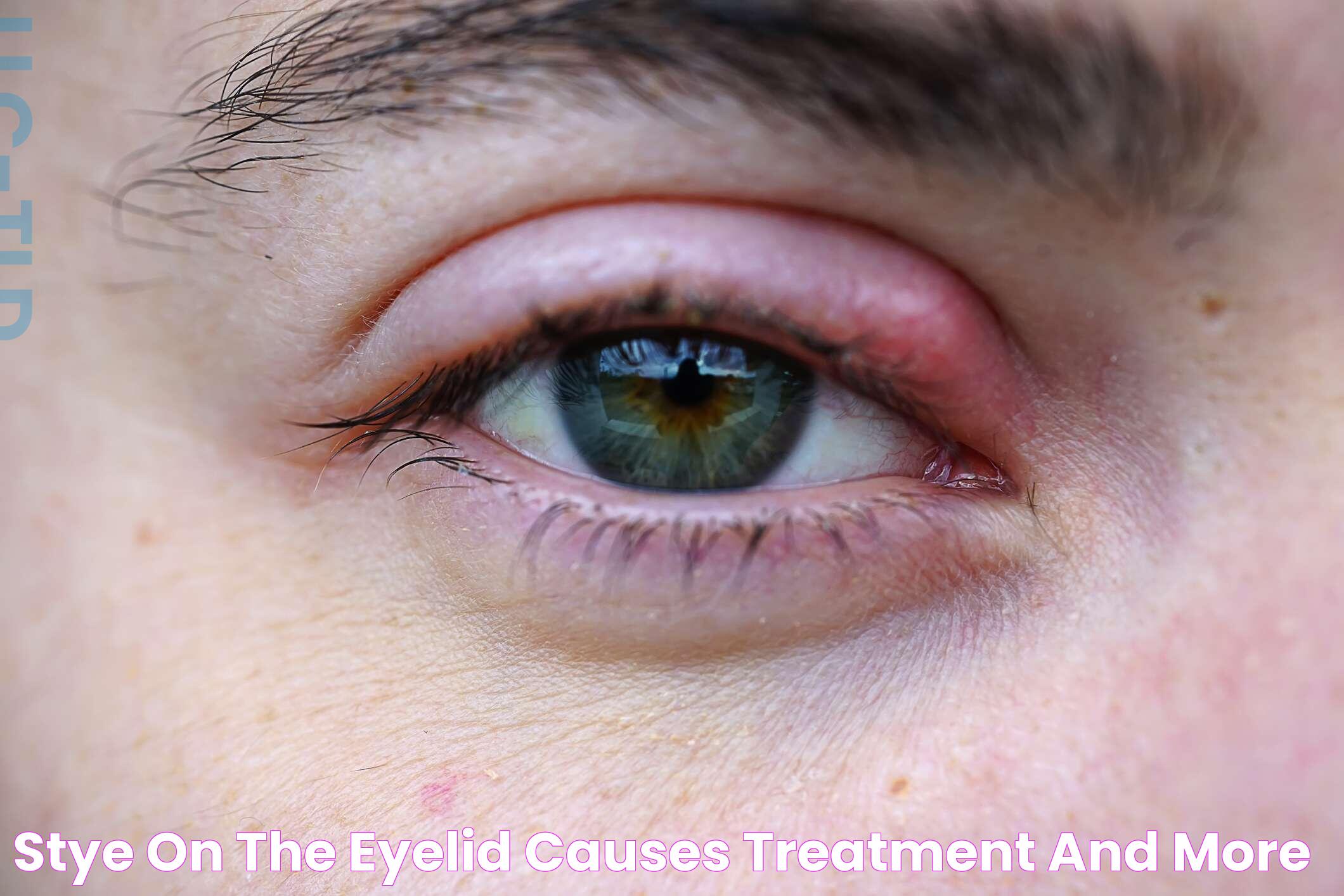
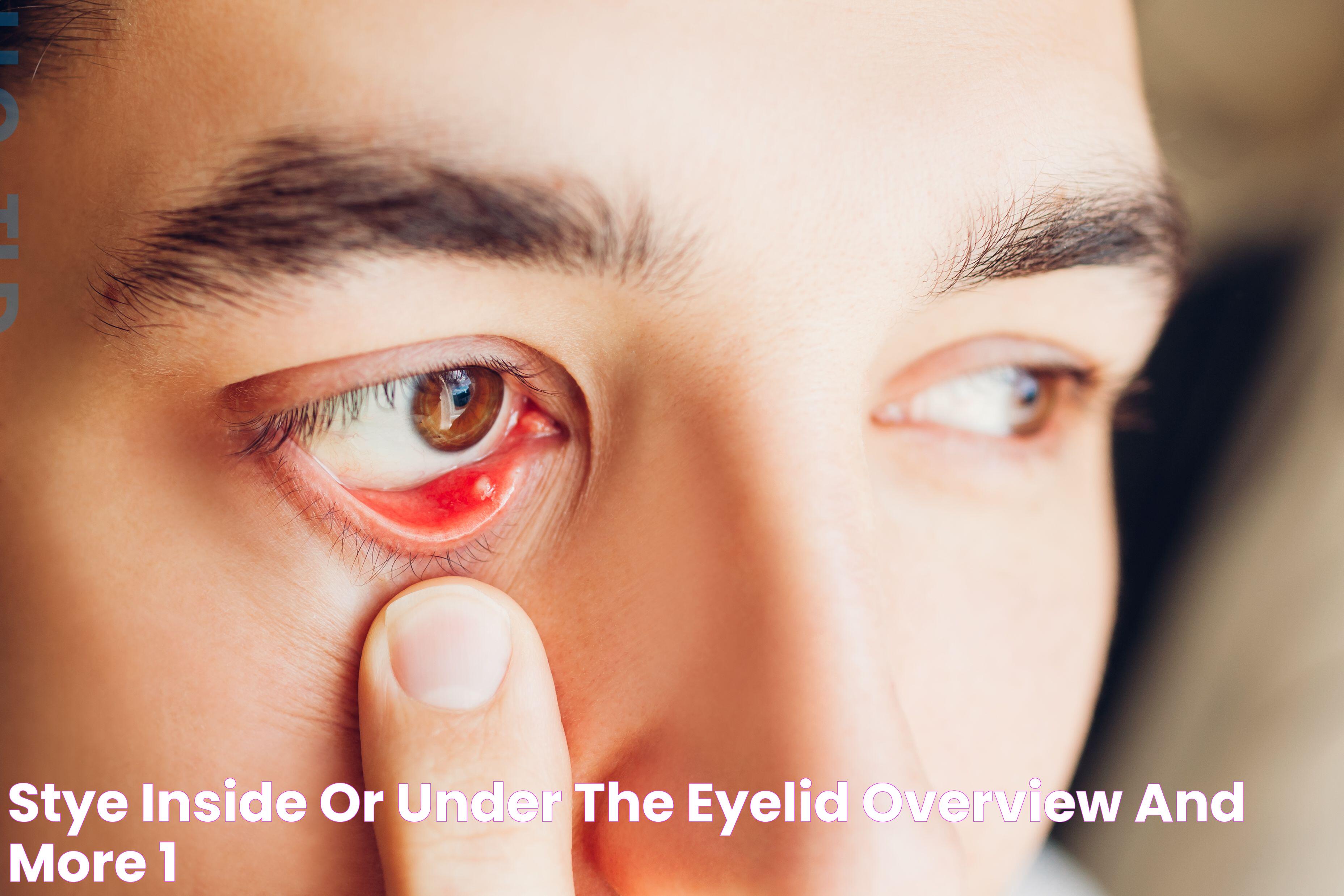
A stye on the inside of the eyelid can be an uncomfortable and often painful condition that affects many individuals at some point in their lives. This small, red, and tender bump may resemble a pimple and typically forms when oil glands or hair follicles become infected, leading to inflammation. While styes are generally harmless and tend to resolve on their own within a week or two, they can cause significant discomfort and inconvenience during their course.
Understanding the intricacies of styes on the inside of the eyelid is crucial for effective management and prevention. This comprehensive guide aims to provide valuable insights into the symptoms, causes, treatment options, and preventive measures for styes. Whether you're experiencing a stye for the first time or seeking ways to prevent future occurrences, this article will equip you with the knowledge to navigate this common eye condition.
As we delve into the various aspects of styes, we'll explore the differences between internal and external styes, the role of hygiene in prevention, and the potential complications associated with untreated styes. By the end of this article, readers will have a thorough understanding of how to address styes on the inside of the eyelid and maintain overall eyelid health.
Read also:Discover The Power Of An Intuitive Personality A Comprehensive Guide
Table of Contents
- What is a Stye on the Inside of the Eyelid?
- Symptoms of an Internal Stye
- What Causes a Stye on the Inside of the Eyelid?
- How is a Stye Diagnosed?
- Effective Treatment Options for Styes
- Can Home Remedies Help with Styes?
- When to Seek Medical Intervention?
- How to Prevent Styes on the Inside of the Eyelid?
- Potential Complications of Untreated Styes
- Internal vs. External Styes: Understanding the Difference
- Why is Hygiene Important in Stye Prevention?
- Can Lifestyle and Diet Affect Stye Development?
- Common Misconceptions About Styes
- FAQs
- Conclusion
What is a Stye on the Inside of the Eyelid?
A stye, also known as a hordeolum, is a localized infection of the eyelid's sebaceous glands or hair follicles, often caused by the bacteria Staphylococcus. While most people are familiar with external styes, which appear on the outer edge of the eyelid, an internal stye forms on the inside of the eyelid. This type of stye can be more painful and harder to diagnose because it is less visible and can cause more significant swelling.
Internal styes develop when the meibomian glands, which are responsible for secreting oils to lubricate the eyes, become blocked and infected. The resulting inflammation leads to the formation of a small, red bump that can cause discomfort, especially when blinking or touching the eye.
It's important to differentiate between a stye and other similar conditions, such as chalazia or cysts, which can also occur on the eyelid. While a stye is an acute bacterial infection, a chalazion is a chronic inflammation often resulting from a blocked oil gland without infection. Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment and management.
Symptoms of an Internal Stye
Recognizing the symptoms of an internal stye is the first step in addressing the condition effectively. Common symptoms include:
- Redness and swelling on the inside of the eyelid
- Pain or tenderness in the affected area
- Increased tearing or watery eyes
- Blurred vision due to swelling affecting the eye's shape
- A sensation of a foreign body in the eye
- Pus-filled bump that may eventually drain
The severity of symptoms can vary based on the extent of the infection and individual sensitivity. In some cases, the stye may cause significant discomfort, making daily activities challenging. Prompt recognition and treatment can help alleviate symptoms and reduce the risk of complications.
What Causes a Stye on the Inside of the Eyelid?
A stye on the inside of the eyelid is primarily caused by a bacterial infection. The Staphylococcus bacteria, which naturally reside on the skin and in the nose, can enter the eyelid's sebaceous glands or hair follicles, leading to infection and inflammation. Several factors can increase the risk of developing a stye:
Read also:Effective Exfoliating Scrub Your Path To Radiant Skin
- Poor eyelid hygiene, allowing bacteria to accumulate
- Touching the eyes with unclean hands
- Using expired or contaminated eye makeup
- Chronic eye conditions, such as blepharitis or rosacea
- Stress, which can weaken the immune system
- Hormonal changes affecting oil production in the eyelids
Understanding these risk factors can help individuals take preventive measures to reduce the likelihood of developing styes. Maintaining good eyelid hygiene and avoiding potential triggers are crucial steps in prevention.
How is a Stye Diagnosed?
Diagnosing a stye on the inside of the eyelid typically involves a physical examination by a healthcare professional. During the examination, the doctor may:
- Inspect the affected eyelid for signs of redness, swelling, and tenderness
- Use a magnifying tool to closely examine the eyelid's glands and follicles
- Ask about any recent eye infections, use of cosmetics, or changes in hygiene practices
In most cases, a stye can be diagnosed based on visual inspection and patient history. However, if the stye is persistent or unresponsive to treatment, additional tests may be necessary to rule out other conditions or complications.
Effective Treatment Options for Styes
While styes often resolve on their own, several treatment options can alleviate symptoms and speed up recovery. Common treatments include:
- Warm compresses: Applying a warm, damp cloth to the affected eye for 10-15 minutes several times a day can help reduce swelling and promote drainage.
- Over-the-counter pain relievers: Medications like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help manage pain and discomfort.
- Antibiotic ointments or drops: In some cases, a doctor may prescribe topical antibiotics to treat or prevent infection.
- Avoiding eye makeup: Refrain from using makeup on the affected eye until the stye has healed to prevent further irritation.
Following these treatment strategies can help minimize discomfort and prevent the stye from worsening. If symptoms persist or worsen, consulting a healthcare professional is recommended.
Can Home Remedies Help with Styes?
Home remedies can be effective in managing mild stye symptoms and promoting healing. Some popular home remedies include:
- Tepid tea bag compress: Placing a warm, moist tea bag over the affected eyelid can help reduce inflammation and soothe the area.
- Turmeric paste: Applying a paste made of turmeric and water to the eyelid can have antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effects.
- Aloe vera gel: Aloe vera's soothing properties can help reduce redness and swelling when applied gently to the eyelid.
While home remedies can offer relief, they should be used with caution and not as a substitute for professional medical advice. It's essential to ensure that any substances applied to the eye area are clean and safe to prevent further irritation or infection.
When to Seek Medical Intervention?
In most cases, styes can be managed at home with proper care and hygiene. However, there are situations where medical intervention may be necessary:
- If the stye does not improve within a week or worsens
- If the swelling and redness spread beyond the eyelid
- If vision is significantly affected or blurred
- If the stye frequently recurs or is accompanied by other eye infections
- If there is severe pain or a fever associated with the stye
In such cases, a healthcare professional can provide a more thorough evaluation and recommend appropriate treatments, which may include prescription medications or minor surgical procedures to drain the stye.
How to Prevent Styes on the Inside of the Eyelid?
Preventing styes involves maintaining good eyelid hygiene and minimizing exposure to risk factors. Here are some preventive measures to consider:
- Regularly clean the eyelid margins with a gentle cleanser
- Wash hands thoroughly before touching the eyes
- Avoid sharing eye makeup or personal items that come into contact with the eyes
- Replace eye makeup regularly to prevent bacterial growth
- Manage chronic eye conditions with appropriate treatments and follow-up care
By incorporating these habits into daily routines, individuals can reduce the likelihood of developing styes and maintain optimal eye health.
Potential Complications of Untreated Styes
While styes are generally benign, untreated or improperly managed styes can lead to complications, such as:
- Chalazion formation: A chronic, non-infectious nodule that remains after the stye resolves
- Preseptal cellulitis: A bacterial infection of the eyelid and surrounding tissues
- Scarring or permanent changes to the eyelid structure
Addressing styes promptly and following appropriate treatment strategies can help minimize the risk of complications and ensure a swift recovery.
Internal vs. External Styes: Understanding the Difference
Styes can occur internally or externally, each presenting distinct characteristics:
- Internal styes: Form inside the eyelid, affecting the meibomian glands, and can be more painful due to their location.
- External styes: Develop at the base of the eyelashes, affecting the eyelash follicles, and are more visible.
Understanding the differences between these types of styes can aid in accurate diagnosis and treatment, ensuring the most effective management approach is utilized.
Why is Hygiene Important in Stye Prevention?
Hygiene plays a critical role in preventing styes, as it helps minimize the presence of bacteria that can lead to infection. Key hygiene practices include:
- Regularly washing the face and eyelids with mild soap and water
- Removing makeup before bed to prevent buildup
- Using clean towels and pillowcases to avoid transferring bacteria
Consistent adherence to these practices can significantly reduce the likelihood of developing styes and other eye infections.
Can Lifestyle and Diet Affect Stye Development?
While lifestyle and diet alone do not directly cause styes, they can influence overall eye health and immune function. Consider the following tips:
- Maintain a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals to support immune health
- Stay hydrated to ensure proper tear production and eyelid lubrication
- Manage stress levels to prevent immune suppression
By adopting a healthy lifestyle, individuals can support their body’s ability to fend off infections, including those that could lead to styes.
Common Misconceptions About Styes
Several misconceptions surround styes, leading to confusion and improper treatment. Common myths include:
- Styes are caused by poor eyesight: Styes are not related to vision quality, but rather to bacterial infections.
- All styes require antibiotics: Many styes resolve without antibiotics, which are only necessary for severe or persistent cases.
- Styes can spread to others: Styes are not contagious and cannot be spread through casual contact.
Debunking these myths can help individuals approach styes with accurate information, leading to better management and outcomes.
FAQs
1. Can a stye on the inside of the eyelid cause permanent damage?
No, a stye on the inside of the eyelid typically does not cause permanent damage if treated properly. However, complications such as chalazia or cellulitis may occur if left untreated.
2. How long does it take for a stye to heal?
Most styes heal within one to two weeks with proper care and treatment. Persistent or recurrent styes may require medical intervention.
3. Are styes a sign of a more serious condition?
While styes themselves are not indicative of a serious condition, frequent styes may suggest underlying issues like blepharitis or rosacea, which require medical evaluation.
4. Can contact lenses cause styes?
Improper use of contact lenses, such as handling them with unclean hands or not cleaning them properly, can increase the risk of stye development due to bacterial contamination.
5. Is it safe to pop a stye?
No, popping a stye can worsen the infection and lead to complications. It is best to allow the stye to drain naturally or seek medical assistance for persistent cases.
6. Can children get styes on the inside of the eyelid?
Yes, children can develop styes, and parents should encourage good hygiene practices and seek medical advice if a stye occurs in a child.
Conclusion
Understanding the nature and management of a stye on the inside of the eyelid is essential for effective treatment and prevention. By recognizing symptoms, identifying causes, and implementing preventive measures, individuals can reduce the risk of styes and maintain optimal eye health. While home remedies and hygiene practices play a vital role, seeking professional medical advice in persistent or severe cases ensures comprehensive care and minimizes potential complications. Armed with the knowledge from this guide, readers can confidently address styes and promote overall eyelid well-being.