Lunar and solar eclipses are some of the most awe-inspiring celestial events visible from Earth. Both involve the alignment of the Earth, the Moon, and the Sun, yet they manifest in distinct ways. While a lunar eclipse occurs when the Earth passes between the Sun and the Moon, casting a shadow on the Moon, a solar eclipse happens when the Moon moves between the Earth and the Sun, obscuring the Sun's light. These phenomena have captivated humans for centuries, inspiring wonder and curiosity about the cosmos.
The differences between lunar and solar eclipses go beyond their visual spectacle, extending to their frequency, visibility, and cultural significance. Lunar eclipses are visible from anywhere on the night side of the Earth and occur approximately every six months. In contrast, solar eclipses are visible only within a narrow path on the Earth's surface and happen more frequently, with about two to five occurring each year. Both types of eclipses have played significant roles in shaping human understanding of the universe, influencing art, religion, and science.
In this article, we will delve into the intricate details of what distinguishes lunar eclipses from solar eclipses, examining their mechanisms, types, and observable features. We will also explore the historical and cultural contexts in which these celestial events have been perceived, offering a comprehensive guide to understanding and appreciating these natural wonders. By the end of this article, you will have a clearer grasp of the unique characteristics of each eclipse type and their fascinating impacts on our world.
Read also:Gain More Melanin When Do You Need More Melinana
Table of Contents
- Mechanisms of Lunar and Solar Eclipses
- What Causes a Lunar Eclipse?
- What Causes a Solar Eclipse?
- Types of Lunar Eclipses
- Types of Solar Eclipses
- How Do Lunar Eclipses Occur?
- How Do Solar Eclipses Occur?
- Visibility of Lunar and Solar Eclipses
- Cultural Significance of Eclipses
- Historical Impact of Eclipses
- Safety Measures During Solar Eclipses
- Observing Lunar Eclipses
- Frequency of Lunar and Solar Eclipses
- How Do Eclipses Affect the Environment?
- FAQs About Lunar and Solar Eclipses
Mechanisms of Lunar and Solar Eclipses
Understanding the mechanisms behind lunar and solar eclipses requires a grasp of celestial mechanics and the orbital dynamics of the Earth-Moon-Sun system. Eclipses occur due to the alignment of these three celestial bodies, creating unique shadow patterns on Earth or the Moon.
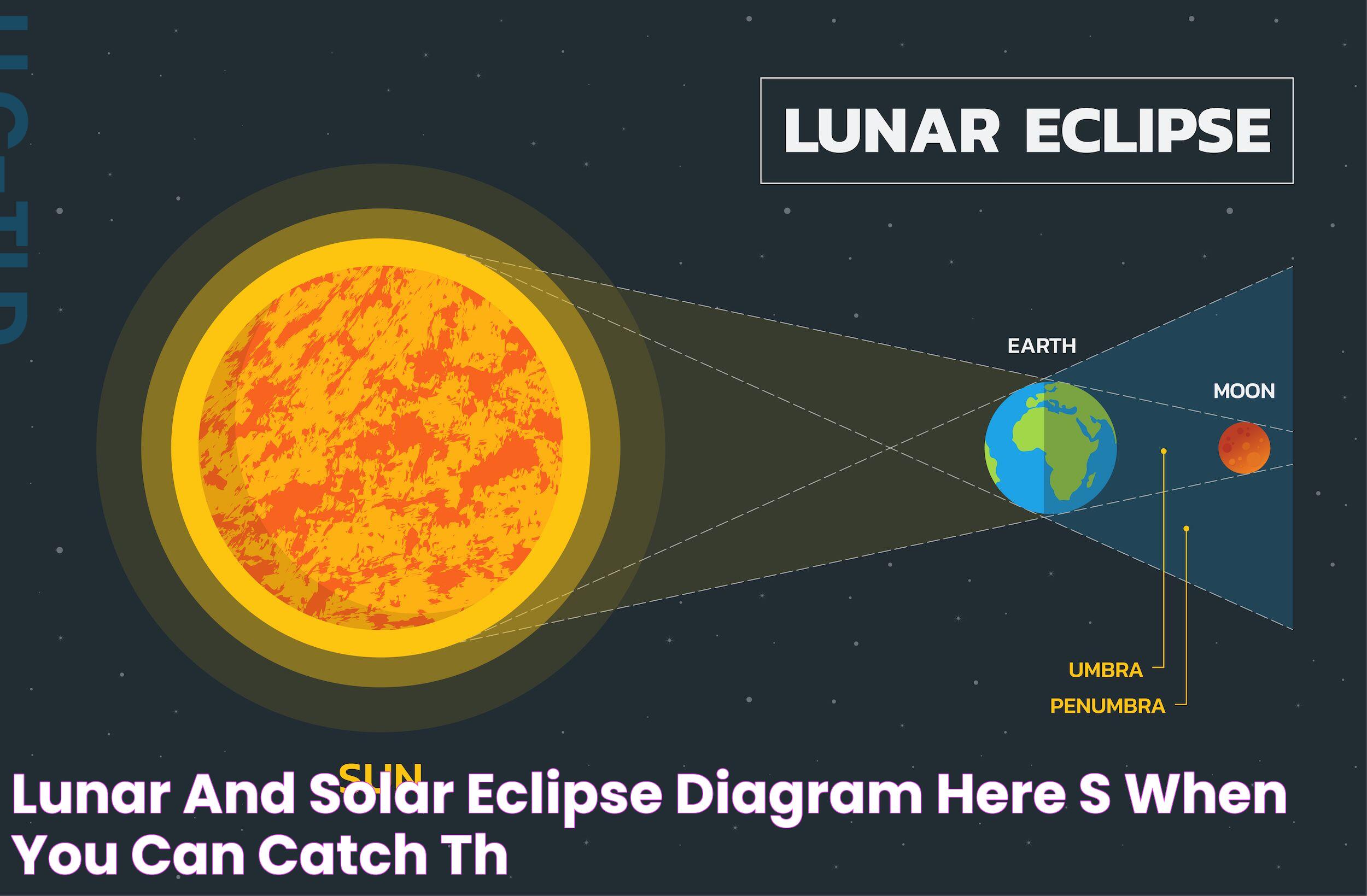
Both lunar and solar eclipses depend on the relative positions of the Earth, Moon, and Sun. During a lunar eclipse, the Earth is positioned between the Sun and the Moon, causing the Earth's shadow to fall on the Moon. In contrast, a solar eclipse occurs when the Moon is situated between the Earth and the Sun, blocking the Sun's light partially or entirely.
The mechanics of these eclipses are governed by the orbital planes of the Earth and the Moon. The plane of the Moon's orbit around the Earth is inclined about 5 degrees to the Earth's orbit around the Sun. This inclination means that eclipses do not occur every month but only when the Moon's orbit intersects the ecliptic plane at points called nodes.
What Causes a Lunar Eclipse?
A lunar eclipse is caused by the Earth's shadow falling on the Moon, an event that can only occur during a full moon when the Sun, Earth, and Moon are closely aligned in a straight line or syzygy. The Earth's shadow consists of two parts: the penumbra, where the shadow is partial, and the umbra, where the shadow is total.
There are three types of lunar eclipses, each determined by the extent to which the Moon enters the Earth's shadow:
- Penumbral Lunar Eclipse: The Moon passes through the Earth's penumbral shadow, causing a subtle shading on the Moon's surface.
- Partial Lunar Eclipse: A portion of the Moon enters the Earth's umbral shadow, resulting in a partial darkening of the Moon.
- Total Lunar Eclipse: The entire Moon enters the Earth's umbral shadow, often giving it a reddish hue due to Rayleigh scattering, commonly referred to as a "blood moon."
The duration and visibility of a lunar eclipse depend on the Moon's path through the Earth's shadow. Total lunar eclipses are visible from anywhere on the night side of the Earth, making them a more common sight for observers compared to solar eclipses.
Read also:Exploring The Intricacies Of Pleasure Playing With My Clit
What Causes a Solar Eclipse?
A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between the Earth and the Sun, temporarily obscuring the Sun's light. This alignment can only happen during a new moon when the Sun and Moon are in conjunction as seen from Earth.
There are three main types of solar eclipses, each defined by the extent of the Sun's coverage by the Moon:
- Total Solar Eclipse: The Moon completely covers the Sun, as seen from a narrow path on Earth. Outside this path, observers see a partial eclipse.
- Partial Solar Eclipse: The Moon only partially covers the Sun, visible from a wide area outside the path of totality.
- Annular Solar Eclipse: The Moon covers the center of the Sun, leaving a ring-like appearance known as the "ring of fire" due to the Sun's outer edges remaining visible.
The path of totality for a solar eclipse is a narrow corridor on the Earth's surface, typically about 100 miles wide. Observers within this path can witness the dramatic sight of a total eclipse, while those outside the path see a partial eclipse. Solar eclipses are less frequent than lunar eclipses but offer a unique and striking visual experience.
Types of Lunar Eclipses
Lunar eclipses are classified into three main types based on the Moon's interaction with the Earth's shadow. Each type offers a different level of visibility and visual spectacle, providing unique experiences for skywatchers.
Penumbral Lunar Eclipse
A penumbral lunar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes through the Earth's penumbral shadow. This type of eclipse is subtle and often hard to notice without precise instruments. Observers may see a slight shading on the Moon's surface, but the event lacks the dramatic visual impact of other eclipse types.
Partial Lunar Eclipse
In a partial lunar eclipse, a portion of the Moon enters the Earth's umbral shadow, leading to a noticeable darkening of the Moon. This type of eclipse is more visually striking than a penumbral eclipse and is easily visible to the naked eye. The degree of obscuration varies depending on the Moon's path through the umbra.
Total Lunar Eclipse
A total lunar eclipse occurs when the entire Moon passes through the Earth's umbral shadow. During this event, the Moon often takes on a reddish color due to the scattering of sunlight through the Earth's atmosphere, a phenomenon known as Rayleigh scattering. This captivating transformation earns the name "blood moon" and provides a memorable viewing experience.
Types of Solar Eclipses
Solar eclipses are categorized into three primary types: total, partial, and annular. Each type varies in terms of the coverage of the Sun by the Moon and the visual experience it offers to observers.
Total Solar Eclipse
A total solar eclipse is a rare and spectacular event where the Moon completely covers the Sun, resulting in a brief period of darkness during the day. The path of totality, where this total coverage is visible, is a narrow strip on the Earth's surface. Observers in this path can witness the Sun's corona, a stunning halo of plasma that becomes visible when the Sun's bright light is blocked.
Partial Solar Eclipse
During a partial solar eclipse, the Moon partially obscures the Sun. This type of eclipse is more common and can be seen over a larger area than a total eclipse. Observers see the Sun as a crescent shape, with varying degrees of coverage depending on their location relative to the path of totality.
Annular Solar Eclipse
An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon covers the center of the Sun, leaving a ring-like appearance known as the "ring of fire." This phenomenon occurs because the Moon is at a point in its orbit where it is farther from Earth, making it appear smaller in the sky. As a result, it does not completely cover the Sun, even during the peak of the eclipse.
How Do Lunar Eclipses Occur?
Lunar eclipses occur when the Earth passes directly between the Sun and the Moon, casting a shadow on the Moon. This alignment can only happen during a full moon when the Sun, Earth, and Moon are in syzygy.
The process of a lunar eclipse begins with the Moon entering the Earth's penumbra, where the shadow is partial. As the Moon continues its orbit, it may enter the umbral shadow, leading to a partial or total eclipse. The duration of the eclipse depends on the Moon's path through the Earth's shadow.
Lunar eclipses are visible from anywhere on the night side of the Earth, making them accessible to a larger audience than solar eclipses. The reddish hue seen during a total lunar eclipse is due to the filtering and bending of sunlight through the Earth's atmosphere, which scatters shorter wavelengths and allows longer wavelengths, such as red, to illuminate the Moon.
How Do Solar Eclipses Occur?
Solar eclipses occur when the Moon moves between the Earth and the Sun, temporarily blocking the Sun's light. This celestial event can only take place during a new moon when the Sun and Moon are in conjunction as viewed from Earth.
The process of a solar eclipse begins with the Moon's shadow touching the Earth's surface. The shadow consists of two parts: the penumbra, where the shadow is partial, and the umbra, where the shadow is total. Observers within the umbra experience a total solar eclipse, while those in the penumbra see a partial eclipse.
The path of totality, where a total solar eclipse is visible, is a narrow corridor on the Earth's surface. The duration of totality can last from a few seconds to several minutes, depending on the alignment and distance of the Moon from Earth. Outside the path of totality, observers witness a partial eclipse, where the Sun is only partially covered by the Moon.
Visibility of Lunar and Solar Eclipses
The visibility of lunar and solar eclipses varies based on the type of eclipse and the observer's location on Earth. Lunar eclipses are generally more accessible due to their occurrence during the night and their visibility from any location on the dark side of the Earth.
During a lunar eclipse, the entire event can be observed without the need for special equipment, as it poses no danger to the eyes. The best views are often from areas with clear skies and minimal light pollution.
In contrast, solar eclipses are visible only within a narrow path on the Earth's surface. Total solar eclipses are particularly rare, with the path of totality often covering remote or sparsely populated areas. Observers outside the path of totality see a partial eclipse, which can be viewed safely using solar viewing glasses or projection methods to protect the eyes.
The rarity and exclusivity of total solar eclipses make them highly anticipated events, drawing enthusiasts and astronomers from around the world to witness the spectacle. Planning and travel are often required to experience the full beauty of a solar eclipse.
Cultural Significance of Eclipses
Throughout history, eclipses have held significant cultural and symbolic meanings across various societies. They have been perceived as omens, divine interventions, and cosmic events that influence human affairs and natural phenomena.
In many ancient cultures, eclipses were seen as harbingers of change or disasters. They were often associated with myths and legends, where celestial beings or deities were believed to be responsible for the temporary darkening of the Sun or Moon. Rituals and ceremonies were conducted to appease these entities and restore cosmic balance.
In contrast, in some cultures, eclipses were viewed as opportunities for reflection and renewal. They were seen as moments of cosmic alignment, where the heavens provided guidance or insight into the future. Astrological interpretations of eclipses have also played a role in shaping beliefs and practices.
Today, eclipses continue to inspire awe and curiosity, drawing attention from people of all ages and backgrounds. They serve as a reminder of the interconnectedness of the Earth, Moon, and Sun, and the intricate dance of celestial bodies in the universe.
Historical Impact of Eclipses
Eclipses have played a crucial role in advancing scientific knowledge and understanding of the cosmos. They have provided opportunities for astronomers to study celestial mechanics, test theories, and make groundbreaking discoveries.
One of the most famous historical events involving an eclipse was the confirmation of Albert Einstein's theory of general relativity. During the total solar eclipse of 1919, astronomers observed the bending of starlight around the Sun, providing evidence for Einstein's predictions about the curvature of space-time.
Eclipses have also been used to refine models of the Earth's rotation, measure the distance to the Moon, and study the Sun's corona. They have contributed to our understanding of the solar system and the dynamics of celestial bodies.
In addition to their scientific significance, eclipses have influenced art, literature, and cultural narratives. They have been depicted in artwork, literature, and music, capturing the imagination and creativity of artists and writers throughout history.
Safety Measures During Solar Eclipses
Observing a solar eclipse is a thrilling experience, but it requires careful attention to safety precautions to protect your eyes from potential harm. Unlike lunar eclipses, which are safe to observe with the naked eye, solar eclipses require special equipment or methods to view safely.
Here are some important safety measures to follow during a solar eclipse:
- Use solar viewing glasses that meet international safety standards (ISO 12312-2) to protect your eyes from harmful solar radiation.
- Avoid using regular sunglasses, as they do not provide adequate protection against the intense light of the Sun.
- Use a pinhole projector or solar telescope with a proper solar filter to view the eclipse indirectly.
- Never look directly at the Sun through binoculars, telescopes, or cameras without proper solar filters.
- Supervise children to ensure they follow safety guidelines and use approved viewing equipment.
By taking these precautions, you can enjoy the spectacle of a solar eclipse while safeguarding your vision and experiencing the awe-inspiring beauty of this celestial event.
Observing Lunar Eclipses
Lunar eclipses offer a captivating opportunity to witness the Earth's shadow dance across the Moon's surface. Unlike solar eclipses, lunar eclipses can be safely observed with the naked eye and do not require special equipment.
Here are some tips for observing a lunar eclipse:
- Find a location with a clear view of the night sky, away from artificial lights and obstructions.
- Check the timing of the eclipse to ensure you catch the event from start to finish.
- Use binoculars or a telescope to enhance your view of the Moon's surface and the shadow's progression.
- Capture the eclipse with a camera or smartphone, using a tripod for steady shots and adjusting exposure settings for optimal results.
- Share the experience with friends or family, making it a memorable event for all.
Lunar eclipses provide an excellent opportunity for amateur astronomers and skywatchers to engage with the wonders of the cosmos, offering a spectacular display of celestial mechanics in action.
Frequency of Lunar and Solar Eclipses
The frequency of lunar and solar eclipses is governed by the orbital dynamics of the Earth-Moon-Sun system. While both types of eclipses occur regularly, their frequency and visibility differ significantly.
Lunar eclipses occur approximately every six months, with at least two and up to five eclipses happening each year. These events are more frequent and accessible, as they can be seen from anywhere on the night side of the Earth.
Solar eclipses, on the other hand, occur between two and five times a year, but total solar eclipses are much rarer. The narrow path of totality limits the number of people who can witness the complete coverage of the Sun, making these events highly anticipated and celebrated.
The Saros cycle, an 18-year period, plays a significant role in predicting the recurrence of eclipses. This cycle allows astronomers to forecast future eclipses with remarkable accuracy, providing opportunities for planning and observing these celestial phenomena.
How Do Eclipses Affect the Environment?
Eclipses have subtle but measurable effects on the environment, influencing temperature, wildlife behavior, and atmospheric conditions. While these impacts are temporary, they offer valuable insights into the interactions between celestial events and the Earth's systems.
During a solar eclipse, the sudden reduction in sunlight can lead to a temporary drop in temperature, affecting local weather patterns and cloud formation. This cooling effect can also influence air pressure and wind speed, creating localized microclimates.
Wildlife behavior is often impacted by eclipses, with animals displaying unusual patterns during these events. Birds may return to their nests, nocturnal animals become active, and insects may change their activity levels in response to the darkness.
The changes in light and temperature during an eclipse can also affect photosynthesis in plants, although the impact is typically short-lived. Overall, eclipses provide a unique opportunity to study the interconnectedness of the Earth's natural systems and their response to celestial events.
FAQs About Lunar and Solar Eclipses
What is the main difference between a lunar and solar eclipse?
The main difference lies in the alignment of celestial bodies. A lunar eclipse occurs when the Earth is between the Sun and the Moon, while a solar eclipse happens when the Moon is between the Earth and the Sun.
How often do total solar eclipses occur?
Total solar eclipses occur approximately every 18 months, but the path of totality is narrow, making them rare events for any given location on Earth.
Can you look at a lunar eclipse without eye protection?
Yes, lunar eclipses can be safely viewed with the naked eye without any risk of harm. Unlike solar eclipses, they do not require special viewing equipment.
Why does a total lunar eclipse appear red?
The red appearance is due to Rayleigh scattering, where Earth's atmosphere scatters shorter wavelengths of light and allows longer wavelengths like red to illuminate the Moon.
What causes the "ring of fire" in an annular solar eclipse?
The "ring of fire" occurs when the Moon is too far from the Earth to completely cover the Sun, leaving a ring-like appearance of the Sun's outer edges visible.
Are there any historical myths associated with eclipses?
Yes, many ancient cultures viewed eclipses as omens or divine interventions, leading to myths and rituals aimed at influencing or understanding these celestial events.
Conclusion
Lunar and solar eclipses are celestial phenomena that offer a glimpse into the intricate dance of the Earth, Moon, and Sun. While both types of eclipses share some similarities, their differences in occurrence, visibility, and cultural significance highlight the diverse ways in which they have been perceived and studied throughout history.
From the scientific insights gained through eclipse observations to the cultural narratives that have shaped human understanding, eclipses continue to captivate and inspire. Whether you are an avid astronomer or a casual skywatcher, these celestial events provide a unique opportunity to connect with the cosmos and appreciate the wonders of our universe.
For more information on eclipses and their impact, visit NASA's Eclipse Page.