The term "stoical" encapsulates a profound philosophy that champions resilience, self-control, and a serene acceptance of life's challenges. Originating from ancient stoicism, this concept encourages individuals to confront adversity with equanimity, emphasizing the importance of maintaining composure in the face of difficulties. In today's fast-paced world, understanding the stoical definition offers a valuable lens through which we can navigate the complexities of our daily lives.
Understanding the stoical definition involves delving into the rich history of Stoicism, a school of philosophy founded in ancient Greece by Zeno of Citium. This philosophy teaches the development of self-control and fortitude as a means of overcoming destructive emotions. The stoical attitude is often seen as a source of inner peace, providing individuals with the strength to endure life's inevitable hardships without succumbing to despair.
In contemporary settings, the stoical definition extends beyond the philosophical domain, influencing various aspects of modern life, from psychological resilience to leadership qualities. By cultivating a stoical mindset, individuals can enhance their emotional intelligence, improve decision-making, and foster a balanced approach to life's challenges. This article explores the nuances of the stoical definition, its historical roots, and its relevance in today's world, offering insights into how embracing stoicism can lead to a more fulfilling and harmonious existence.
Read also:Epsom Salt Bath Effects On Hair And Scalp Health
Table of Contents
- Biography of Stoicism
- What is the Origin of Stoicism?
- Key Principles of Stoicism
- How Does Stoicism Relate to Modern Life?
- The Impact of Stoicism on Psychological Resilience
- Stoicism and Emotional Intelligence
- Is Stoicism Relevant in Leadership?
- The Role of Stoicism in Educational Settings
- How Can Stoicism Enhance Personal Development?
- Practical Ways to Apply Stoicism in Daily Life
- Challenges in Embracing a Stoical Mindset
- Famous Stoic Philosophers and Their Contributions
- Stoicism in Popular Culture
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
Biography of Stoicism
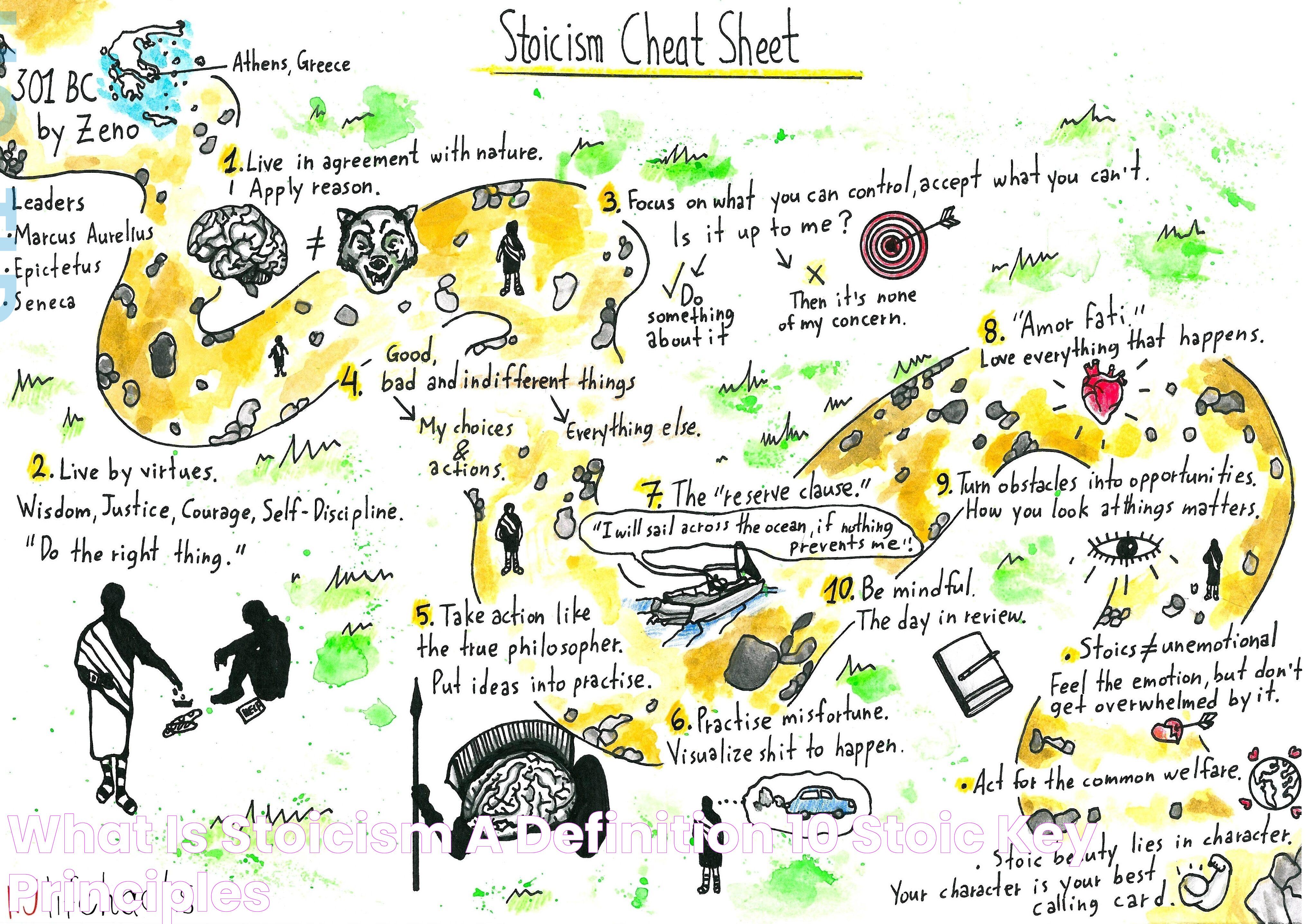
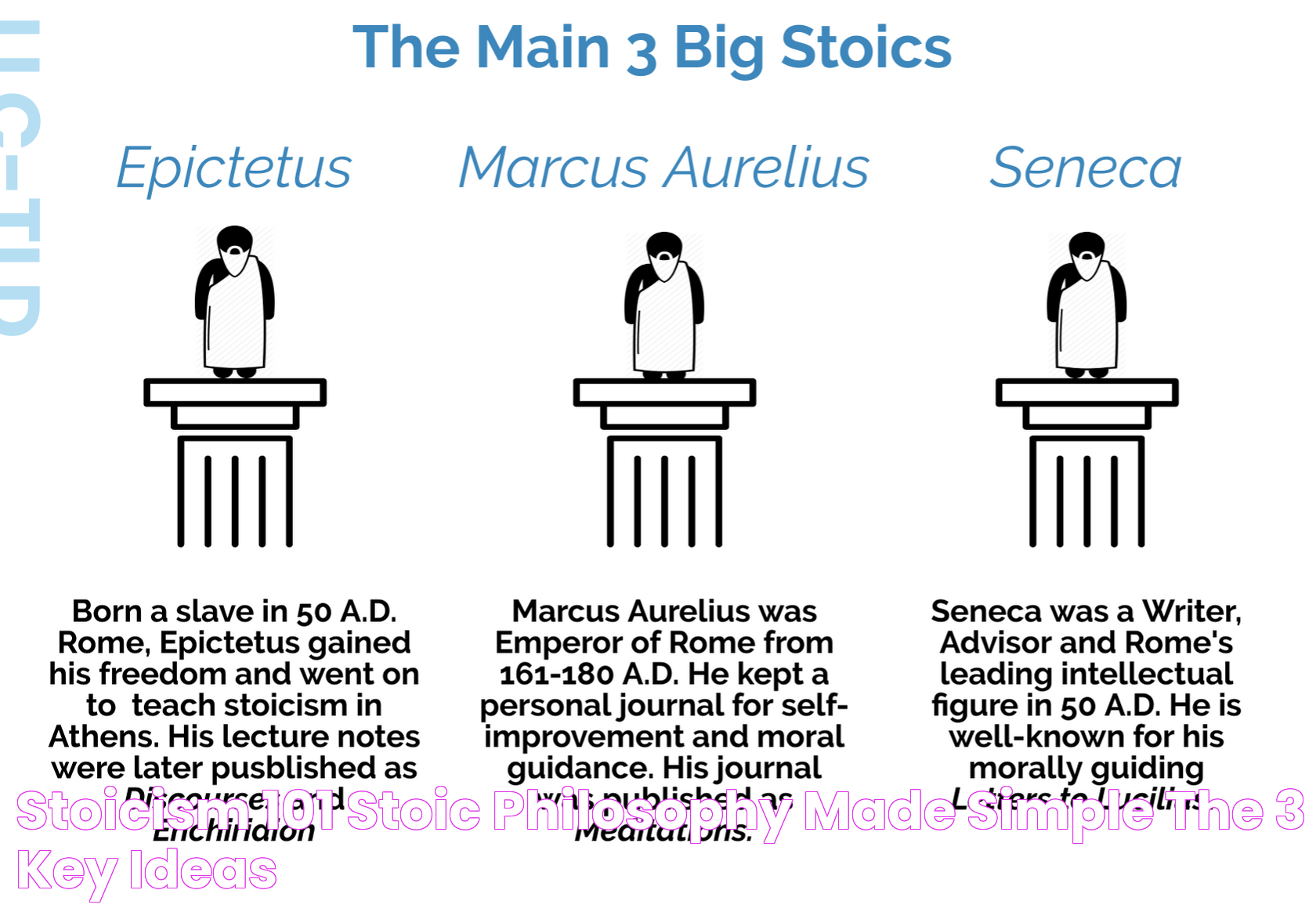
Stoicism, a prominent school of thought in ancient Greece, was founded by Zeno of Citium in the early 3rd century BC. The philosophy is rooted in the teachings of Socratic logic and the natural world, emphasizing reason and virtue as the path to personal excellence. Stoicism quickly gained popularity in ancient Rome, profoundly influencing Roman thinkers such as Seneca, Epictetus, and Marcus Aurelius.
At its core, Stoicism advocates for the cultivation of self-control and rational thought to master one's emotions and desires. It encourages individuals to maintain inner tranquility by focusing on what they can control and accepting what they cannot. The stoical definition, therefore, embodies a disciplined approach to life, advocating for resilience in the face of adversity and a commitment to virtuous living.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Founder | Zeno of Citium |
| Era | 3rd Century BC |
| Key Figures | Seneca, Epictetus, Marcus Aurelius |
| Core Tenets | Virtue, Reason, Self-Control |
| Influence | Ancient Rome, Modern Philosophy |
What is the Origin of Stoicism?
The origin of Stoicism can be traced back to the vibrant intellectual landscape of ancient Greece, particularly Athens, where Zeno of Citium established the philosophy around 300 BC. Zeno's teachings were influenced by earlier philosophical doctrines, including the ideas of Socrates and the Cynics, who emphasized living in harmony with nature and rejecting materialism.
Stoicism was initially disseminated through public lectures held at the Stoa Poikile, a painted porch in Athens, which is where the philosophy derives its name. Zeno's successors, including Cleanthes and Chrysippus, further developed and systematized Stoic doctrines, laying the foundation for future generations of Stoic thinkers.
As Stoicism evolved, it spread beyond Greece, gaining prominence in Rome where it found a receptive audience among statesmen and intellectuals. Roman Stoics like Seneca and Epictetus played a crucial role in adapting Stoic principles to Roman culture, emphasizing practical ethics and personal improvement. The Meditations of Marcus Aurelius, a Roman Emperor, remain one of the most celebrated works in Stoic literature, offering timeless insights into the stoical definition and its application to life's challenges.
Key Principles of Stoicism
Stoicism is built upon a set of core principles that guide individuals toward a life of virtue and wisdom. These principles emphasize the importance of aligning one's actions with nature and reason, fostering an understanding of what is truly valuable and under one's control.
Read also:Scalp Spa Your Ultimate Guide To A Healthy Scalp
- Virtue is the Highest Good: Stoics believe that living virtuously is the ultimate goal of life. Virtue, for the Stoics, is synonymous with moral excellence and encompasses qualities such as wisdom, courage, justice, and temperance.
- Focus on What You Can Control: A central tenet of Stoicism is distinguishing between what is within our control and what is not. By focusing on actions and thoughts that we can influence, Stoics maintain inner peace and resilience.
- Accept Fate with Equanimity: Stoicism teaches the acceptance of fate, recognizing that external events are beyond our control. By embracing this mindset, individuals can maintain calmness and composure in the face of adversity.
- Live in Accordance with Nature: Stoics advocate for living in harmony with the natural world, understanding that humans are a part of a larger, interconnected cosmos.
- Practice Self-Reflection: Regular self-examination helps Stoics assess their actions and align them with their values, fostering personal growth and ethical behavior.
By internalizing these principles, individuals can cultivate a stoical perspective that empowers them to face life's challenges with grace and fortitude, leading to a more fulfilling and meaningful existence.
How Does Stoicism Relate to Modern Life?
In the modern world, where stress and uncertainty are prevalent, the stoical definition offers valuable insights into managing life's challenges with resilience and composure. Stoicism's focus on self-control, rationality, and acceptance of the uncontrollable aligns closely with contemporary movements in psychology and personal development, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and mindfulness.
Stoicism encourages individuals to cultivate emotional intelligence by understanding and managing their emotions effectively. By recognizing that our perceptions influence our emotional responses, Stoics can develop strategies to remain calm and focused, even in difficult situations. This mindset fosters a sense of empowerment, enabling individuals to make reasoned decisions and maintain a balanced perspective.
Moreover, the stoical definition resonates with modern leadership principles, emphasizing the importance of ethical decision-making, perseverance, and integrity. Leaders who embody Stoic values inspire trust and respect, fostering a positive organizational culture and guiding their teams through challenges with wisdom and poise.
In educational settings, Stoic principles can be integrated into curricula to promote critical thinking, resilience, and ethical reasoning among students. By teaching young people to embrace a stoical mindset, educators can prepare them to navigate the complexities of the modern world with confidence and clarity.
The Impact of Stoicism on Psychological Resilience
Stoicism has a profound impact on psychological resilience, offering practical tools for managing stress, adversity, and emotional turmoil. By focusing on what is within our control and accepting what is not, individuals can cultivate a mindset that fosters resilience and adaptability.
One of the key aspects of Stoicism is its emphasis on cognitive reframing, a technique that involves changing one's perspective on a situation to alter its emotional impact. This approach is similar to cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), which helps individuals challenge negative thought patterns and develop healthier ways of thinking. By practicing cognitive reframing, Stoics can transform challenges into opportunities for growth and learning.
Furthermore, Stoicism encourages mindfulness and present-moment awareness, helping individuals stay grounded and focused amidst uncertainty. By cultivating an attitude of acceptance, Stoics can reduce anxiety and stress, enhancing their ability to cope with life's ups and downs.
Ultimately, the stoical definition provides a framework for building psychological resilience, empowering individuals to face adversity with strength and grace. By embracing Stoic principles, individuals can navigate life's challenges with confidence, maintaining a sense of inner peace and well-being even in turbulent times.
Stoicism and Emotional Intelligence
Emotional intelligence, the ability to recognize, understand, and manage our own emotions and those of others, is a crucial skill in today's world. Stoicism offers valuable insights into developing emotional intelligence, emphasizing self-awareness, empathy, and effective communication.
Stoics believe that emotions are rooted in our perceptions and judgments. By examining and challenging these underlying beliefs, individuals can gain greater control over their emotional responses. This process of self-reflection and introspection enhances self-awareness, a key component of emotional intelligence.
Moreover, Stoicism encourages empathy and compassion, recognizing the interconnectedness of all human beings. By understanding and acknowledging the perspectives and emotions of others, Stoics can build stronger relationships and foster a sense of community and cooperation.
Effective communication is another important aspect of emotional intelligence that Stoicism supports. By practicing active listening and expressing thoughts and feelings clearly and respectfully, Stoics can navigate social interactions with confidence and poise.
By integrating Stoic principles into their lives, individuals can enhance their emotional intelligence, leading to improved personal and professional relationships, greater self-awareness, and a more fulfilling and balanced life.
Is Stoicism Relevant in Leadership?
Stoicism remains highly relevant in leadership, offering timeless principles that can guide leaders in making ethical decisions, managing stress, and inspiring others. The stoical definition aligns closely with modern leadership qualities, emphasizing integrity, resilience, and empathy.
Stoic leaders prioritize ethical decision-making, guided by their commitment to virtue and moral excellence. By focusing on what is right and just, Stoic leaders can earn the trust and respect of their teams, fostering a positive organizational culture and promoting long-term success.
Resilience is another key aspect of Stoic leadership. By maintaining composure and equanimity in the face of challenges, Stoic leaders can guide their teams through adversity with confidence and clarity. This ability to remain calm under pressure inspires others and creates a sense of stability within the organization.
Empathy and effective communication are also integral to Stoic leadership. By understanding and addressing the needs and concerns of their team members, Stoic leaders can build strong relationships and foster a sense of belonging and collaboration.
By embracing Stoic principles, leaders can navigate the complexities of the modern world with wisdom and grace, inspiring others to reach their full potential and creating a positive and productive work environment.
The Role of Stoicism in Educational Settings
Stoicism plays a significant role in educational settings, offering valuable insights and tools for promoting critical thinking, resilience, and ethical reasoning among students. By integrating Stoic principles into curricula, educators can prepare students to navigate the complexities of modern life with confidence and clarity.
One of the key benefits of incorporating Stoicism into education is its emphasis on self-reflection and personal growth. By encouraging students to examine their thoughts, beliefs, and actions, educators can help them develop a deeper understanding of themselves and their values, fostering a sense of self-awareness and purpose.
Stoicism also promotes resilience by teaching students to focus on what is within their control and accept what is not. This mindset encourages students to approach challenges with a positive attitude, viewing setbacks as opportunities for learning and growth.
Moreover, Stoicism's emphasis on ethical reasoning and virtuous living aligns with the goals of character education, helping students develop a strong moral compass and guiding them in making ethical decisions.
By incorporating Stoic principles into their teaching, educators can equip students with the skills and mindset needed to thrive in the modern world, fostering a generation of thoughtful, resilient, and ethical individuals.
How Can Stoicism Enhance Personal Development?
Stoicism offers a powerful framework for personal development, providing individuals with the tools and principles needed to cultivate self-awareness, resilience, and ethical behavior. By embracing the stoical definition, individuals can embark on a journey of self-improvement and personal growth.
One of the key aspects of Stoicism that enhances personal development is its emphasis on self-reflection and introspection. By regularly examining their thoughts, beliefs, and actions, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of themselves and their motivations, leading to greater self-awareness and personal growth.
Stoicism also promotes resilience by teaching individuals to focus on what is within their control and accept what is not. This mindset encourages individuals to approach challenges with a positive attitude, viewing setbacks as opportunities for learning and growth.
Furthermore, Stoicism emphasizes the importance of living in accordance with one's values and principles. By aligning their actions with their values, individuals can lead a more authentic and fulfilling life, fostering a sense of purpose and meaning.
Ultimately, the stoical definition provides a pathway for personal development, empowering individuals to navigate life's challenges with confidence and grace, leading to a more fulfilling and meaningful existence.
Practical Ways to Apply Stoicism in Daily Life
Applying Stoicism in daily life involves integrating its principles and practices into everyday actions and decisions. By embracing the stoical definition, individuals can cultivate a mindset that fosters resilience, self-control, and inner peace.
Here are some practical ways to apply Stoicism in daily life:
- Practice Mindfulness: Stay present and focused on the present moment, cultivating an attitude of acceptance and gratitude.
- Reflect on Your Values: Regularly examine your thoughts and actions to ensure they align with your values and principles.
- Focus on What You Can Control: Identify the aspects of your life that are within your control and direct your energy and efforts toward them.
- Challenge Negative Thoughts: Use cognitive reframing to change your perspective on challenging situations and reduce their emotional impact.
- Practice Gratitude: Cultivate an attitude of gratitude by acknowledging and appreciating the positive aspects of your life.
By incorporating these practices into your daily routine, you can enhance your resilience, self-awareness, and emotional intelligence, leading to a more fulfilling and balanced life.
Challenges in Embracing a Stoical Mindset
While embracing a stoical mindset offers numerous benefits, it also presents certain challenges that individuals may encounter on their journey toward personal growth and self-improvement.
One of the primary challenges is overcoming deeply ingrained thought patterns and beliefs that may conflict with Stoic principles. Individuals may struggle to let go of negative emotions and attachments, making it difficult to fully embrace the stoical definition of accepting what is beyond their control.
Another challenge is the societal pressure to conform to external standards of success and happiness, which can conflict with Stoic values of inner peace and virtue. Individuals may find it challenging to prioritize their own values and principles in a world that often emphasizes materialism and external validation.
Additionally, embracing a stoical mindset requires consistent practice and self-discipline, which can be challenging for those who are new to Stoicism or who have not yet developed the necessary habits and skills.
Despite these challenges, individuals can overcome these obstacles by seeking support from like-minded individuals, engaging in regular self-reflection, and gradually incorporating Stoic practices into their daily lives.
Famous Stoic Philosophers and Their Contributions
Throughout history, several notable philosophers have contributed to the development and dissemination of Stoic principles, each leaving a lasting impact on the philosophy and its application.
- Zeno of Citium: The founder of Stoicism, Zeno established the foundational principles of the philosophy and taught at the Stoa Poikile in Athens.
- Seneca: A Roman statesman and philosopher, Seneca's writings on ethics and personal development have inspired generations of Stoics.
- Epictetus: A former slave turned philosopher, Epictetus taught that true freedom comes from within and emphasized the importance of self-discipline and rationality.
- Marcus Aurelius: As a Roman Emperor, Marcus Aurelius applied Stoic principles to leadership and governance, and his Meditations remain a classic work of Stoic literature.
By studying the works and teachings of these influential philosophers, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of the stoical definition and its relevance in both historical and modern contexts.
Stoicism in Popular Culture
Stoicism has made its way into popular culture, influencing literature, film, and even modern self-help movements. Its timeless principles resonate with audiences seeking guidance and inspiration in navigating life's challenges.
In literature, Stoic themes are often explored through characters who exhibit resilience, self-control, and moral integrity. These qualities are celebrated in stories that emphasize the importance of virtuous living and personal growth.
In film, Stoic characters are often portrayed as wise mentors or leaders who embody the principles of Stoicism, guiding others through adversity with grace and wisdom.
Additionally, Stoicism has gained popularity in modern self-help and personal development circles, with many authors and speakers drawing on Stoic principles to offer practical advice for achieving personal and professional success.
By embracing the stoical definition and integrating Stoic principles into their lives, individuals can find inspiration and guidance in popular culture, enhancing their understanding of Stoicism and its relevance in today's world.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the stoical definition?
The stoical definition refers to a philosophy that emphasizes resilience, self-control, and acceptance of life's challenges, originating from ancient Stoicism.
2. How can Stoicism help with stress management?
Stoicism helps with stress management by encouraging individuals to focus on what is within their control, accept what is not, and practice mindfulness and cognitive reframing.
3. Can Stoicism be applied in modern workplaces?
Yes, Stoicism can be applied in modern workplaces by promoting ethical decision-making, resilience, empathy, and effective communication among leaders and team members.
4. Is Stoicism compatible with other philosophies or religions?
Stoicism is a philosophy that can complement other philosophies or religions, as it emphasizes universal principles such as virtue, reason, and ethical living.
5. How can I start practicing Stoicism in my daily life?
To start practicing Stoicism, focus on self-reflection, mindfulness, cognitive reframing, and aligning your actions with your values and principles.
6. Are there any famous Stoic quotes to inspire me?
Yes, some famous Stoic quotes include Marcus Aurelius's "The happiness of your life depends upon the quality of your thoughts" and Seneca's "Luck is what happens when preparation meets opportunity."
Conclusion
The stoical definition offers a timeless framework for navigating life's challenges with resilience, self-control, and inner peace. Rooted in ancient philosophy, Stoicism provides valuable insights into personal development, psychological resilience, and ethical living. By embracing Stoic principles, individuals can cultivate a mindset that empowers them to face adversity with grace and wisdom, leading to a more fulfilling and meaningful existence. Whether applied in personal life, leadership, or education, the stoical definition continues to inspire and guide those seeking to live virtuously and harmoniously in the modern world.
For further reading on Stoicism and its application in modern life, consider exploring resources such as the Wikipedia page on Stoicism.