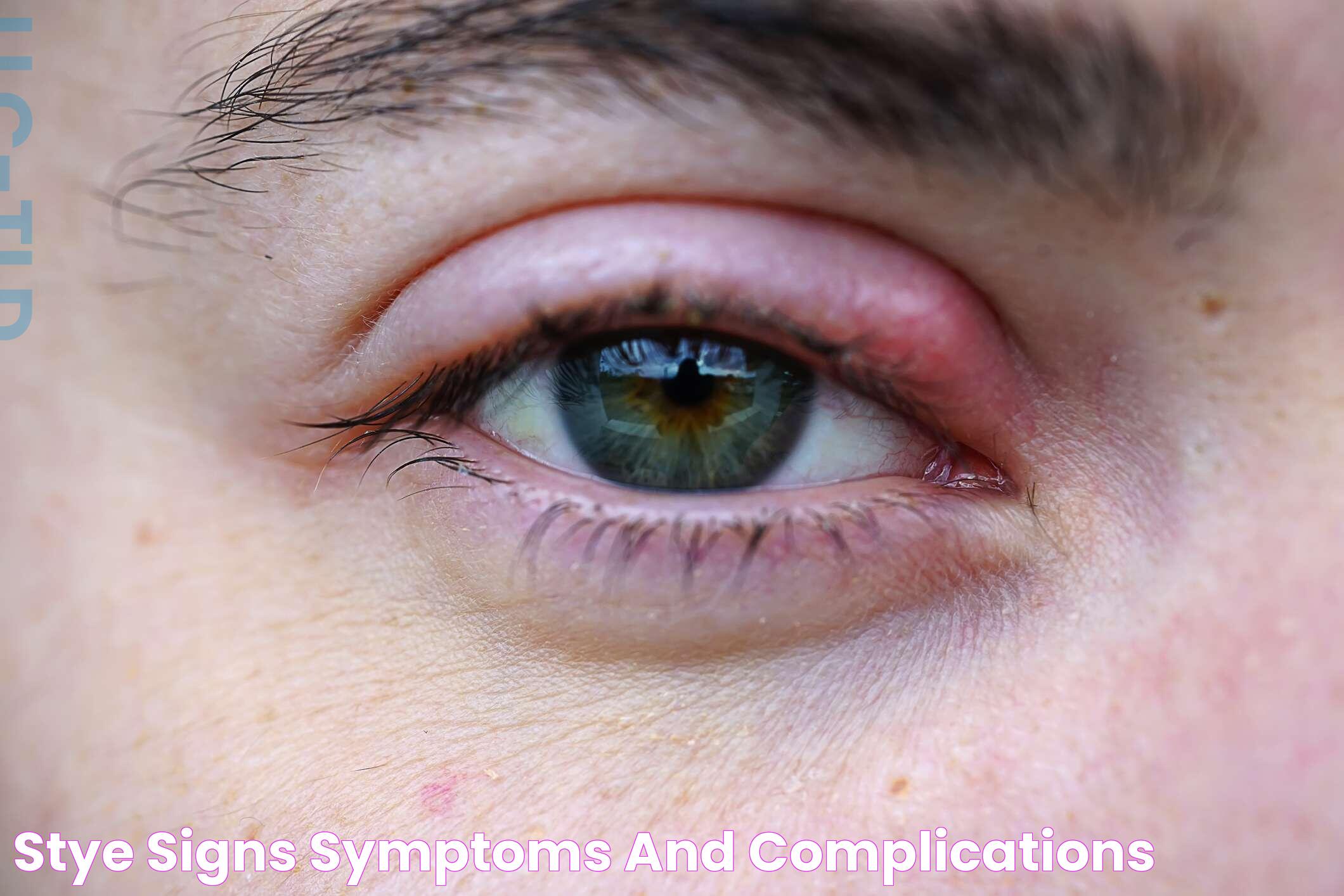
Eye styes, those small, painful lumps that can form on the upper eyelid, are a common eye ailment that affects people of all ages. While they can be uncomfortable and unsightly, they are typically harmless and can be treated effectively with proper care. Eye styes occur when the oil glands at the base of the eyelash become clogged and infected, leading to redness, swelling, and tenderness. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for eye styes can help alleviate discomfort and prevent future occurrences.
Despite their small size, eye styes can have a significant impact on daily activities, making it difficult to blink or fully close the eye. They are often mistaken for other eye conditions, such as chalazion or blepharitis, but they have distinct characteristics that set them apart. Eye styes usually appear as red, pus-filled bumps on the upper eyelid and can develop over a few days. In most cases, they resolve on their own within one to two weeks, but there are ways to speed up the healing process and reduce discomfort.
Proper hygiene and care are essential for managing eye styes and preventing them from becoming a recurring issue. Simple home remedies, such as warm compresses, can aid in healing, while over-the-counter medications may provide additional relief. In rare cases, medical intervention may be necessary to address persistent or severe styes. By understanding the nature of eye styes and taking proactive measures, individuals can maintain healthy eyelids and minimize the risk of infection.
Read also:Mastering The Art Of Being Quick Witted A Guide To Sharp Thinking
Table of Contents
- What is an Eye Stye?
- Causes of Eye Styes
- Symptoms of an Eye Stye
- How to Prevent Eye Styes?
- Diagnosis and Medical Evaluation
- Treatment Options for Eye Styes
- Home Remedies for Eye Styes
- When to See a Doctor?
- Complications from Untreated Eye Styes
- Differentiating Between Eye Stye and Chalazion
- Eye Stye Upper Eyelid: Specific Considerations
- Children and Eye Styes
- Adults and Eye Styes
- Myths and Facts About Eye Styes
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
What is an Eye Stye?
An eye stye, also known as a hordeolum, is a small, painful lump that forms on the eyelid, often at the base of an eyelash. Eye styes are caused by a bacterial infection in the oil glands of the eyelid, which leads to the development of a red, swollen bump. They are common and can affect anyone, regardless of age or gender.
There are two main types of eye styes: external and internal. External styes occur on the outside edge of the eyelid and are typically associated with the hair follicles of the eyelashes. Internal styes, on the other hand, develop on the inner side of the eyelid and are often linked to the meibomian glands, which produce the oily component of tears.
Characteristics of Eye Styes
Eye styes are characterized by several distinct features, including:
- Redness and swelling of the affected eyelid
- Pain and tenderness at the site of the stye
- A small, pus-filled bump resembling a pimple
- Increased tearing or watery eyes
- Crustiness around the eyelid margins
How Long Do Eye Styes Last?
In most cases, eye styes resolve on their own within one to two weeks. However, the duration can vary depending on factors such as the size of the stye and the individual's immune response. Proper care and treatment can help expedite the healing process and reduce discomfort.
Causes of Eye Styes
The primary cause of eye styes is a bacterial infection, most commonly caused by Staphylococcus aureus. This bacterium is naturally present on the skin and can enter the oil glands of the eyelid through small cuts or abrasions. Several factors can increase the likelihood of developing an eye stye, including:
Poor Eyelid Hygiene
Inadequate cleaning of the eyelids can lead to the accumulation of oil, debris, and bacteria, increasing the risk of infection. Individuals who wear makeup, especially eye makeup, are advised to remove it thoroughly before bedtime.
Read also:Shaving Your Arms Benefits Techniques And Considerations
Touching or Rubbing the Eyes
Frequent touching or rubbing of the eyes can transfer bacteria from the hands to the eyelids, leading to infection. It is essential to wash hands regularly and avoid touching the face to prevent the spread of bacteria.
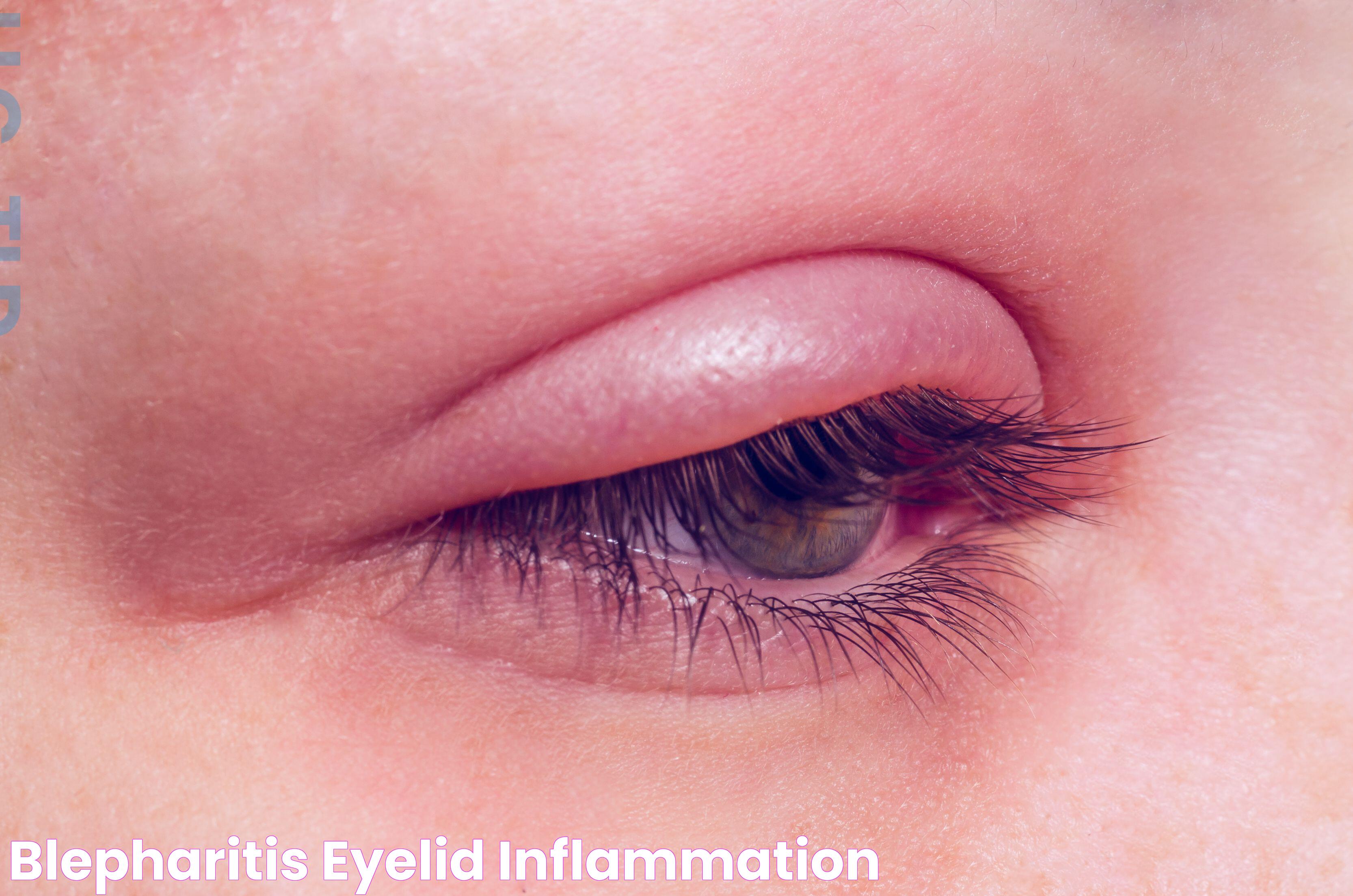
Chronic Blepharitis
Blepharitis is a chronic inflammation of the eyelid margins that can predispose individuals to eye styes. Managing blepharitis through proper eyelid hygiene can help reduce the risk of developing styes.
Other Contributing Factors
Additional factors that may contribute to the development of eye styes include:
- Hormonal changes
- Stress and fatigue
- Underlying skin conditions, such as rosacea or seborrheic dermatitis
Symptoms of an Eye Stye
Recognizing the symptoms of an eye stye is crucial for early intervention and treatment. The most common symptoms include:
Initial Signs of a Stye
Early symptoms of an eye stye may include:
- Soreness or tenderness in the affected eyelid
- Localized swelling and redness
- A small, painful lump at the base of an eyelash
Progression of Symptoms
As the stye develops, additional symptoms may occur, such as:
- Formation of a yellowish pus-filled head at the center of the lump
- Increased tearing or watery eyes
- Sensitivity to light
- Crusting along the eyelid margins
When to Seek Medical Attention
While most eye styes resolve without medical intervention, it is important to seek medical attention if:
- The stye does not improve within one to two weeks
- The swelling and redness spread to other parts of the eyelid or face
- Vision is affected or impaired
- The stye recurs frequently
How to Prevent Eye Styes?
Preventing eye styes involves adopting good hygiene practices and minimizing exposure to risk factors. Here are some effective strategies for preventing eye styes:
Maintain Good Eyelid Hygiene
Regularly clean the eyelids using a gentle cleanser or pre-moistened eyelid wipes. This helps remove excess oil, debris, and bacteria that can contribute to stye formation.
Avoid Rubbing the Eyes
Refrain from touching or rubbing the eyes, especially with unwashed hands. If you need to touch your eyes, wash your hands thoroughly beforehand.
Remove Eye Makeup Properly
Ensure all eye makeup is removed before going to bed. Use a gentle makeup remover to clean the eyelids and lashes thoroughly.
Other Preventive Measures
Additional preventive measures include:
- Using clean towels and washcloths for the face
- Avoiding the sharing of eye makeup and cosmetic tools
- Replacing eye makeup and brushes regularly to prevent bacterial buildup
Diagnosis and Medical Evaluation
If an eye stye does not improve with home treatment or if complications arise, a medical evaluation may be necessary. During a medical evaluation, a healthcare professional will:
Conduct a Visual Examination
The healthcare provider will examine the affected eye and eyelid to assess the stye's appearance and determine the appropriate course of action.
Assess Symptoms and Medical History
A detailed medical history will be taken to identify any underlying conditions or factors contributing to the stye.
Additional Diagnostic Tests
In rare cases, additional diagnostic tests may be required, such as:
- Swabbing the stye to test for bacterial cultures
- Blood tests to evaluate immune function or identify underlying health issues
Treatment Options for Eye Styes
There are several treatment options available for managing eye styes, ranging from home remedies to medical interventions. The choice of treatment depends on the severity of the stye and the individual's overall health.
Home Remedies
Home remedies are often the first line of treatment for eye styes and can be highly effective in promoting healing. Some common home remedies include:
- Warm compresses applied to the affected eyelid to reduce swelling and promote drainage
- Over-the-counter pain relievers to alleviate discomfort
- Avoiding makeup and contact lenses until the stye heals
Medical Treatments
If home remedies are not effective or if the stye is severe, medical treatments may be necessary. These can include:
- Topical antibiotics to treat bacterial infection
- Drainage of the stye by a healthcare professional
- Oral antibiotics for recurrent or severe styes
When Surgery is Required
Surgery is rarely needed for eye styes, but it may be considered in cases where:
- The stye does not respond to other treatments
- There is significant pain or discomfort
- The stye affects vision
Home Remedies for Eye Styes
Home remedies play a crucial role in managing eye styes and can help alleviate symptoms and speed up recovery. Here are some effective home remedies for treating eye styes:
Warm Compresses
Applying a warm compress to the affected eyelid several times a day can help reduce swelling and promote drainage of the stye. To make a warm compress:
- Soak a clean, soft cloth in warm water.
- Wring out excess water and place the cloth over the affected eyelid.
- Hold the compress in place for 10-15 minutes, rewarming as needed.
- Repeat the process 3-4 times a day until the stye improves.
Gentle Eyelid Massage
Gently massaging the eyelid can help promote drainage and relieve discomfort. Use clean fingers to apply light pressure to the area around the stye, taking care not to press directly on the stye itself.
Other Home Remedies
Additional home remedies include:
- Cleaning the eyelid with a gentle eyelid scrub or baby shampoo
- Avoiding contact lenses and eye makeup during treatment
- Using over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen
When to See a Doctor?
While most eye styes can be managed at home, there are certain situations where medical attention is necessary. It is important to see a doctor if:
Persistent or Recurrent Styes
If a stye does not improve with home treatment within one to two weeks or if it recurs frequently, a healthcare provider should be consulted for further evaluation and treatment.
Spread of Infection
Seek medical attention if the redness and swelling spread beyond the eyelid or if there are signs of a more serious infection, such as fever or chills.
Vision Impairment
If the stye affects vision or causes significant discomfort, a healthcare provider should be consulted to assess the need for medical intervention.
Complications from Untreated Eye Styes
While eye styes are typically harmless, untreated or improperly managed styes can lead to complications. Some potential complications include:
Spread of Infection
If the stye is not properly treated, the infection can spread to other parts of the eyelid or the surrounding tissues, leading to conditions such as cellulitis.
Chalazion Formation
An untreated stye can sometimes develop into a chalazion, a painless lump caused by blocked oil glands. Chalazia may require medical intervention if they do not resolve on their own.
Vision Problems
In rare cases, a large or persistent stye can exert pressure on the eye, causing vision problems. Prompt treatment can help prevent these complications.
Differentiating Between Eye Stye and Chalazion
Eye styes and chalazia are similar in appearance but have distinct differences. Understanding these differences can aid in accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Appearance and Symptoms
Eye styes are typically red, painful, and filled with pus, while chalazia are usually painless, firm lumps that develop slowly over time.
Causes and Treatment
Styes are caused by bacterial infections, whereas chalazia result from blocked oil glands. Treatment for styes often involves warm compresses and antibiotics, while chalazia may require surgical removal if they do not resolve naturally.
When to Seek Medical Advice
If you are unsure whether you have a stye or a chalazion, or if the lump does not improve with home treatment, it is advisable to consult a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Eye Stye Upper Eyelid: Specific Considerations
Eye styes can occur on any part of the eyelid, but they are more common on the upper eyelid. There are specific considerations for treating eye styes on the upper eyelid:
Impact on Vision and Comfort
Styes on the upper eyelid can be more uncomfortable and may affect vision if they grow large enough to exert pressure on the eye.
Treatment Challenges
Treating styes on the upper eyelid may require additional care to ensure that the compresses and medications reach the affected area effectively.
Prevention Tips
Preventing styes on the upper eyelid involves maintaining good eyelid hygiene and avoiding habits that can introduce bacteria to the eyelids.
Children and Eye Styes
Children are susceptible to eye styes due to their increased likelihood of touching their eyes and face. Managing eye styes in children involves special considerations:
Common Causes in Children
Eye styes in children are often caused by poor hygiene, frequent eye rubbing, and exposure to bacteria.
Treatment Approaches
Treatment for children typically involves warm compresses and avoiding eye rubbing. In severe cases, a pediatrician may prescribe antibiotics.
Preventive Measures
Encouraging children to wash their hands regularly and teaching them to avoid touching their eyes can help prevent styes.
Adults and Eye Styes
Adults are also prone to eye styes, and proper management is essential to prevent complications:
Risk Factors for Adults
Risk factors for adults include stress, hormonal changes, and underlying skin conditions. Proper eyelid hygiene is crucial for prevention.
Effective Treatments
Adults can benefit from home remedies such as warm compresses and over-the-counter medications. Persistent styes may require medical evaluation.
Preventive Strategies
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, managing stress, and practicing good eyelid hygiene can help reduce the risk of styes in adults.
Myths and Facts About Eye Styes
There are several myths and misconceptions about eye styes. Understanding the facts can help dispel these myths and promote effective treatment:
Myth: Styes are Contagious
Fact: Styes are not contagious and cannot be spread from person to person through casual contact.
Myth: Styes are Caused by Poor Hygiene Alone
Fact: While poor hygiene is a contributing factor, other factors such as stress and hormonal changes can also play a role in stye formation.
Other Common Myths
Additional myths about styes include:
- Styes can be "popped" like pimples (Fact: Popping styes can worsen the infection)
- Styes are always a sign of a serious health issue (Fact: Most styes are harmless and resolve on their own)
Frequently Asked Questions
- Can eye styes cause permanent damage?
- Are eye styes contagious?
- How can I tell if I have a stye or a chalazion?
- What should I do if my stye doesn't go away?
- Can wearing makeup cause eye styes?
- Are there any home remedies for preventing styes?
No, eye styes do not cause permanent damage. They are typically harmless and resolve with proper treatment.
No, eye styes are not contagious and cannot be spread through casual contact.
Styes are painful, red, and pus-filled, while chalazia are painless, firm lumps. A healthcare provider can help diagnose the condition accurately.
If a stye does not improve within one to two weeks, consult a healthcare provider for further evaluation and treatment.
Wearing makeup can contribute to stye formation if makeup is not removed properly, leading to clogged oil glands.
Maintaining good eyelid hygiene, avoiding eye rubbing, and removing makeup thoroughly can help prevent styes.
Conclusion
Eye styes, while uncomfortable and often inconvenient, are generally harmless and can be effectively managed with proper care. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, individuals can take proactive steps to prevent and treat styes, ensuring healthy eyelids and minimizing the risk of recurrence. Adopting good hygiene practices, seeking medical advice when necessary, and dispelling common myths can contribute to better eye health and overall well-being.
For further information on eye styes and related eye conditions, visit the American Academy of Ophthalmology's website: American Academy of Ophthalmology.