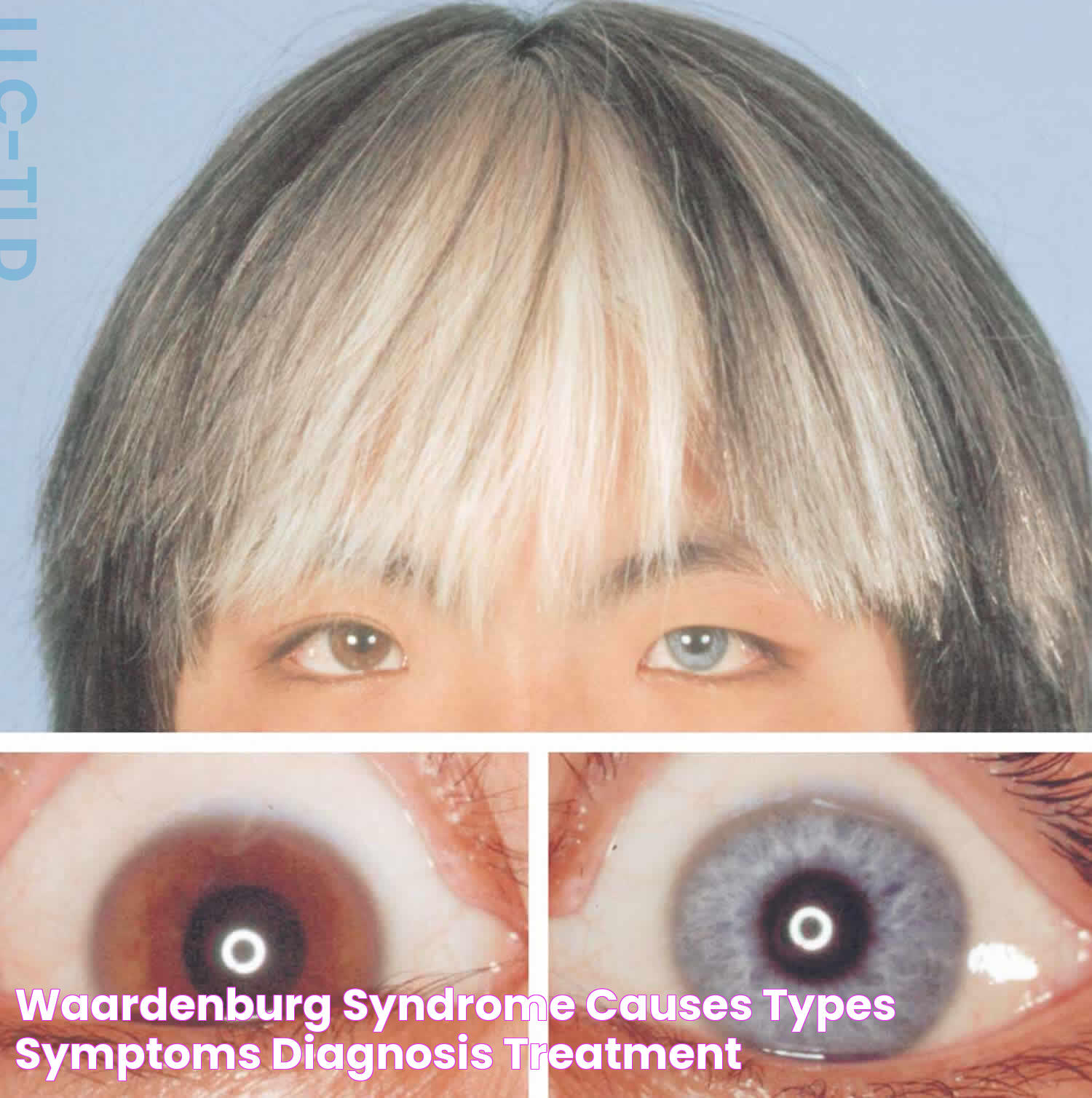
Waardenburg syndrome eyes are a fascinating aspect of a rare genetic condition that can affect the color and structure of a person's eyes. This syndrome is named after the Dutch ophthalmologist Petrus Johannes Waardenburg, who first described the condition in 1951. It is characterized by varying degrees of hearing loss, changes in pigment of the skin, hair, and eyes, as well as possible structural abnormalities. The intriguing ocular manifestations often make Waardenburg syndrome eyes a subject of interest among medical professionals and genetic researchers.
Individuals with Waardenburg syndrome may exhibit unusual eye colors, such as brilliant blue eyes or differences in coloration between the two eyes, a condition known as heterochromia. This can result in one eye being blue while the other is brown or green. The changes in eye color are due to a lack of melanin, the pigment responsible for coloring the iris, as well as the skin and hair. Such unique eye traits can help in diagnosing the syndrome and are often accompanied by other symptoms, forming a distinctive phenotype that aids geneticists and clinicians in identifying the condition.
Waardenburg syndrome eyes are not only a hallmark of the condition but also play a crucial role in understanding the genetic mechanisms behind the syndrome. By studying the genetic mutations linked to the development of these characteristic eye features, researchers aim to unlock further insights into the pathways that control pigmentation and auditory development. These insights are pivotal in developing potential therapeutic interventions for not only Waardenburg syndrome but also other related genetic conditions. As such, the study of Waardenburg syndrome eyes remains a vital component of ongoing genetic research and clinical practice.
Read also:Paulas Choice Vitamin C Your Ultimate Skincare Solution
Table of Contents
- What is Waardenburg Syndrome?
- Characteristics of Waardenburg Syndrome
- How Does Waardenburg Syndrome Affect the Eyes?
- The Genetic Basis of Waardenburg Syndrome
- Types of Waardenburg Syndrome
- Diagnostic Approaches for Waardenburg Syndrome
- Treatment and Management of Waardenburg Syndrome
- Living with Waardenburg Syndrome
- The Role of Genetic Counseling in Waardenburg Syndrome
- Research and Future Directions
- Can Waardenburg Syndrome Be Prevented?
- Who is at Risk for Waardenburg Syndrome?
- How Do Waardenburg Syndrome Eyes Affect Vision?
- Support and Resources for Waardenburg Syndrome
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
What is Waardenburg Syndrome?
Waardenburg syndrome is a genetic disorder known for its diverse array of symptoms, primarily affecting pigmentation and hearing. This autosomal dominant condition can present with varying degrees of severity, and its hallmark features are typically noticeable at birth. The syndrome is divided into four main types, each distinguished by specific genetic mutations and clinical manifestations. While all types share common features such as hearing loss and pigmentary abnormalities, each type also presents unique characteristics that assist in diagnosis and management.
Characteristics of Waardenburg Syndrome
Waardenburg syndrome is characterized by a combination of features, including hearing loss of varying degrees, changes in pigmentation of the hair, skin, and eyes, and sometimes structural abnormalities. The most recognizable traits include:
- Distinctive eye color changes, such as heterochromia (different colored eyes) or bright blue eyes
- Patches of white hair, often seen as a forelock
- Wide-set eyes, a condition known as dystopia canthorum
- Possible congenital hearing loss
- Skin pigmentation changes, including light patches
These features can vary significantly among individuals with the syndrome, even within the same family. This variability is attributed to the different gene mutations that can cause Waardenburg syndrome.
How Does Waardenburg Syndrome Affect the Eyes?
Waardenburg syndrome eyes are a defining feature of this genetic condition. The syndrome affects the eyes in several ways, primarily through changes in pigmentation. These changes can lead to heterochromia, where the eyes have different colors, or to very pale blue eyes due to reduced melanin. Additionally, the syndrome can cause dystopia canthorum, which is the lateral displacement of the inner canthi of the eyes, giving the appearance of wide-set eyes.
The Genetic Basis of Waardenburg Syndrome
Waardenburg syndrome is a genetic condition resulting from mutations in several genes, including PAX3, MITF, EDN3, and SOX10. These genes play crucial roles in the development of pigment cells and auditory pathways. The mutations lead to the characteristic features of the syndrome, such as pigmentation abnormalities and hearing loss. Understanding these genetic underpinnings is vital for diagnosing the syndrome and exploring potential treatments.
Types of Waardenburg Syndrome
There are four recognized types of Waardenburg syndrome, each associated with specific genetic mutations and clinical features:
Read also:Exquisite Pink And White Acrylic Nails A Guide To Style And Care
- Type 1: Characterized by dystopia canthorum, hearing loss, and pigmentary disturbances. It is often linked to mutations in the PAX3 gene.
- Type 2: Similar to Type 1 but without dystopia canthorum. It is associated with mutations in the MITF gene.
- Type 3 (Klein-Waardenburg syndrome): Includes limb abnormalities in addition to the features of Type 1. It is also linked to PAX3 mutations.
- Type 4 (Waardenburg-Shah syndrome): Combines the features of Waardenburg syndrome with Hirschsprung disease, a condition affecting the intestines. This type is associated with mutations in the EDN3, EDNRB, and SOX10 genes.
Diagnostic Approaches for Waardenburg Syndrome
Diagnosing Waardenburg syndrome involves a combination of clinical evaluation and genetic testing. Clinicians assess the characteristic features, such as eye color variations, hearing loss, and other physical traits. Genetic testing is used to confirm the diagnosis by identifying mutations in genes associated with the syndrome. Early diagnosis is crucial for managing the condition, especially in addressing hearing loss to improve communication skills.
Treatment and Management of Waardenburg Syndrome
While there is no cure for Waardenburg syndrome, treatment focuses on managing symptoms and improving quality of life. This may include:
- Hearing aids or cochlear implants for hearing loss
- Speech therapy to support communication development
- Regular eye examinations to monitor eye health
- Genetic counseling for families to understand inheritance patterns and risks
Management plans are tailored to the individual's specific needs and symptoms, ensuring comprehensive care.
Living with Waardenburg Syndrome
Individuals with Waardenburg syndrome can lead fulfilling lives with appropriate support and management. Early intervention for hearing loss and speech therapy can significantly enhance communication abilities. Additionally, support from genetic counselors and healthcare providers can help families navigate the challenges associated with the syndrome, promoting a positive outlook for those affected.
The Role of Genetic Counseling in Waardenburg Syndrome
Genetic counseling is an essential component of care for individuals with Waardenburg syndrome and their families. Counselors provide information about the genetic aspects of the condition, inheritance patterns, and potential risks for future children. This guidance helps families make informed decisions about family planning and management of the disorder.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research into Waardenburg syndrome aims to deepen the understanding of its genetic basis and develop innovative treatments. Studies focus on exploring the molecular mechanisms underlying the syndrome's features, which may pave the way for targeted therapies. Additionally, advancements in gene editing technologies hold promise for correcting genetic mutations and potentially preventing the syndrome in the future.
Can Waardenburg Syndrome Be Prevented?
Currently, there is no way to prevent Waardenburg syndrome, as it is a genetic condition inherited from parents. However, genetic counseling can assist in assessing the risk of passing the syndrome to offspring and provide guidance on family planning options. Advances in genetic research may offer potential preventive strategies in the future, but these are still in the early stages of development.
Who is at Risk for Waardenburg Syndrome?
Waardenburg syndrome is inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern, meaning that an affected individual has a 50% chance of passing the condition to their children. The syndrome affects both males and females equally, and there is no known ethnic or geographical predisposition. Families with a history of Waardenburg syndrome or related genetic conditions may have a higher risk of having children with the syndrome.
How Do Waardenburg Syndrome Eyes Affect Vision?
In most cases, Waardenburg syndrome eyes do not directly impact vision. The primary ocular manifestations are related to changes in pigmentation and the structural positioning of the eyes, such as heterochromia and dystopia canthorum. However, regular eye examinations are recommended to monitor eye health and address any potential vision-related issues that may arise over time.
Support and Resources for Waardenburg Syndrome
Numerous support groups and resources are available for individuals and families affected by Waardenburg syndrome. These organizations offer information, advocacy, and community support to help navigate the challenges of living with the condition. Connecting with others who have similar experiences can provide valuable emotional support and practical advice.
Frequently Asked Questions
What causes Waardenburg syndrome?
Waardenburg syndrome is caused by mutations in specific genes involved in pigment development and auditory pathways, such as PAX3, MITF, EDN3, and SOX10.
Can Waardenburg syndrome be cured?
There is currently no cure for Waardenburg syndrome, but symptoms can be managed with appropriate interventions, such as hearing aids and speech therapy.
Is Waardenburg syndrome inherited?
Yes, Waardenburg syndrome is inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern, meaning a parent with the syndrome has a 50% chance of passing it on to their children.
Are there different types of Waardenburg syndrome?
Yes, there are four main types of Waardenburg syndrome, each with distinct genetic mutations and clinical features.
How is Waardenburg syndrome diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves clinical evaluation of symptoms and genetic testing to identify mutations in related genes.
What is the prognosis for individuals with Waardenburg syndrome?
With proper management, individuals with Waardenburg syndrome can lead healthy and fulfilling lives, although they may require ongoing support for hearing and communication challenges.
Conclusion
Waardenburg syndrome eyes are a significant aspect of a multifaceted genetic disorder that affects pigmentation and auditory functions. Understanding the genetic basis and clinical manifestations of the syndrome is crucial for diagnosis and management. While there is no cure, early intervention and tailored management plans can greatly enhance the quality of life for affected individuals. Ongoing research continues to explore new avenues for treatment and prevention, offering hope for future advancements in the care of those with Waardenburg syndrome.