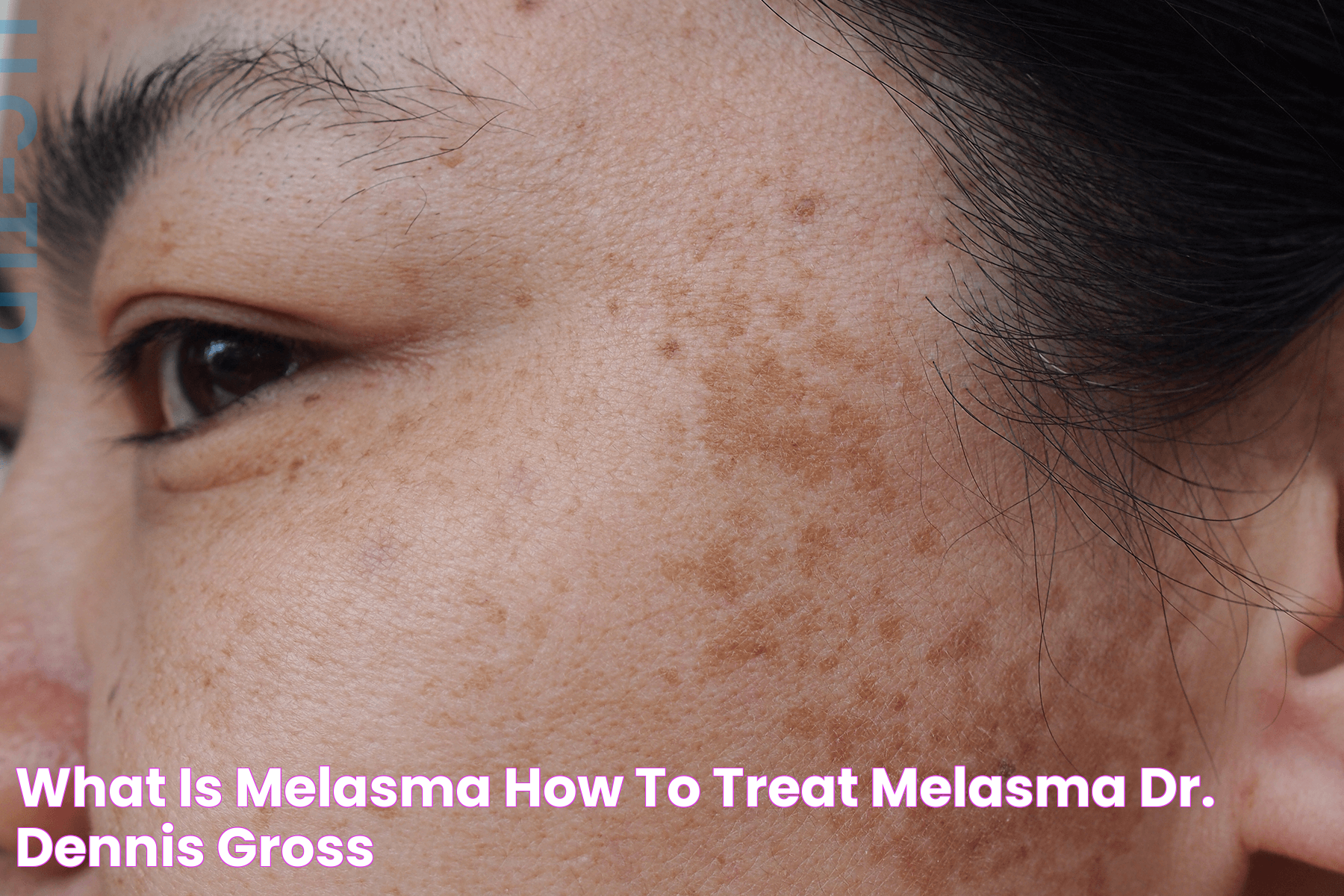
Melasma, often referred to as the "mask of pregnancy," is a common skin condition characterized by dark, discolored patches on the skin. These patches typically appear on the face, especially on the cheeks, forehead, bridge of the nose, and the upper lip, but they can also occur on other parts of the body that are exposed to the sun. While melasma isn't harmful, it can cause significant cosmetic concern, leading individuals to seek various treatment options. The word "melasma" is derived from the Greek word "melas," meaning black or dark, which accurately describes the hyperpigmentation associated with this condition. Although it's more prevalent in women, particularly during pregnancy, men can also develop melasma. Understanding the underlying causes and effective treatments for melasma is crucial for those affected by this condition.
The exact cause of melasma is not fully understood, but it is believed to result from a combination of genetic, hormonal, and environmental factors. Hormonal changes, such as those occurring during pregnancy, the use of oral contraceptives, or hormone replacement therapy, are known to trigger melasma. Additionally, sun exposure is a significant contributing factor, as ultraviolet (UV) light stimulates melanocytes, the cells that produce pigment in the skin, leading to the appearance of dark patches. Stress and thyroid disorders have also been linked to melasma, further complicating its management.
Treating melasma effectively requires a comprehensive approach, often involving a combination of topical treatments, sun protection, and lifestyle modifications. Dermatologists may prescribe hydroquinone, a topical bleaching agent, or other skin-lightening agents such as retinoids and corticosteroids. Chemical peels, laser therapy, and microdermabrasion are also used to improve the appearance of melasma. However, prevention is equally important; using sunscreen daily, wearing protective clothing, and minimizing sun exposure can help prevent melasma from worsening. By understanding what is melasma and exploring various treatment options, individuals can manage this condition and improve their skin's appearance.
Read also:Ultimate Guide To Choosing The Best Shampoo To Get For Your Hair Type
Table of Contents
- What is Melasma?
- What Causes Melasma?
- Who is Most at Risk for Melasma?
- How is Melasma Diagnosed?
- What are Common Symptoms of Melasma?
- What Treatment Options are Available for Melasma?
- How Can Melasma be Prevented?
- Are There Natural Remedies for Melasma?
- How Does Sun Exposure Affect Melasma?
- What is the Role of Hormones in Melasma?
- What Lifestyle Changes Can Help Manage Melasma?
- How Effective are Laser Treatments for Melasma?
- Can Diet Influence Melasma?
- What are the Psychological Impacts of Melasma?
- FAQs about Melasma
- Conclusion
What is Melasma?
Melasma is a chronic skin condition that results in brown or gray-brown patches, primarily on the face. It is a form of hyperpigmentation and is more common in women than men. While melasma is not harmful or painful, its cosmetic effects can be distressing for those affected. The condition is more prevalent in individuals with darker skin tones, including those of Hispanic, Asian, and Middle Eastern descent. Understanding what is melasma involves recognizing its appearance, common triggers, and impact on individuals' lives.
The hallmark of melasma is its symmetrical appearance, with patches often forming matching patterns on both sides of the face. The condition is primarily caused by an increase in melanin production, influenced by various factors including genetics, hormonal changes, and environmental exposures. While melasma can fade over time, particularly when the triggering factors are removed, it can also be persistent and require treatment to improve its appearance.
Given its prevalence and impact, melasma has been the focus of numerous studies aimed at understanding its pathophysiology and finding effective treatments. Research continues to explore the complex interplay of genetic predisposition, hormonal influences, and environmental triggers that contribute to melasma. By gaining a deeper understanding of what is melasma and its causes, dermatologists and researchers can develop better strategies for managing and treating this condition.
What Causes Melasma?
The exact cause of melasma is not completely understood, but it is believed to arise from a combination of genetic, hormonal, and environmental factors. Key contributing factors include:
- Hormonal Changes: Melasma is often linked to hormonal fluctuations, particularly those occurring during pregnancy, the use of oral contraceptives, or hormone replacement therapy. These hormonal changes can stimulate melanocytes, increasing melanin production and leading to the characteristic dark patches of melasma.
- Sun Exposure: Ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun is a significant trigger for melasma. UV light stimulates melanocytes, leading to increased melanin production and the formation of dark patches. This is why melasma is often more pronounced in the summer months and can improve during the winter.
- Genetic Factors: A genetic predisposition may also play a role in the development of melasma, as it is more common in individuals with a family history of the condition. Those with darker skin types are more susceptible to developing melasma, although it can affect individuals of all skin tones.
- Medications: Certain medications, including some anti-seizure drugs, may trigger melasma as a side effect.
- Stress and Thyroid Disorders: Stress and thyroid abnormalities have been linked to melasma, although the mechanisms are not fully understood.
Understanding these contributing factors can aid in the prevention and management of melasma. Individuals who are aware of their risk factors can take proactive steps to minimize their exposure to triggers and seek appropriate treatment when necessary. By recognizing what is melasma and its causes, people can better manage this condition and improve their quality of life.
Who is Most at Risk for Melasma?
Melasma can affect anyone, but certain groups are at higher risk due to their genetic makeup, hormonal levels, and lifestyle choices. Those most at risk include:
Read also:Top Picks For Good Teeth Whitening Toothpaste Effective And Safe Options
- Women: Melasma is more common in women, particularly during pregnancy, due to hormonal fluctuations. It is often referred to as "the mask of pregnancy" because of its prevalence during this time.
- Individuals with Darker Skin Types: People with Fitzpatrick skin types III to VI, which include Hispanic, Asian, African, and Middle Eastern individuals, are more susceptible to melasma.
- Those with a Family History: A genetic predisposition to melasma increases the likelihood of developing the condition. If close family members have melasma, the risk is higher.
- Sun Exposure: Individuals who spend a lot of time in the sun without adequate protection are at a greater risk of developing melasma due to UV-induced melanin production.
- Hormonal Influences: Those taking hormonal medications, such as oral contraceptives or undergoing hormone replacement therapy, are at increased risk.
Recognizing these risk factors allows individuals to take preventive measures, such as using sunscreen and wearing protective clothing, to reduce their risk of developing melasma. By understanding what is melasma and identifying those at risk, healthcare providers can offer tailored advice and treatment options.
How is Melasma Diagnosed?
Diagnosing melasma typically involves a physical examination by a dermatologist or healthcare professional. The diagnosis is primarily based on the appearance and distribution of the hyperpigmented patches on the skin. In some cases, additional diagnostic tools may be used:
- Wood's Lamp Examination: A Wood's lamp, which emits UV light, can help to distinguish between different types of pigmentation and assess the depth of melasma. This examination can provide valuable information about the extent of melanocyte activity.
- Skin Biopsy: In rare cases, a dermatologist may perform a skin biopsy to rule out other skin conditions that may mimic melasma.
It is essential to consult a dermatologist if melasma is suspected, as they can provide an accurate diagnosis and recommend appropriate treatment options. Understanding what is melasma and how it is diagnosed can help individuals seek timely medical advice and manage the condition effectively.
What are Common Symptoms of Melasma?
The primary symptom of melasma is the appearance of dark, discolored patches on the skin. These patches are typically:
- Symmetrical: Melasma often appears in symmetrical patterns on both sides of the face.
- Brown or Gray-Brown: The patches vary in color from light brown to dark brown or gray-brown.
- Irregularly Shaped: The edges of the patches are often irregular, but the overall distribution is uniform.
- Commonly Found on the Face: The most affected areas are the cheeks, forehead, nose, and upper lip, but melasma can also occur on the neck, arms, and other sun-exposed areas.
While melasma is not associated with any physical discomfort, such as itching or pain, its cosmetic effects can be distressing for individuals. Understanding what is melasma and recognizing its symptoms can prompt those affected to seek appropriate treatment and improve their skin's appearance.
What Treatment Options are Available for Melasma?
Treating melasma effectively requires a multifaceted approach that combines topical treatments, sun protection, and lifestyle modifications. Some of the most common treatments for melasma include:
- Topical Treatments: Dermatologists often prescribe skin-lightening agents, such as hydroquinone, to reduce pigmentation. Other topical treatments include retinoids, corticosteroids, and azelaic acid.
- Chemical Peels: Chemical peels can help to remove the outer layer of skin, reducing pigmentation and improving the appearance of melasma.
- Laser Therapy: Laser and light-based treatments, such as fractional laser therapy and intense pulsed light (IPL), can target melanin and reduce the appearance of melasma.
- Microdermabrasion: This procedure involves the gentle exfoliation of the skin's surface to improve pigmentation and texture.
- Sun Protection: Daily use of broad-spectrum sunscreen is essential to prevent melasma from worsening. Sunscreen should be applied generously and reapplied throughout the day.
It is important to consult a dermatologist for a personalized treatment plan, as the effectiveness of these treatments can vary based on individual skin type and the severity of melasma. Understanding what is melasma and exploring available treatment options can empower individuals to take control of their skin health and improve their quality of life.
How Can Melasma be Prevented?
Preventing melasma involves minimizing exposure to known triggers and adopting protective measures. Effective prevention strategies include:
- Sun Protection: Consistent use of broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher is crucial. Sunscreen should be applied every day, even on cloudy days, and reapplied every two hours when outdoors.
- Protective Clothing: Wearing hats, sunglasses, and long-sleeved clothing can provide additional protection against UV exposure.
- Avoiding Peak Sun Hours: Limiting outdoor activities during peak sun hours, typically between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m., can reduce UV exposure.
- Hormonal Management: Consulting a healthcare provider about alternative contraceptive options or hormone therapies can help manage the hormonal triggers of melasma.
- Stress Management: Engaging in stress-reduction techniques, such as yoga, meditation, or exercise, may help in managing melasma, as stress is a potential trigger.
By understanding what is melasma and implementing these preventive measures, individuals can reduce their risk of developing melasma or prevent its worsening. Prevention is a key component of managing this condition effectively.
Are There Natural Remedies for Melasma?
While there is limited scientific evidence to support the effectiveness of natural remedies for melasma, some individuals have found relief through the use of natural ingredients. Popular natural remedies include:
- Aloe Vera: Aloe vera is known for its soothing properties and may help to lighten melasma patches when applied topically.
- Apple Cider Vinegar: The acetic acid in apple cider vinegar may help to exfoliate the skin and reduce pigmentation.
- Turmeric: Turmeric contains curcumin, which has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties that may improve skin tone.
- Lemon Juice: Lemon juice has natural bleaching properties that may help to lighten dark patches. However, it can be irritating, so it should be used with caution.
- Green Tea Extract: Green tea extract contains antioxidants that may protect the skin and improve its appearance.
While natural remedies can be a part of a holistic approach to managing melasma, it is important to consult a dermatologist before using them, as they may not be suitable for all skin types or may interact with other treatments. Understanding what is melasma and considering natural remedies as part of a broader treatment plan can provide additional support in managing this condition.
How Does Sun Exposure Affect Melasma?
Sun exposure plays a significant role in the development and exacerbation of melasma. Ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun stimulates melanocytes, the cells responsible for producing melanin, leading to increased pigmentation and the formation of dark patches. Key points about sun exposure and melasma include:
- UV-Induced Melanin Production: UV radiation triggers the production of melanin as a protective response, but in individuals with melasma, this can result in uneven pigmentation.
- Worsening of Symptoms: Melasma tends to worsen with increased sun exposure, making sun protection a critical component of managing the condition.
- Seasonal Variations: Melasma can become more pronounced during the summer months when UV exposure is higher and may improve during the winter.
Effective sun protection measures, such as the use of sunscreen, wearing protective clothing, and seeking shade, can help prevent melasma from worsening and improve treatment outcomes. Understanding what is melasma and the impact of sun exposure can empower individuals to take proactive steps to protect their skin and manage this condition effectively.
What is the Role of Hormones in Melasma?
Hormones play a significant role in the development and progression of melasma. Hormonal fluctuations, particularly those involving estrogen and progesterone, can trigger melasma by stimulating melanocytes and increasing melanin production. Key points about hormones and melasma include:
- Pregnancy-Related Hormonal Changes: Melasma is commonly associated with pregnancy due to the surge in estrogen and progesterone levels, leading to the condition's nickname "the mask of pregnancy."
- Oral Contraceptives and Hormone Replacement Therapy: The use of hormonal medications, such as birth control pills or hormone replacement therapy, can increase the risk of developing melasma.
- Thyroid Disorders: Thyroid abnormalities have also been linked to melasma, although the exact mechanisms are not fully understood.
Understanding the hormonal influences on melasma can help individuals make informed decisions about their contraceptive and hormone therapy options and seek appropriate treatment to manage the condition. By recognizing what is melasma and the role of hormones, healthcare providers can offer personalized advice and support to those affected.
What Lifestyle Changes Can Help Manage Melasma?
Adopting certain lifestyle changes can help manage melasma and improve treatment outcomes. Key lifestyle changes include:
- Sun Protection: Consistent use of sunscreen, wearing protective clothing, and avoiding peak sun hours are essential for managing melasma.
- Stress Management: Engaging in stress-reducing activities, such as yoga, meditation, or exercise, can help minimize the impact of stress on melasma.
- Balanced Diet: A healthy, balanced diet rich in antioxidants and vitamins can support skin health and potentially improve melasma.
- Avoiding Irritants: Avoiding harsh skincare products and irritants that can exacerbate melasma is crucial for maintaining healthy skin.
- Regular Dermatologist Visits: Regular check-ins with a dermatologist can help monitor the condition and adjust treatment plans as needed.
Implementing these lifestyle changes can provide additional support in managing melasma and improve overall skin health. By understanding what is melasma and making informed lifestyle choices, individuals can take proactive steps to manage this condition effectively.
How Effective are Laser Treatments for Melasma?
Laser treatments can be effective in reducing the appearance of melasma, but their success largely depends on the individual's skin type and the severity of the condition. Key points about laser treatments for melasma include:
- Types of Laser Treatments: Common laser treatments for melasma include fractional laser therapy, Q-switched lasers, and intense pulsed light (IPL) therapy. These treatments target melanin and help to break down pigmentation.
- Effectiveness: Laser treatments can provide significant improvements in melasma, but results can vary. Some individuals experience a reduction in pigmentation, while others may require multiple sessions to achieve desired results.
- Potential Side Effects: Laser treatments can cause side effects, such as redness, swelling, and temporary darkening of the skin. It is important to consult a dermatologist to determine the most appropriate treatment and minimize risks.
Understanding the potential benefits and risks of laser treatments can help individuals make informed decisions about their treatment options. By recognizing what is melasma and considering laser treatments as part of a comprehensive treatment plan, individuals can achieve better outcomes and improve their skin's appearance.
Can Diet Influence Melasma?
While there is limited scientific evidence to support a direct link between diet and melasma, certain dietary choices may support skin health and potentially influence melasma. Key dietary considerations include:
- Antioxidant-Rich Foods: A diet rich in antioxidants, such as fruits, vegetables, and green tea, can help protect the skin from oxidative stress and support overall skin health.
- Vitamin C and E: These vitamins are known for their skin-protective properties and may help to improve skin tone and texture.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Found in fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts, omega-3 fatty acids have anti-inflammatory properties that may benefit the skin.
While dietary changes alone may not significantly impact melasma, they can complement other treatments and contribute to overall skin health. Understanding what is melasma and considering dietary choices as part of a holistic approach can provide additional support in managing this condition.
What are the Psychological Impacts of Melasma?
Melasma can have significant psychological impacts on individuals, affecting their self-esteem and quality of life. Key psychological considerations include:
- Self-Esteem and Confidence: The visible nature of melasma can lead to feelings of self-consciousness and reduced self-esteem, particularly in social and professional settings.
- Emotional Distress: Individuals with melasma may experience emotional distress, anxiety, and frustration due to the persistent nature of the condition and the challenges associated with treatment.
- Support and Counseling: Seeking support from mental health professionals, support groups, or counseling can help individuals cope with the emotional impacts of melasma and improve their quality of life.
Understanding what is melasma and its potential psychological impacts can help individuals seek appropriate support and resources to manage both the physical and emotional aspects of the condition. By addressing the psychological impacts of melasma, individuals can improve their overall well-being and quality of life.
FAQs about Melasma
- Can melasma go away on its own? Melasma can fade over time, especially when the triggering factors, such as hormonal changes, are removed. However, it can also be persistent and require treatment.
- Is melasma hereditary? There is a genetic component to melasma, and individuals with a family history of the condition may be at higher risk.
- Can men get melasma? Yes, while melasma is more common in women, men can also develop the condition.
- What is the best sunscreen for melasma? A broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher is recommended for melasma. Sunscreens with physical blockers, such as zinc oxide or titanium dioxide, are often preferred.
- Can melasma be cured permanently? There is currently no permanent cure for melasma, but it can be effectively managed with appropriate treatments and preventive measures.
- Does stress affect melasma? Stress has been linked to melasma, and managing stress through relaxation techniques or counseling may help in managing the condition.
Conclusion
Melasma is a common skin condition characterized by dark, discolored patches on the skin. While it is not harmful, its cosmetic effects can be distressing for individuals. Understanding what is melasma, its causes, and available treatment options can empower individuals to take proactive steps to manage this condition effectively. By adopting preventive measures, seeking appropriate treatment, and making informed lifestyle choices, individuals can improve their skin's appearance and quality of life. Additionally, addressing the psychological impacts of melasma and seeking support can enhance overall well-being and confidence. With continued research and advancements in treatment options, individuals affected by melasma can look forward to improved outcomes and greater control over their skin health.