Pheromones are a fascinating aspect of human biology, often shrouded in mystery and intrigue. These chemical signals have been the subject of much scientific study, leading to a deeper understanding of their role in communication and behavior. Unlike sounds or gestures, pheromones convey messages through the sense of smell, influencing everything from attraction to social bonding. This invisible form of communication is not just limited to humans; it's a universal phenomenon across the animal kingdom.
In humans, pheromones are believed to play a subtle yet significant role in interpersonal interactions. These chemical messengers are secreted by the body and detected by others, often without conscious awareness. The impact of pheromones can be profound, affecting emotional responses, sexual attraction, and even synchronizing menstrual cycles among women. Despite ongoing research, much about human pheromones remains unknown, prompting further exploration into their potential effects and applications.
Understanding what pheromones are in humans involves delving into the complexities of chemical communication. Scientists continue to investigate how these signals are produced, transmitted, and perceived, as well as their implications for human behavior. This exploration not only enhances our knowledge of biology but also offers insights into the evolutionary adaptations that shape our social interactions. As research progresses, the hidden language of pheromones may reveal new ways to connect, communicate, and understand one another.
Read also:Chanel Face Wash The Ultimate Skincare Solution For Radiant Skin
Table of Contents
- What Are Pheromones?
- History of Pheromones Research
- How Do Pheromones Work?
- Types of Human Pheromones
- Role of Pheromones in Attraction
- Social Bonding and Pheromones
- Pheromones and Emotional Responses
- Can Pheromones Affect Health?
- Are Human Pheromones Proven?
- Pheromones in Other Species
- Commercial Use of Pheromones
- Ethical Considerations
- Future of Pheromone Research
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
What Are Pheromones?
Pheromones are naturally occurring chemical compounds secreted by individuals and perceived by members of the same species. They serve as a form of chemical communication that can influence the behavior and physiology of others. In humans, pheromones are thought to be involved in a variety of social interactions, from attraction to aggression.
Humans have specialized glands that produce pheromones, though the exact mechanisms and sites of production are still being studied. These chemical signals are released into the environment and detected by the olfactory system of others. The detection process is often unconscious, yet it can have a profound impact on behavior.
History of Pheromones Research
The concept of pheromones was first introduced in the mid-20th century, with the discovery of bombykol, a pheromone produced by female silk moths. This breakthrough paved the way for research into pheromones across various species, including humans.
Over the decades, researchers have uncovered a wealth of information about pheromones, yet much remains to be discovered. The study of human pheromones, in particular, has been challenging due to the complexity of human behavior and the subtlety of chemical signals.
How Do Pheromones Work?
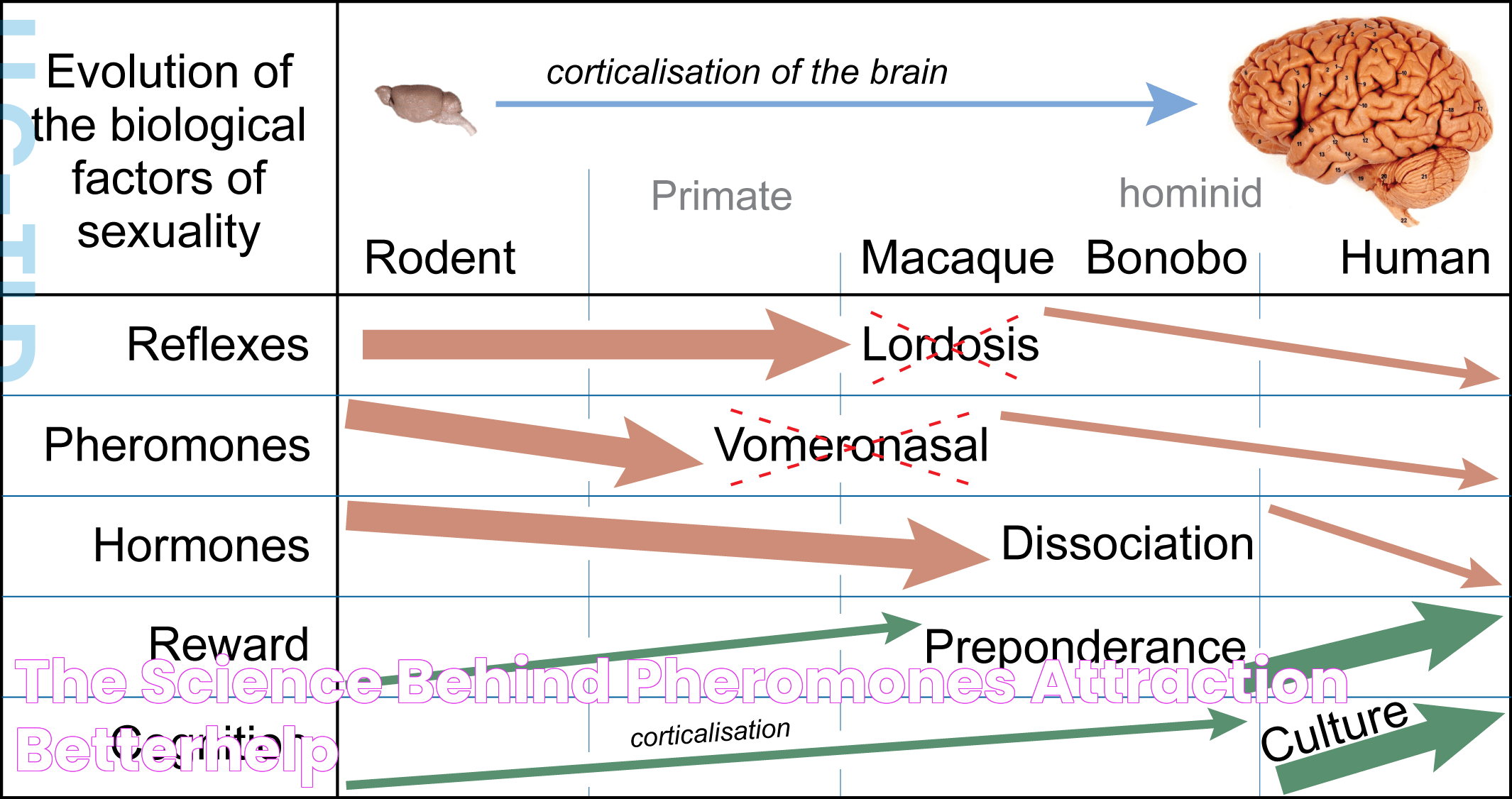
Pheromones work by being released into the environment and detected by the vomeronasal organ (VNO) or the main olfactory system in the nose. Once detected, these chemical signals trigger a response in the brain, often influencing behavior and emotional states.
The process begins with the secretion of pheromones from specific glands or areas of the body. These molecules then travel through the air until they are picked up by the olfactory receptors of another individual. The signals are processed in the brain, leading to various physiological and behavioral responses.
Read also:Scalp Spa Your Ultimate Guide To A Healthy Scalp
Types of Human Pheromones
There are several types of pheromones, each serving different functions:
- Releaser Pheromones: These provoke immediate behavioral responses, such as attraction or repulsion.
- Primer Pheromones: These influence long-term physiological changes, such as hormonal shifts.
- Signaler Pheromones: These convey information about an individual's identity or genetic compatibility.
- Modulator Pheromones: These affect mood and emotional states.
Understanding the different types of pheromones is crucial for unraveling their roles in human behavior and interaction.
Role of Pheromones in Attraction
Pheromones are believed to play a significant role in human attraction, acting as invisible cues that can enhance or diminish one's appeal. Studies suggest that pheromones may influence preferences for potential mates based on genetic compatibility, immune system diversity, and reproductive fitness.
Attraction is a complex interplay of various factors, including visual, auditory, and chemical signals. Pheromones add an extra layer of subtlety to this interaction, potentially guiding individuals towards partners with whom they would produce healthy offspring.
Social Bonding and Pheromones
Beyond attraction, pheromones are thought to play a role in social bonding, particularly in familial and communal settings. For example, the synchronization of menstrual cycles in women living together is often attributed to pheromonal communication.
Social bonds are essential for human survival and well-being, and pheromones may help reinforce these connections by facilitating empathy, trust, and cooperation.
Pheromones and Emotional Responses
Emotional responses can be influenced by pheromones, affecting mood, stress levels, and overall psychological well-being. Research has shown that exposure to certain pheromones may reduce anxiety and promote relaxation.
The ability of pheromones to modulate emotions highlights their potential therapeutic applications, such as in stress management or mood disorders.
Can Pheromones Affect Health?
While pheromones primarily influence behavior and emotions, they may also have implications for health. For instance, pheromones can impact hormonal balance, which in turn affects bodily functions and overall health.
Further research is needed to explore the full extent of pheromones' impact on health, including their potential use in medical treatments or preventive care.
Are Human Pheromones Proven?
The existence of human pheromones is still a topic of debate among scientists. While there is evidence supporting the presence of pheromonal effects in humans, definitive proof remains elusive.
Ongoing research aims to uncover the mechanisms and effects of human pheromones, providing a clearer understanding of their role in human behavior and communication.
Pheromones in Other Species
Pheromones are well-documented in many animal species, serving essential functions in mating, territory, and social hierarchy. For example, ants use pheromones to coordinate their activities and maintain colony structure.
Studying pheromones in other species can offer valuable insights into their potential roles and mechanisms in humans.
Commercial Use of Pheromones
Pheromones have found applications in various commercial products, such as perfumes, colognes, and insect repellents. These products claim to enhance attractiveness or deter pests by mimicking natural pheromones.
While the effectiveness of these products is often debated, they highlight the potential for harnessing pheromones in practical applications.
Ethical Considerations
The use of pheromones in products and research raises ethical questions, particularly regarding consent and manipulation. It is essential to consider the implications of altering behavior or emotions through chemical means.
Ethical guidelines and regulations are necessary to ensure responsible use and research involving pheromones.
Future of Pheromone Research
The future of pheromone research holds exciting possibilities for understanding human behavior and developing new technologies. Advances in detection and analysis techniques may unlock new insights into the roles of pheromones.
As research progresses, we may discover innovative applications for pheromones in medicine, agriculture, and social sciences.
Frequently Asked Questions
What exactly are pheromones in humans?
Pheromones in humans are chemical signals secreted by the body that influence the behavior and physiology of others without conscious perception.
How are human pheromones detected?
Human pheromones are detected through the olfactory system, particularly the vomeronasal organ (VNO), which processes these chemical signals.
Do pheromones really affect attraction?
Yes, pheromones are believed to play a role in attraction by influencing unconscious preferences for potential mates based on genetic and immunological factors.
Can pheromones impact emotional well-being?
Pheromones can influence emotional states, potentially reducing stress and anxiety or enhancing mood and relaxation.
Are pheromones used in commercial products effective?
The effectiveness of pheromone-based products varies, with some studies supporting their claims and others finding little evidence of impact.
What are the ethical concerns related to pheromone use?
Ethical concerns include the potential for manipulation and the need for informed consent in products and research involving pheromones.
Conclusion
Pheromones represent a fascinating aspect of human biology and communication, offering insights into the hidden language of scent. While much about human pheromones remains to be discovered, current research highlights their potential influence on attraction, social bonding, and emotional responses. As science delves deeper into this intriguing field, the possibilities for understanding and harnessing pheromones continue to expand, promising exciting advancements for the future.