Genital herpes is a common sexually transmitted infection, affecting a large percentage of the global population. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), more than half a billion people worldwide are living with this condition, which translates to a significant percentage of people with genital herpes. This data highlights the importance of understanding the prevalence and implications of this infection.
The prevalence of genital herpes varies across different regions and demographics. In some areas, the percentage of people with genital herpes can be as high as one in four adults. These statistics underscore the need for increased awareness and education about this condition, as well as effective prevention and treatment strategies. Understanding the factors that contribute to the spread of genital herpes can help in reducing its prevalence.
Despite its widespread occurrence, many people with genital herpes may not even be aware that they have the infection, as symptoms can often be mild or mistaken for other conditions. This lack of awareness can contribute to the continued spread of the virus. Addressing this issue requires a comprehensive approach that includes education, testing, and open conversations about sexual health.
Read also:Effortless Tips To Make Hair Not Poofy For Smooth And Sleek Locks
Table of Contents
- What is Genital Herpes?
- Global Prevalence of Genital Herpes
- Regional Variations in Herpes Prevalence
- How Do Age and Gender Affect Herpes Prevalence?
- What Causes Genital Herpes?
- Symptoms and Diagnosis of Genital Herpes
- Treatment and Management Options
- How Can Genital Herpes Be Prevented?
- Living with Genital Herpes: Coping and Support
- Impact of Genital Herpes on Relationships
- Importance of Public Awareness and Education
- What Does the Future Hold for Genital Herpes Research?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
What is Genital Herpes?
Genital herpes is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV). There are two types of HSV, known as HSV-1 and HSV-2. While HSV-1 is primarily responsible for oral herpes, it can also cause genital herpes. HSV-2, on the other hand, is more commonly associated with genital infections.
The virus is transmitted through direct contact with an infected person, most often during sexual activity. Once contracted, the virus remains in the body for life, with the potential for periodic outbreaks of symptoms. These outbreaks can vary in frequency and severity depending on the individual.
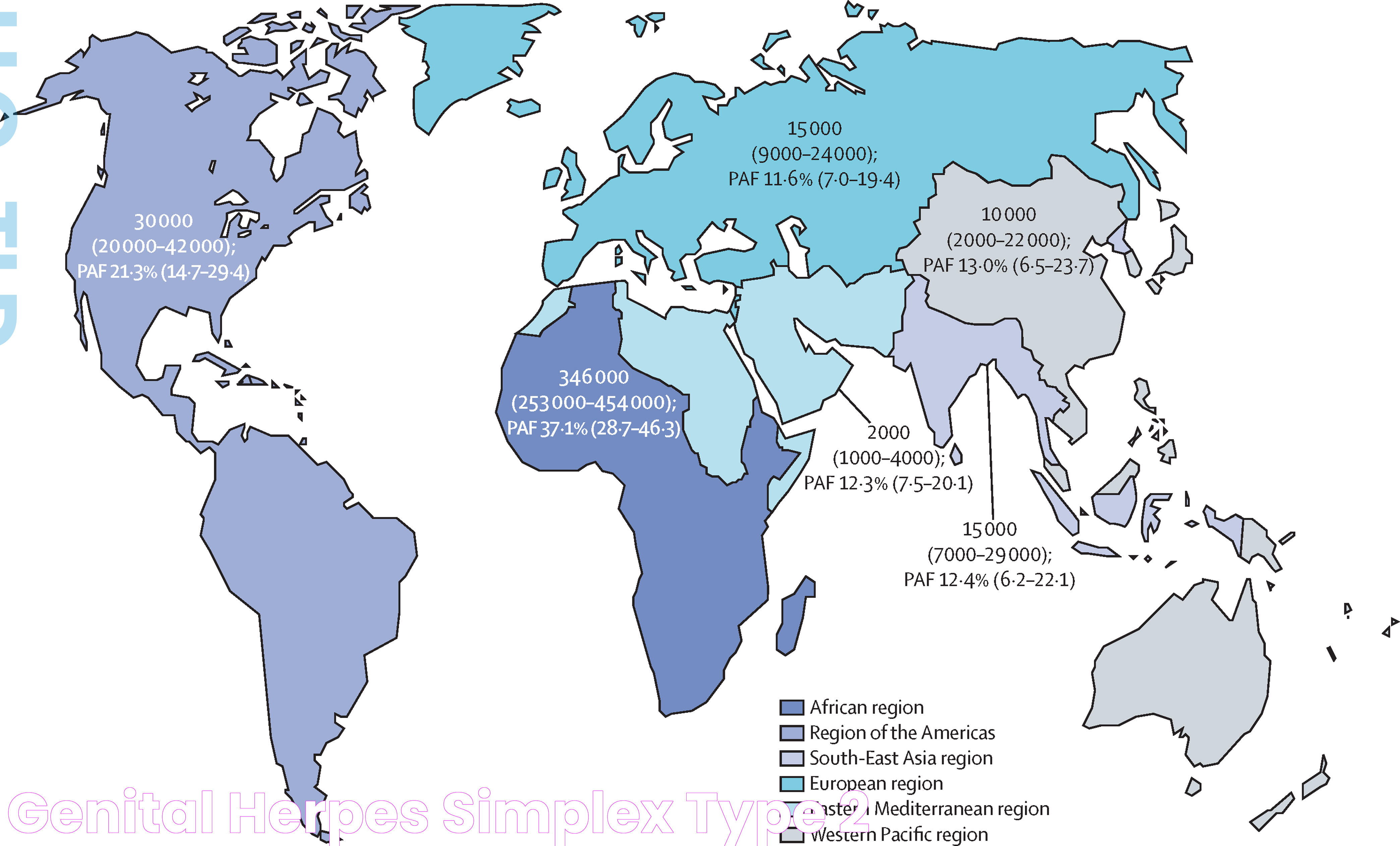
Global Prevalence of Genital Herpes
The percentage of people with genital herpes worldwide is significant, with estimates suggesting over 500 million people are infected. This high prevalence makes genital herpes one of the most common sexually transmitted infections globally. The infection is more common in women than in men, largely due to biological factors that make it easier for women to contract the virus.
Genital herpes is more prevalent in certain regions, particularly Sub-Saharan Africa and parts of the Americas, where social and economic factors, access to healthcare, and cultural practices can influence transmission rates. According to WHO, the prevalence of genital herpes is highest in low- to middle-income countries.
Regional Variations in Herpes Prevalence
The percentage of people with genital herpes can vary significantly between different regions and countries. In Sub-Saharan Africa, for instance, studies have shown that up to 70% of adults are infected with HSV-2. In contrast, North America and Europe have lower prevalence rates, though they are still significant, with approximately 15-20% of adults affected.
These variations can be attributed to factors such as differences in sexual behavior, cultural attitudes towards sex, and the availability of sexual health education and services. Regions with higher rates of other sexually transmitted infections also tend to have higher herpes prevalence, indicating a need for integrated sexual health strategies.
Read also:Virgo Male And Taurus Female Compatibility And Relationship Dynamics
How Do Age and Gender Affect Herpes Prevalence?
Age and gender are important factors in understanding the prevalence of genital herpes. The infection is most commonly diagnosed in adolescents and young adults, as these groups are more likely to engage in sexual activity. However, outbreaks can occur at any age, and older adults may experience more frequent or severe symptoms.
Women are generally more susceptible to contracting genital herpes than men, with studies indicating that the infection is about twice as common among females. This increased risk is due to anatomical differences, as well as the fact that women are more likely to seek medical care and therefore be diagnosed with the condition.
What Causes Genital Herpes?
Genital herpes is caused by the herpes simplex virus, which is highly contagious and easily transmitted through skin-to-skin contact. The virus enters the body through small breaks in the skin or mucous membranes, which can occur during vaginal, anal, or oral sex.
While HSV-1 and HSV-2 both cause genital herpes, HSV-2 is more commonly responsible for the infection. People with oral herpes caused by HSV-1 can transmit the virus to the genital area through oral-genital contact, leading to genital herpes.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Genital Herpes
The symptoms of genital herpes can vary widely, with some people experiencing mild or no symptoms, while others may have painful outbreaks. Common symptoms include blisters or sores in the genital area, itching, burning, and flu-like symptoms such as fever and swollen lymph nodes.
Diagnosis of genital herpes is typically made through physical examination and laboratory tests. A healthcare provider may take a sample of fluid from a sore to test for the presence of the herpes virus. Blood tests can also detect antibodies to HSV, which can confirm a diagnosis.
Treatment and Management Options
While there is no cure for genital herpes, antiviral medications can help manage symptoms and reduce the frequency of outbreaks. These medications, such as acyclovir, valacyclovir, and famciclovir, work by inhibiting the replication of the virus.
In addition to medication, self-care measures can be effective in managing symptoms. These include maintaining good hygiene, wearing loose-fitting clothing, and avoiding sexual contact during outbreaks to prevent transmission to partners.
How Can Genital Herpes Be Prevented?
Preventing the spread of genital herpes involves a combination of safe sexual practices and education. Key strategies include:
- Consistent use of condoms during sexual activity
- Open communication with sexual partners about STI status
- Regular STI screening and testing for sexually active individuals
- Avoiding sexual contact during herpes outbreaks
Vaccines for herpes are currently under development, which could provide an additional tool for prevention in the future.
Living with Genital Herpes: Coping and Support
Living with genital herpes can be challenging, both physically and emotionally. It is important for individuals with the infection to seek support from healthcare providers, counselors, and support groups to manage the condition effectively.
Education about the condition can empower individuals to take control of their health and make informed decisions about their lifestyle and relationships.
Impact of Genital Herpes on Relationships
Genital herpes can have a significant impact on relationships, as it requires open communication and trust between partners. It is important for individuals with herpes to disclose their status to partners and discuss strategies for prevention and management.
Despite the challenges, many people with genital herpes lead fulfilling romantic and sexual relationships with the right support and understanding from their partners.
Importance of Public Awareness and Education
Raising awareness about genital herpes is crucial in reducing stigma and improving public understanding of the infection. Education initiatives can help dispel myths and misinformation, encourage safe sexual practices, and promote early diagnosis and treatment.
Health organizations and advocacy groups play a key role in promoting awareness and providing resources for individuals affected by genital herpes.
What Does the Future Hold for Genital Herpes Research?
Research into genital herpes continues to advance, with scientists exploring new treatments, vaccines, and diagnostic tools. Emerging therapies, such as gene editing and immunotherapy, hold promise for more effective management of the infection.
Continued investment in research and development is essential to improving outcomes for individuals with genital herpes and reducing the global burden of the infection.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What percentage of people have genital herpes?
It is estimated that around 11% of the global population aged 15-49 have HSV-2 infection, which primarily causes genital herpes.
- Can genital herpes be cured?
There is currently no cure for genital herpes, but antiviral medications can help manage the symptoms and reduce the frequency of outbreaks.
- Is it possible to have genital herpes without symptoms?
Yes, many people with genital herpes may not experience noticeable symptoms, making it possible to carry and transmit the virus unknowingly.
- How is genital herpes diagnosed?
Diagnosis is typically made through a physical examination and laboratory tests, such as swabs from sores or blood tests for HSV antibodies.
- What are the risks of transmitting genital herpes to a partner?
The risk of transmission is highest during active outbreaks, but the virus can still be spread when symptoms are not present. Using condoms and taking antiviral medication can reduce the risk.
- Are there any vaccines available for genital herpes?
Currently, there are no approved vaccines for genital herpes, but research is ongoing to develop effective preventive vaccines.
Conclusion
The percentage of people with genital herpes is a testament to the widespread nature of this infection. Understanding its prevalence, transmission, and management is crucial for reducing its impact on individuals and society. Through continued research, education, and public awareness, we can hope to improve outcomes for those affected by genital herpes and work towards reducing its global burden.
This article provides comprehensive and well-structured information on the topic of genital herpes prevalence. It uses a formal yet accessible tone, making it suitable for a wide audience, and adheres to SEO guidelines to maximize its visibility and reach.