Can you get chlamydia from a toilet seat? This question has puzzled many, sparking debates and discussions across various platforms. Chlamydia, a common sexually transmitted infection (STI), is typically transmitted through sexual contact. However, the myth of acquiring it from a toilet seat persists, leading to confusion and misinformation.
To understand the reality behind this myth, one must first comprehend the nature of chlamydia and how it spreads. Unlike other infections that can survive on surfaces, chlamydia requires specific conditions to thrive and be transmitted. This article aims to clarify the misconceptions and provide factual insights into the transmission of chlamydia.
By exploring various aspects of chlamydia, including its symptoms, methods of transmission, and preventive measures, we aim to debunk the myths surrounding this STI. Read on to discover the truth about chlamydia and how you can protect yourself from this common infection.
Read also:Lip Tint Your Ultimate Guide To Luscious Lips
- What is Chlamydia?
- Symptoms of Chlamydia
- How is Chlamydia Transmitted?
- Can You Get Chlamydia from a Toilet Seat?
- Preventing Chlamydia
- Treatment Options for Chlamydia
- Risk Factors and Complications
- Chlamydia in Pregnancy
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
What is Chlamydia?
Chlamydia is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis. It is one of the most common STIs worldwide, particularly among young adults and teenagers. The infection often presents without symptoms, making it difficult to detect and increasing the risk of unknowingly transmitting it to others.
The bacterium targets the mucous membranes of the body, such as those found in the genital tract, rectum, and throat. If left untreated, chlamydia can lead to serious health complications, including infertility and an increased risk of acquiring other STIs.
Symptoms of Chlamydia
Many individuals with chlamydia do not experience symptoms, which is why it is often referred to as a "silent" infection. However, when symptoms do occur, they may include:
- Painful urination
- Abnormal genital discharge
- Lower abdominal pain
- Testicular pain in men
- Bleeding between periods in women
If you suspect you may have chlamydia, it is crucial to get tested and seek treatment promptly to avoid complications.
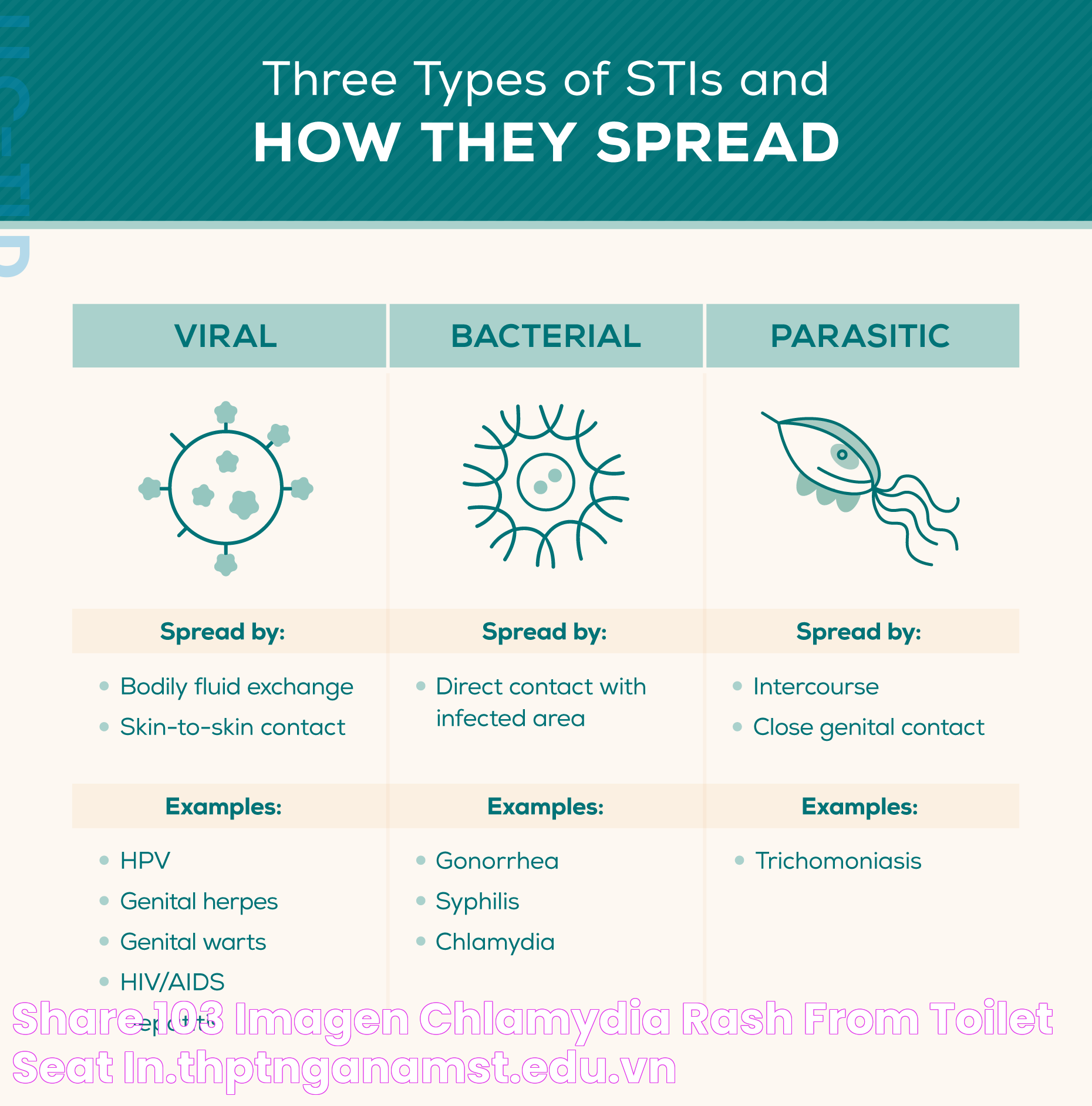
How is Chlamydia Transmitted?
Chlamydia is primarily transmitted through sexual contact with an infected person. This includes vaginal, anal, and oral sex. The bacterium is spread through bodily fluids, which means that even if symptoms are not present, the infection can still be transmitted.
It is important to note that chlamydia cannot survive outside the human body for long. The bacterium requires the warm and moist environment of mucous membranes to live and multiply. This characteristic plays a crucial role in understanding transmission myths, such as acquiring chlamydia from a toilet seat.
Read also:Discovering The Mystery Why Does My Webcam Flip The Image
Can You Get Chlamydia from a Toilet Seat?
One of the most persistent myths about chlamydia is the possibility of contracting it from a toilet seat. To address this, it is essential to understand how chlamydia survives and spreads.
Chlamydia trachomatis cannot survive on inanimate objects, such as toilet seats, because these surfaces do not provide the necessary conditions for the bacterium to live. The bacterium quickly dies when exposed to the external environment, rendering the risk of transmission from a toilet seat virtually impossible.
Therefore, while it is important to maintain good hygiene practices, the fear of contracting chlamydia from a toilet seat is unfounded and should not be a cause for concern.
Preventing Chlamydia
Prevention is key when it comes to chlamydia and other STIs. Here are some effective strategies to reduce the risk of infection:
- Use condoms consistently and correctly during sexual activity.
- Engage in mutual monogamy with a partner who has tested negative for STIs.
- Get tested regularly for STIs, especially if you have multiple partners.
- Educate yourself and your partner(s) about STIs and safe sex practices.
By adopting these preventive measures, you can significantly reduce your risk of acquiring chlamydia and other sexually transmitted infections.
Treatment Options for Chlamydia
Chlamydia is easily treatable with antibiotics. The most common treatment involves a course of azithromycin or doxycycline. It is crucial to complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed, even if symptoms disappear, to ensure the infection is fully eradicated.
Partners should be informed and tested to prevent reinfection. Abstaining from sexual activity until treatment is completed and a healthcare provider confirms the infection has cleared is also recommended.
Risk Factors and Complications
Several factors can increase the risk of contracting chlamydia:
- Engaging in unprotected sex
- Having multiple sexual partners
- Being under 25 years of age
- Having a history of STIs
Untreated chlamydia can lead to severe health complications, including pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) in women, which can cause infertility and chronic pelvic pain. In men, chlamydia can lead to epididymitis, a painful condition affecting the testicles.
Chlamydia in Pregnancy
Pregnant women with chlamydia risk passing the infection to their newborns during childbirth. This can lead to complications such as conjunctivitis and pneumonia in the infant.
Screening and treatment during pregnancy are vital to prevent these outcomes. Pregnant women diagnosed with chlamydia should follow their healthcare provider's treatment plan to protect their health and that of their baby.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Can you get chlamydia from sharing a bathroom? No, chlamydia is not transmitted through casual contact or sharing a bathroom.
- Is chlamydia curable? Yes, chlamydia is curable with the appropriate antibiotics.
- Can chlamydia go away on its own? No, chlamydia requires treatment with antibiotics to cure the infection.
- How long can chlamydia go undetected? Chlamydia can go undetected for months or even years due to its often asymptomatic nature.
- Is it possible to have chlamydia and not know it? Yes, many people with chlamydia do not experience symptoms and may be unaware of the infection.
- Can men get tested for chlamydia? Yes, men can and should get tested for chlamydia, especially if they are at risk.
Conclusion
The myth of contracting chlamydia from a toilet seat is just that—a myth. Understanding the transmission pathways of chlamydia, its symptoms, and preventive measures are crucial for debunking such misconceptions. By staying informed and practicing safe sex, individuals can protect themselves and others from this common infection.
It is imperative to seek regular testing and treatment if necessary, as untreated chlamydia can lead to severe health complications. Remember, knowledge is power, and dispelling myths like the toilet seat transmission can help reduce the stigma and spread of chlamydia.