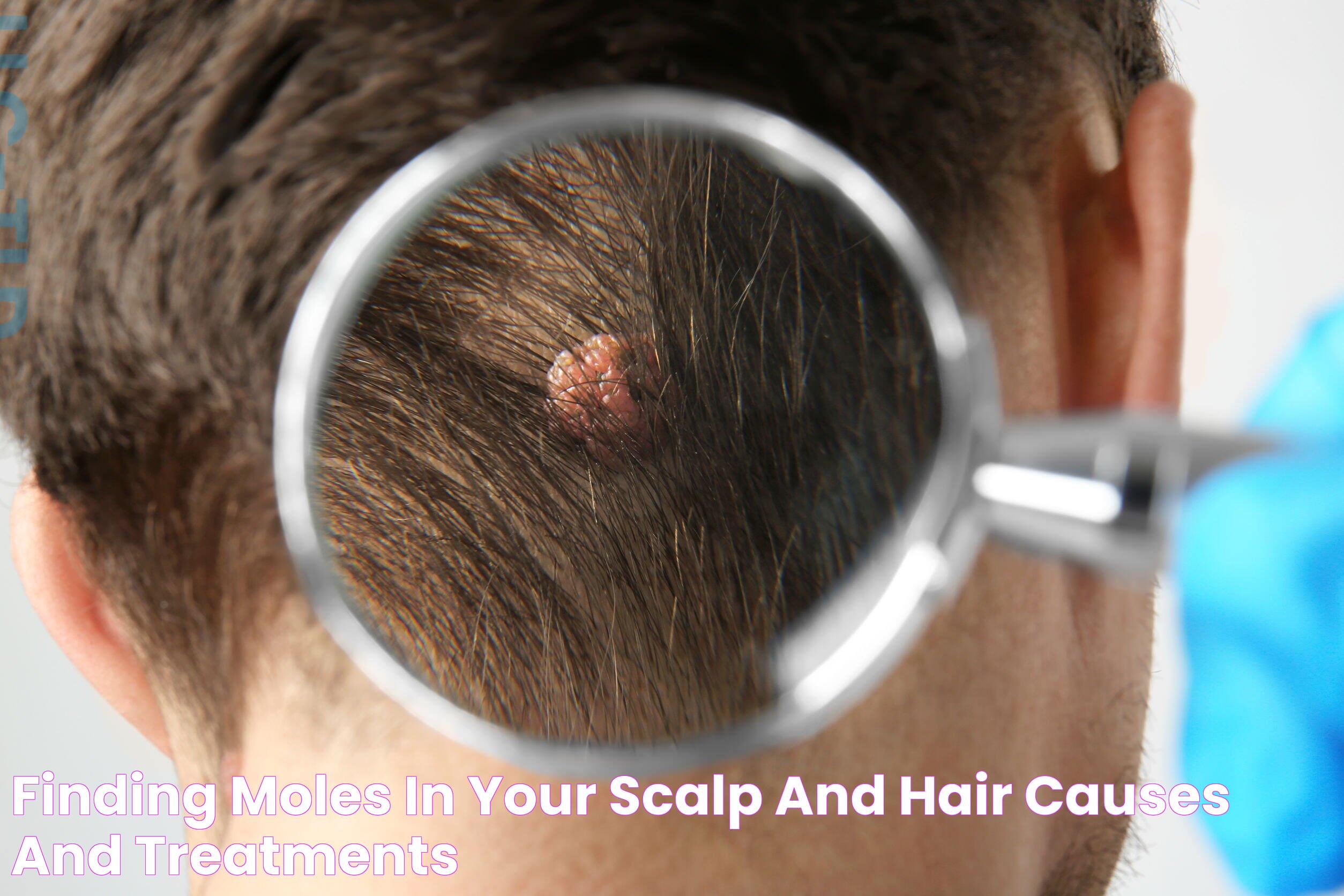
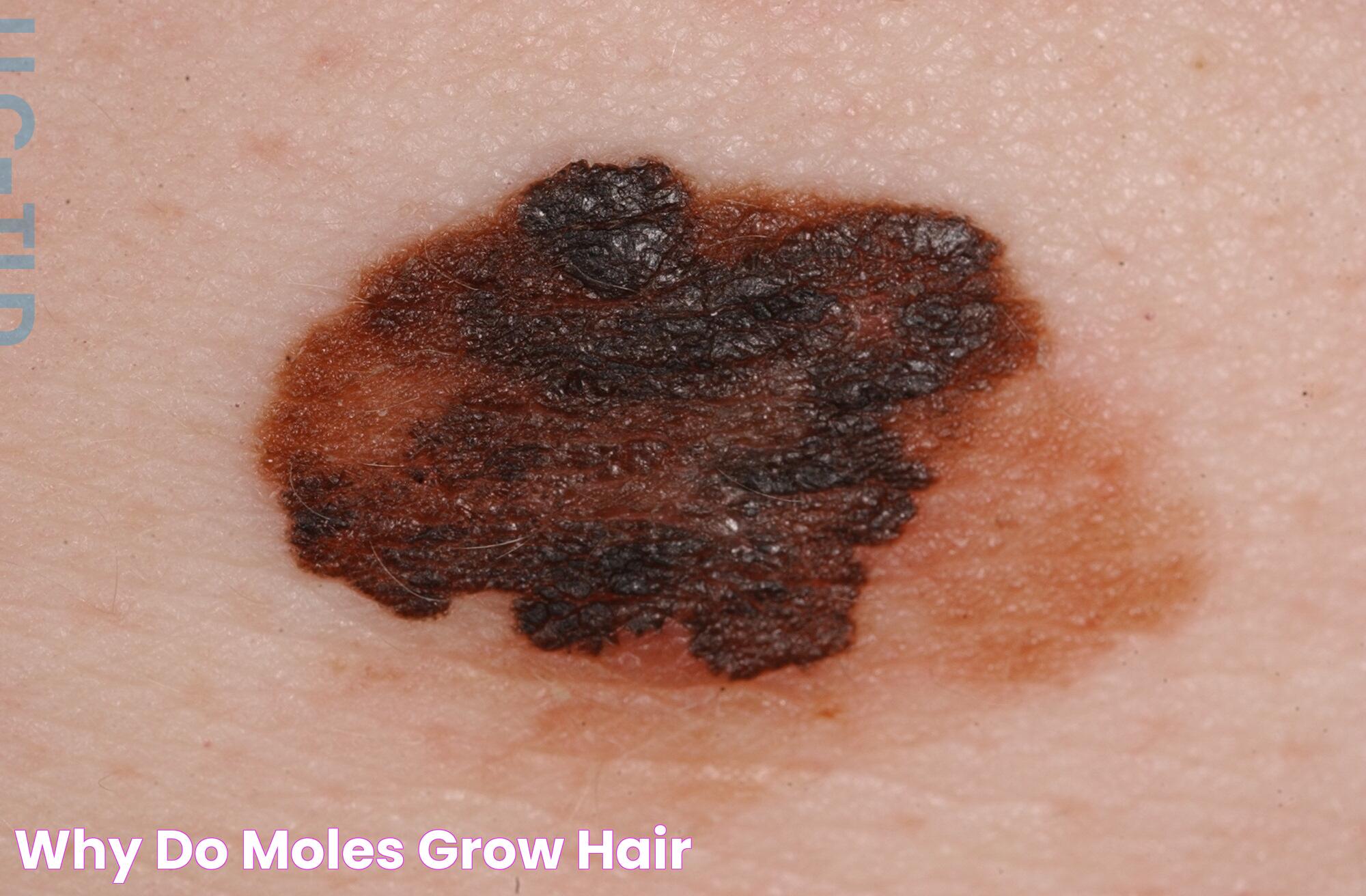
Have you ever noticed a hair sprouting from a mole and wondered why this happens? You're not alone. Many people are curious about this peculiar phenomenon, which is surprisingly common. While it might seem unusual, the presence of hair in moles is typically harmless. Understanding the reasons behind this occurrence can help alleviate concerns and provide insights into skin health.
Moles are growths on the skin formed by clusters of melanocytes, the cells responsible for skin pigmentation. These growths can appear anywhere on the body and vary in color, size, and texture. Some moles have hair growing from them, which may prompt curiosity or concern. However, the occurrence of hair in moles is a natural process and is generally not a cause for alarm.
The growth of hair in moles is linked to the same biological mechanisms that cause hair to grow elsewhere on the body. Hair follicles, located within the skin, can sometimes develop within moles, leading to the growth of hair. While the presence of hair in moles is usually benign, it's crucial to monitor any changes in moles, such as alterations in color, shape, or size, as these can be indicators of potential skin issues. In this article, we'll delve deeper into why hairs grow out of moles, providing a thorough understanding of this phenomenon.
Read also:Your Ultimate Guide To The True Meaning A Comprehensive Analysis
Table of Contents
- What Are Moles?
- How Do Moles Form?
- Why Do Hairs Grow Out of Moles?
- Are Hairy Moles Dangerous?
- How to Monitor Moles?
- When to See a Doctor?
- Can You Remove Hairs from Moles?
- Methods of Hair Removal on Moles
- Preventing Mole Formation
- Genetic Factors and Moles
- Lifestyle Impacts on Moles
- Skin Care and Mole Health
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
What Are Moles?
Moles, medically known as nevi, are common skin growths consisting of clusters of pigment-producing cells called melanocytes. These cells give moles their characteristic color, which can range from brown to black, pink, or even skin-toned. Moles can appear anywhere on the skin, either alone or in groups.
They are typically round or oval, and while their size can vary greatly, most moles are less than a quarter of an inch in diameter. Moles can develop throughout a person's life, with most appearing during childhood and adolescence. Although moles are generally benign, some individuals may opt for removal due to cosmetic concerns or if the moles are located in areas prone to irritation.
It's important to note that while most moles are harmless, changes in their appearance or new mole development in adulthood should be monitored for potential signs of skin cancer, such as melanoma. Regular skin checks and dermatologist visits can help ensure any concerning changes are addressed promptly.
How Do Moles Form?
Moles form when melanocytes grow in clusters or clumps, rather than being evenly distributed throughout the skin. This clustering can occur due to a combination of genetic factors and environmental influences, such as sun exposure. Ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or tanning beds can stimulate melanocytes, leading to increased mole formation.
Genetic predisposition also plays a significant role in mole development. Individuals with a family history of moles or skin cancer are more likely to develop moles themselves. Additionally, hormonal changes during puberty and pregnancy can trigger the development of new moles or changes in existing ones.
While most moles are acquired, some individuals are born with congenital moles. These moles can be larger and carry a slightly higher risk of developing into melanoma. However, regular monitoring and protective measures, such as using sunscreen and wearing protective clothing, can help mitigate these risks.
Read also:Visual Insights Into Fluorouracil Treatment Pictures And More
Why Do Hairs Grow Out of Moles?
Hairs growing out of moles is a common phenomenon due to the presence of hair follicles within or near the mole. Hair follicles are microscopic structures within the skin responsible for hair production. When these follicles are located within a mole, they can lead to hair growth.
The presence of hair in moles is typically benign and indicates that the mole is healthy, as cancerous moles often lack hair. Hair growth in moles occurs due to the same biological processes that enable hair growth on other parts of the body. The root of the hair follicle is embedded in the skin's dermal layer, where it receives nutrients and signals to grow.
While hairs growing out of moles are usually harmless, it's essential to monitor moles for any changes in their appearance or behavior. Changes such as rapid growth, irregular borders, or color variation can be signs of potential skin issues and should be evaluated by a dermatologist.
Are Hairy Moles Dangerous?
Hairy moles are generally not dangerous and are often a sign of a healthy mole. The presence of hair in a mole suggests that the mole's skin cells are functioning normally, allowing hair follicles to produce hair. However, it's crucial to remember that not all moles with hair are benign, and regular monitoring is necessary to ensure skin health.
While the presence of hair in a mole is not inherently dangerous, changes in the mole's characteristics should be taken seriously. Warning signs include:
- Asymmetry: One half of the mole does not match the other half.
- Border: The edges of the mole are irregular, ragged, or blurred.
- Color: The mole has uneven colors, including shades of black, brown, or tan.
- Diameter: The mole is larger than the size of a pencil eraser (about 6mm).
- Evolving: The mole changes in size, shape, or color over time.
If any of these changes are observed, it's important to consult a dermatologist to rule out the possibility of skin cancer. Regular self-examinations and professional skin checks can help detect any concerning changes early.
How to Monitor Moles?
Monitoring moles is a crucial step in maintaining skin health and preventing potential skin issues. Regular self-examinations can help identify any changes in moles that may require further evaluation. Here are some tips for effectively monitoring moles:
1. Perform Monthly Self-Examinations: Conduct a thorough skin check once a month, examining all areas of the body, including hard-to-see places like the scalp, back, and soles of the feet.
2. Use the ABCDE Rule: Asymmetry, Border, Color, Diameter, and Evolving are the key characteristics to assess when examining moles. Any changes in these areas should be noted.
3. Take Photographs: Documenting moles with photographs can help track any changes over time. Ensure the images are clear and include a ruler or coin for scale.
4. Keep a Record: Maintain a record of the number, size, and location of moles. Update this record regularly to note any new moles or changes in existing ones.
5. Know Your Risk Factors: Understanding personal risk factors, such as family history or excessive sun exposure, can help prioritize monitoring efforts.
6. Consult a Dermatologist: Schedule regular dermatologist visits, especially if there are many moles or if there is a family history of skin cancer. A dermatologist can provide professional evaluations and guidance.
By following these steps, individuals can effectively monitor their moles and ensure any concerning changes are addressed promptly.
When to See a Doctor?
Knowing when to seek medical attention for moles is essential for maintaining skin health and detecting potential issues early. While most moles are benign, certain changes or characteristics may warrant a consultation with a dermatologist. Here are some indications that it's time to see a doctor:
- Rapid Changes: Any sudden changes in the size, shape, or color of a mole should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
- Bleeding or Oozing: Moles that bleed, ooze, or develop a crust should be examined by a dermatologist.
- Itching or Pain: Persistent itching, tenderness, or pain in a mole is a reason to seek medical advice.
- New Moles in Adulthood: The appearance of new moles after the age of 30 should be assessed by a healthcare provider.
- Family History: Individuals with a family history of skin cancer or atypical moles should have regular dermatological check-ups.
In addition to these signs, individuals who have a large number of moles or congenital moles may require more frequent monitoring. Consulting a dermatologist can provide peace of mind and ensure any potential issues are addressed promptly.
Can You Remove Hairs from Moles?
Removing hairs from moles is generally safe, but it should be done with caution to avoid irritation or infection. The most common methods for hair removal from moles include:
1. Trimming: Using small scissors to carefully trim the hair close to the skin's surface is a safe and effective method.
2. Tweezing: Plucking the hair with clean tweezers is another option, though it may cause temporary discomfort.
3. Shaving: Gently shaving the hair with a razor can be done, but care should be taken to avoid nicking the mole.
4. Laser Hair Removal: This method involves using a laser to target hair follicles, reducing hair growth over time. It should be performed by a trained professional to ensure safety.
It's important to note that while hair removal from moles is generally safe, any changes in the mole's appearance or symptoms of irritation should be monitored. Consulting a dermatologist before attempting hair removal can provide guidance on the best approach based on individual circumstances.
Methods of Hair Removal on Moles
There are several methods for removing hair from moles, each with its own advantages and considerations. Here, we explore the most common techniques and their suitability for different individuals:
Trimming
Trimming is a simple and safe method for removing hair from moles. Using clean, sharp scissors, hair can be cut close to the skin's surface without affecting the mole itself. This method minimizes the risk of irritation and is suitable for individuals who prefer a non-invasive approach.
Tweezing
Tweezing involves using clean tweezers to pluck hair from the mole. While this method can be effective, it may cause temporary discomfort and should be done with care to avoid irritating the skin. It's important to clean the tweezers before use to prevent infection.
Shaving
Shaving is another option for removing hair from moles. Using a razor, hair can be shaved close to the skin's surface. Care should be taken to avoid cutting the mole, and it's advisable to use a sharp, clean razor to minimize irritation.
Laser Hair Removal
Laser hair removal is a more permanent solution for reducing hair growth from moles. This method uses a laser to target and damage hair follicles, inhibiting future growth. It should be performed by a trained professional to ensure safety and effectiveness. Laser hair removal is suitable for individuals seeking a long-term solution, but it may require multiple sessions and can be more costly than other methods.
Before choosing a hair removal method, individuals should consider their skin type, mole characteristics, and personal preferences. Consulting a dermatologist can provide personalized recommendations and ensure safe hair removal practices.
Preventing Mole Formation
While some factors contributing to mole formation, such as genetics, cannot be controlled, there are steps individuals can take to reduce the likelihood of developing new moles. Preventative measures primarily focus on minimizing sun exposure and protecting the skin from UV radiation.
1. Use Sunscreen: Applying broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30 can protect the skin from harmful UV rays. Sunscreen should be applied generously and reapplied every two hours, especially during outdoor activities.
2. Wear Protective Clothing: Clothing such as long sleeves, wide-brimmed hats, and sunglasses can provide additional protection against the sun's rays. Ultraviolet Protection Factor (UPF) clothing offers enhanced protection.
3. Seek Shade: Limiting time spent in direct sunlight, particularly during peak hours (10 a.m. to 4 p.m.), can reduce UV exposure and help prevent mole formation.
4. Avoid Tanning Beds: Artificial tanning devices emit UV radiation, which can increase the risk of skin damage and mole formation. Opting for sunless tanning products can provide a safer alternative.
5. Stay Informed: Understanding individual risk factors, such as skin type and family history, can help individuals take proactive measures to protect their skin.
By adopting these preventative strategies, individuals can reduce their risk of developing new moles and promote overall skin health. Regular skin checks and dermatologist visits can complement these efforts, ensuring any changes in moles are addressed promptly.
Genetic Factors and Moles
Genetics play a significant role in the development of moles, influencing both their number and characteristics. Individuals with a family history of moles or skin cancer are more likely to develop moles themselves. Understanding the genetic factors involved can provide insights into mole development and potential risks.
1. Family History: A strong family history of moles or melanoma can increase an individual's likelihood of developing moles. Genetic predisposition can affect both the number and size of moles.
2. Skin Type: Certain skin types, particularly fair skin with a tendency to burn rather than tan, are more susceptible to mole development. Individuals with lighter skin tones may have a higher genetic predisposition to moles.
3. Congenital Moles: Some individuals are born with congenital moles, which can be larger and carry a slightly higher risk of developing into melanoma. These moles are present from birth and are influenced by genetic factors.
4. Gene Mutations: Specific gene mutations, such as those in the CDKN2A gene, can increase the risk of melanoma and atypical moles. Genetic testing may be considered for individuals with a strong family history of skin cancer.
While genetic factors are beyond an individual's control, understanding one's genetic predisposition can inform personalized skin care strategies and monitoring practices. Regular skin checks and dermatologist consultations can help manage genetic risks and ensure any changes in moles are addressed promptly.
Lifestyle Impacts on Moles
Lifestyle choices can significantly influence the development and management of moles. While genetics and environmental factors play a role, certain lifestyle habits can either promote or reduce the risk of mole formation. Here, we explore how lifestyle choices impact moles and provide tips for maintaining skin health.
Sun Exposure
Excessive sun exposure is a leading factor in mole formation and skin damage. UV radiation from the sun can stimulate melanocytes, leading to increased mole development. To minimize this risk, individuals should practice sun safety measures, including using sunscreen, wearing protective clothing, and seeking shade.
Diet and Nutrition
A balanced diet rich in antioxidants can support skin health and protect against UV damage. Foods high in vitamins C and E, beta-carotene, and omega-3 fatty acids can provide protective benefits. Staying hydrated and maintaining a healthy diet can contribute to overall skin resilience.
Skin Care Routine
Establishing a consistent skin care routine can help maintain healthy skin and minimize irritation. Gentle cleansing, moisturizing, and exfoliation can support skin health. It's important to choose skin care products suitable for individual skin types and avoid harsh chemicals that may irritate the skin.
Smoking and Alcohol Consumption
Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can negatively impact skin health, contributing to premature aging and potential mole formation. Reducing or eliminating these habits can improve skin health and reduce the risk of skin issues.
By making informed lifestyle choices and adopting healthy habits, individuals can support their skin health and reduce the risk of mole formation. Regular skin checks and dermatologist consultations can complement these efforts, ensuring any changes in moles are addressed promptly.
Skin Care and Mole Health
Maintaining a proper skin care routine is essential for promoting mole health and overall skin wellness. A consistent routine can help protect the skin from environmental damage, reduce irritation, and support healthy mole management. Here are some key components of an effective skin care routine:
Gentle Cleansing
Cleansing the skin with a mild, non-irritating cleanser helps remove dirt, oil, and impurities without stripping the skin of its natural moisture. It's important to choose a cleanser suitable for individual skin types and avoid harsh ingredients that may cause irritation.
Moisturizing
Moisturizing is essential for maintaining skin hydration and barrier function. Using a moisturizer appropriate for individual skin types can help lock in moisture and prevent dryness. Moisturizers with added antioxidants or UV protection can provide additional benefits.
Sun Protection
Protecting the skin from UV radiation is crucial for mole health and overall skin wellness. Applying a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30 daily can help prevent sun damage and reduce the risk of mole formation. Sunscreen should be reapplied every two hours, especially during outdoor activities.
Regular Exfoliation
Exfoliating the skin helps remove dead skin cells and promote cell turnover, contributing to a smoother, more radiant complexion. It's important to choose gentle exfoliants and avoid over-exfoliation, which can cause irritation.
By incorporating these skin care practices into daily routines, individuals can support their skin health and promote healthy mole management. Regular self-examinations and dermatologist consultations can complement these efforts, ensuring any changes in moles are addressed promptly.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions about hairs growing out of moles and their answers:
1. Why do hairs grow out of moles?
Hairs grow out of moles because hair follicles can be present within or near the mole, leading to hair growth. This is a natural process and usually indicates a healthy mole.
2. Are hairy moles more likely to be cancerous?
No, hairy moles are not more likely to be cancerous. In fact, the presence of hair often suggests that the mole is benign, as cancerous moles typically lack hair.
3. Can I remove hair from a mole safely?
Yes, you can safely remove hair from a mole using methods like trimming, tweezing, or shaving. However, it's important to be cautious and avoid irritating the mole. Consulting a dermatologist can provide guidance on the best method.
4. What should I do if a mole changes suddenly?
If a mole changes in size, shape, color, or develops symptoms like itching or bleeding, it's important to consult a dermatologist. These changes could indicate potential skin issues that require evaluation.
5. How can I prevent new moles from forming?
While genetics play a role in mole formation, minimizing sun exposure and practicing sun safety measures can reduce the risk of developing new moles. Using sunscreen, wearing protective clothing, and avoiding tanning beds are effective strategies.
6. Do moles with hair require special care?
Moles with hair do not require special care beyond regular monitoring for any changes. Maintaining a consistent skin care routine and protecting the skin from UV exposure can support mole health.
Conclusion
Understanding why hairs grow out of moles and their implications can provide valuable insights into skin health. While the presence of hair in moles is typically benign and indicates a healthy mole, regular monitoring and preventive measures are essential for maintaining skin wellness. By adopting a proactive approach to skin care, individuals can reduce the risk of potential skin issues and ensure any concerning changes are addressed promptly.
Whether it's practicing sun safety, maintaining a balanced diet, or establishing a consistent skin care routine, these efforts can contribute to healthy skin and mole management. Consulting a dermatologist for regular check-ups and professional evaluations can provide additional reassurance and guidance.
Ultimately, being informed about the reasons behind hair growth in moles and taking proactive steps to care for your skin can promote overall health and peace of mind.