaging in activities such as active listening, perspective-taking, and mindfulness, we can enhance our empathetic abilities.
Why is empathy important in leadership?
Empathy is a critical leadership skill, enabling leaders to connect with their team, understand their needs, and foster a supportive and inclusive environment. By incorporating empathy into their leadership style, leaders can enhance their effectiveness and promote a positive organizational culture.
How does empathy impact communication?
Empathy enhances communication by enabling us to understand others' perspectives and respond with care and consideration. By fostering empathy in our interactions, we can improve our communication skills and build stronger, more meaningful relationships.
What role does empathy play in conflict resolution?
Empathy plays a crucial role in conflict resolution, enabling us to understand and address the underlying emotions and needs of all parties involved. By fostering empathy, we can facilitate more constructive and compassionate solutions, reducing tension and promoting harmony.
How does technology affect empathy?
Technology has transformed the way we communicate and interact with others, offering new opportunities for connection and collaboration. However, it can also present challenges in fostering empathy, as digital communication often lacks the emotional cues and context that facilitate understanding and connection.
Conclusion
Empathy is a vital skill that enables us to understand and connect with others, fostering meaningful relationships and promoting emotional well-being. By understanding the empathize meaning and incorporating empathy into our interactions, we can improve our communication skills, enhance our leadership abilities, and contribute to a more compassionate and understanding society. As we navigate the complexities of the digital age and an increasingly interconnected world, empathy remains an essential tool for building strong, supportive connections and creating a more inclusive and harmonious global community.
For more information on empathy and its applications, visit Psychology Today.