Understanding whether you are experiencing body dysmorphia is crucial for seeking appropriate help and support. Many people struggle silently, unaware that their thoughts and behaviors are symptomatic of this condition. Recognizing the signs is the first step towards healing and improving one's quality of life. This article aims to provide an in-depth exploration of body dysmorphia, helping you identify its signs, symptoms, and potential treatments. Despite the challenges associated with body dysmorphia, there is hope for recovery. With the right guidance, individuals can learn to manage their symptoms and embrace a more positive self-image. By shedding light on this condition, we aim to empower those affected to take the necessary steps toward a healthier mental state. Join us as we delve into the complexities of body dysmorphia and provide insights to help you discern if you or someone you know might be experiencing this disorder.
| Table of Contents |
|---|
| 1. What is Body Dysmorphia? |
| 2. How Common is Body Dysmorphia? |
| 3. Recognizing the Signs of Body Dysmorphia |
| 4. How to Know if You Have Body Dysmorphia? |
| 5. The Psychological Impact of Body Dysmorphia |
| 6. Physical and Behavioral Symptoms |
| 7. What Causes Body Dysmorphia? |
| 8. How is Body Dysmorphia Diagnosed? |
| 9. Treatment Options for Body Dysmorphia |
| 10. Coping Strategies and Self-Help Tips |
| 11. The Role of Social Media and Cultural Influences |
| 12. How to Support Someone with Body Dysmorphia? |
| 13. FAQs |
| 14. Conclusion |
1. What is Body Dysmorphia?
Body dysmorphia, or Body Dysmorphic Disorder (BDD), is a mental health condition where an individual becomes obsessively concerned with perceived defects or flaws in their physical appearance. These perceived imperfections are often minor or non-existent but can cause significant distress and lead to compulsive behaviors aimed at concealing or fixing the flaws.
The disorder falls under the category of obsessive-compulsive disorders and shares some similarities with obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD). Individuals with body dysmorphia may engage in repetitive behaviors such as mirror checking, excessive grooming, or seeking reassurance that their appearance is acceptable. These actions, however, only provide temporary relief and often exacerbate the anxiety associated with the perceived flaws.
Read also:Mortician Responsibilities Exploring The Role And Duties
Body dysmorphia affects both men and women, and it can manifest at any age, though it often begins in adolescence. The disorder can focus on any part of the body, but common areas of concern include the skin, hair, nose, and weight. Understanding the nature of body dysmorphia is essential for recognizing its signs and seeking appropriate treatment.
2. How Common is Body Dysmorphia?
Body dysmorphia is more prevalent than many people realize. It's estimated that between 1.7% to 2.4% of the general population meet the diagnostic criteria for body dysmorphic disorder. This prevalence rate suggests that millions of individuals worldwide are affected by this condition.
The disorder can affect anyone, regardless of gender, age, or cultural background. However, certain populations may be more susceptible due to societal pressures and cultural ideals related to beauty and appearance. For instance, individuals working in industries that emphasize physical appearance, such as modeling or athletics, may experience higher rates of body dysmorphia.
Despite its prevalence, body dysmorphia remains underdiagnosed and undertreated. This is partly due to the stigma surrounding mental health issues and the tendency for individuals to dismiss their concerns as vanity rather than recognizing them as symptoms of a disorder. Increasing awareness and education about body dysmorphia is crucial in encouraging those affected to seek help.
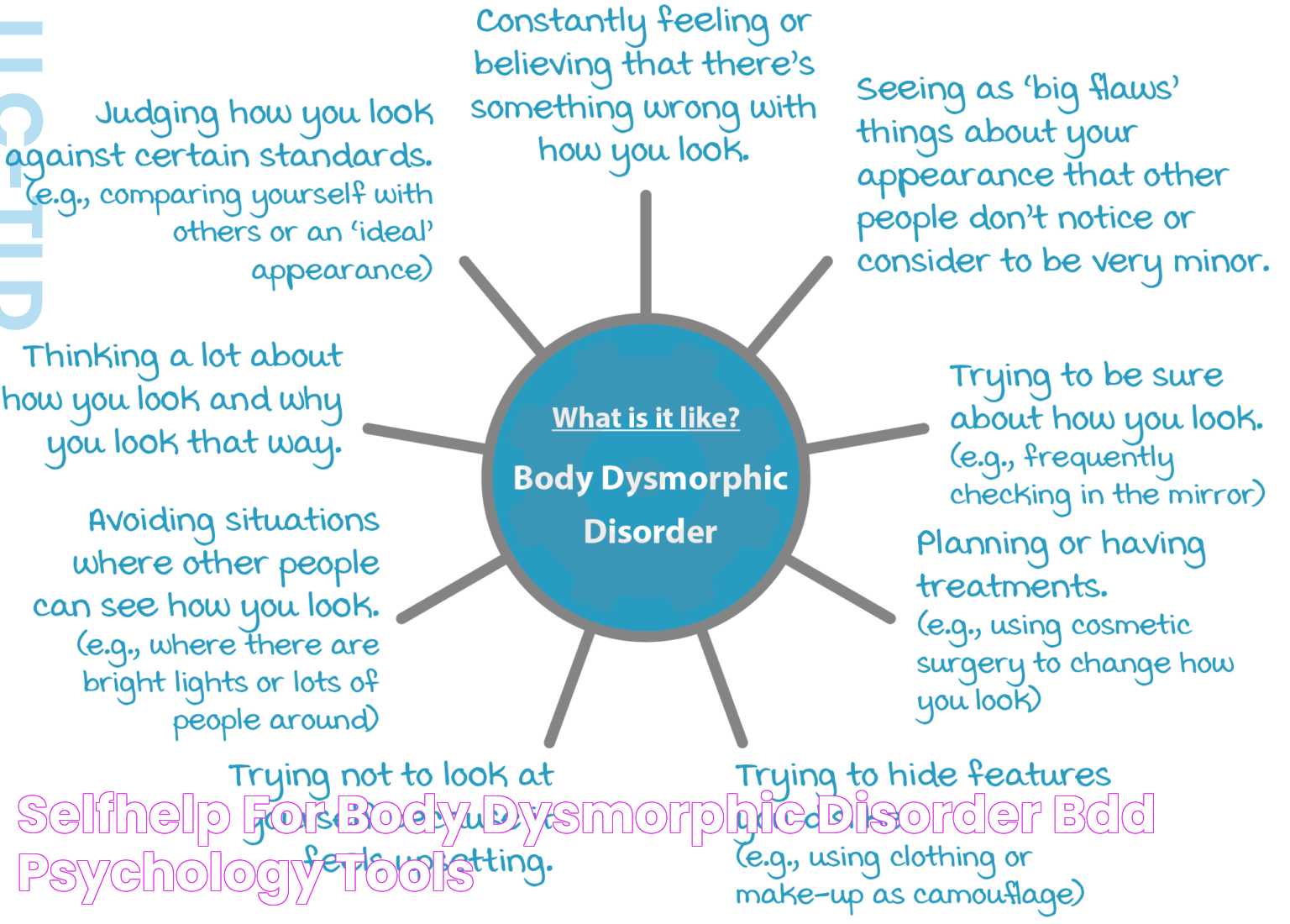
3. Recognizing the Signs of Body Dysmorphia
Recognizing the signs of body dysmorphia can be challenging, as the symptoms often mimic typical concerns about appearance. However, the key difference lies in the intensity and impact of these concerns on an individual's life. Here are some signs that may indicate the presence of body dysmorphia:
- Preoccupation with perceived physical flaws that are not apparent to others.
- Frequent mirror checking or avoidance of mirrors altogether.
- Excessive grooming or camouflaging behaviors, such as wearing excessive makeup or clothing to hide perceived flaws.
- Seeking constant reassurance from others about appearance.
- Comparing one's appearance to others obsessively.
- Avoidance of social situations due to appearance concerns.
- Engaging in unnecessary cosmetic procedures or surgeries.
If these behaviors interfere with daily functioning or cause significant distress, it may be indicative of body dysmorphia. Early recognition of these signs is vital for seeking appropriate treatment and support.
Read also:Ultimate Guide To Shu Uemura Shampoo Benefits Usage And More
4. How to Know if You Have Body Dysmorphia?
Determining whether you have body dysmorphia involves recognizing patterns of thought and behavior related to your appearance. Here are some questions to consider that might help identify if you are experiencing body dysmorphia:
- Do you spend a significant amount of time each day thinking about perceived flaws in your appearance?
- Does your concern about your appearance cause you distress or interfere with your daily activities?
- Have you engaged in excessive grooming, checking, or seeking reassurance about your appearance?
- Do you avoid social situations because of self-consciousness about your appearance?
- Have you considered or undergone cosmetic procedures to change your appearance?
If you find yourself answering 'yes' to most of these questions, it may be indicative of body dysmorphia. Consulting a mental health professional for a thorough evaluation and diagnosis is crucial for understanding and addressing these concerns effectively.
5. The Psychological Impact of Body Dysmorphia
Body dysmorphia can have profound psychological effects on individuals, impacting their mental health and overall well-being. The relentless focus on perceived flaws can lead to significant emotional distress, anxiety, and depression. Here are some of the psychological impacts associated with body dysmorphia:
- Anxiety and Depression: The constant worry and obsession over appearance can contribute to heightened anxiety and depression, affecting an individual's mood and outlook on life.
- Low Self-Esteem: Individuals with body dysmorphia often struggle with self-esteem issues, believing that their worth is tied to their appearance and perceived flaws.
- Social Withdrawal: Due to self-consciousness and fear of judgment, individuals may withdraw from social situations, leading to isolation and loneliness.
- Obsessive-Compulsive Behaviors: The disorder often involves compulsive behaviors aimed at fixing or hiding perceived flaws, which can exacerbate anxiety and distress.
Addressing the psychological impact of body dysmorphia is an essential component of treatment, helping individuals develop healthier thought patterns and coping mechanisms.
6. Physical and Behavioral Symptoms
Body dysmorphia manifests in both physical and behavioral symptoms, often intertwining to perpetuate the cycle of obsession and distress. Understanding these symptoms can aid in recognizing the disorder and seeking appropriate help.
Physical Symptoms
- Frequent cosmetic procedures or surgeries to alter perceived flaws.
- Excessive grooming routines, such as skin picking or hair removal.
- Noticeable changes in appearance due to compulsive behavior.
Behavioral Symptoms
- Avoiding mirrors or obsessively checking appearance in them.
- Constantly seeking validation from others regarding looks.
- Engaging in rituals to hide flaws, like wearing certain clothes or makeup.
Recognizing these symptoms and understanding their impact on daily life is crucial for identifying body dysmorphia and pursuing intervention.
7. What Causes Body Dysmorphia?
The exact cause of body dysmorphia remains unknown, but several factors are believed to contribute to its development. These factors often interplay, creating a complex picture of the disorder. Here are some potential causes:
- Genetic Factors: Family history of mental health disorders, including obsessive-compulsive disorder and anxiety, may increase susceptibility to body dysmorphia.
- Biological Factors: Abnormalities in brain structure or chemistry, such as serotonin dysregulation, may play a role in the disorder's development.
- Environmental Factors: Cultural and societal pressures emphasizing appearance and beauty standards can contribute to body dysmorphia.
- Psychological Factors: Experiencing trauma, bullying, or criticism related to appearance during childhood or adolescence may increase risk.
Understanding these potential causes can aid in developing targeted treatment approaches and preventive measures.
8. How is Body Dysmorphia Diagnosed?
Diagnosing body dysmorphia involves a comprehensive evaluation by a mental health professional. The process typically includes:
- A detailed clinical interview to assess symptoms, duration, and impact on daily life.
- Use of standardized diagnostic criteria, such as those outlined in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5).
- Consideration of co-occurring mental health conditions, such as anxiety or depression.
- Rule out other medical or psychiatric conditions that may mimic body dysmorphia.
Receiving an accurate diagnosis is essential for developing an effective treatment plan and addressing the underlying causes of the disorder.
9. Treatment Options for Body Dysmorphia
Treating body dysmorphia involves a combination of therapeutic approaches tailored to the individual's needs. Here are some common treatment options:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): This evidence-based therapy helps individuals identify and change distorted thought patterns and behaviors related to appearance.
- Medication: Antidepressants, particularly selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), may be prescribed to alleviate symptoms of depression and anxiety.
- Group Therapy: Participating in group therapy sessions with others experiencing similar challenges can provide support and reduce feelings of isolation.
- Family Therapy: Involving family members in therapy can help address underlying dynamics and provide support for the individual.
Collaborating with a mental health professional to develop a personalized treatment plan is crucial for managing body dysmorphia effectively.
10. Coping Strategies and Self-Help Tips
In addition to professional treatment, individuals with body dysmorphia can benefit from self-help strategies to manage symptoms and improve well-being. Here are some tips:
- Practice self-compassion and challenge negative self-talk.
- Limit exposure to triggering media and social media content.
- Engage in activities that promote self-esteem and body positivity.
- Establish a support network of friends and family who understand your experiences.
- Consider mindfulness and relaxation techniques to reduce anxiety and stress.
Incorporating these strategies into daily life can complement professional treatment and support recovery.
11. The Role of Social Media and Cultural Influences
Social media and cultural influences play a significant role in shaping perceptions of beauty and appearance, potentially exacerbating body dysmorphia. Here's how:
- Unrealistic Beauty Standards: Social media platforms often promote idealized and edited images, leading individuals to compare themselves unfavorably.
- Peer Pressure: The desire to fit in and gain approval can lead to increased focus on appearance and perceived flaws.
- Influence of Influencers: Online influencers may perpetuate beauty standards, impacting self-esteem and body image.
- Cultural Norms: Societal and cultural norms emphasizing physical appearance can contribute to body dysmorphia.
Understanding these influences is crucial for developing strategies to mitigate their impact and promote a healthier body image.
12. How to Support Someone with Body Dysmorphia?
Supporting someone with body dysmorphia requires empathy, understanding, and encouragement. Here are some ways to provide support:
- Listen actively and validate their feelings without judgment.
- Encourage them to seek professional help and offer to assist in finding resources.
- Promote positive self-talk and discourage negative comments about appearance.
- Be patient and understanding, recognizing that recovery takes time.
- Educate yourself about body dysmorphia to better understand their experiences.
Providing a supportive and non-judgmental environment can make a significant difference in the recovery process.
13. FAQs
What is the difference between body dysmorphia and low self-esteem?
While both body dysmorphia and low self-esteem involve negative perceptions of oneself, body dysmorphia is characterized by an obsessive preoccupation with perceived physical flaws, often leading to compulsive behaviors. Low self-esteem, on the other hand, encompasses a broader sense of inadequacy and self-doubt but may not involve such intense focus on appearance.
Can body dysmorphia be cured?
While there is no definitive cure for body dysmorphia, it can be effectively managed with appropriate treatment and support. Many individuals experience significant improvement in symptoms through therapy, medication, and self-help strategies.
Is body dysmorphia more common in women than men?
Body dysmorphia affects both men and women, although societal and cultural pressures may cause it to manifest differently. While some studies suggest slightly higher prevalence rates among women, it's important to recognize that men also experience this disorder.
How does body dysmorphia affect relationships?
Body dysmorphia can impact relationships by causing individuals to withdraw socially, seek constant reassurance, or become fixated on appearance-related issues. This can lead to misunderstandings and strain in relationships, highlighting the importance of communication and support.
What role does therapy play in treating body dysmorphia?
Therapy, particularly cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), plays a crucial role in treating body dysmorphia by helping individuals identify and challenge distorted thought patterns and develop healthier coping mechanisms. Therapy can also provide a supportive environment for addressing underlying emotional issues.
Can body dysmorphia lead to other mental health issues?
Yes, body dysmorphia can contribute to or exacerbate other mental health issues, such as anxiety, depression, and obsessive-compulsive disorder. Addressing body dysmorphia through treatment can help mitigate these additional challenges.
14. Conclusion
Recognizing and understanding body dysmorphia is essential for addressing its impact on individuals' lives. By identifying the signs and seeking appropriate treatment, those affected can work toward recovery and improve their mental health and overall well-being. With increased awareness and support, individuals with body dysmorphia can embrace a more positive self-image and lead fulfilling lives.
For further information and resources on body dysmorphia, consider visiting reputable mental health organizations such as the Anxiety and Depression Association of America (ADAA) or the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH).