The human body is a marvel of biological engineering, and melanin is one of its most fascinating components. This pigment not only determines the color of our skin, hair, and eyes but also plays a crucial role in protecting us from the harmful effects of ultraviolet (UV) radiation. Despite its important role, many people are unaware of how melanin functions and why they might need more of it. Understanding "when do you need more melinana" can offer valuable insights into how we care for our skin and overall health.
Melanin is not just about aesthetics; it is a crucial factor in safeguarding our skin from the potential dangers posed by UV rays. With increasing environmental challenges and the ever-rising levels of UV exposure, it's essential to evaluate whether our melanin levels are sufficient for optimal protection. This article delves into the circumstances under which you might need more melanin, offering a comprehensive guide to understanding its role in our lives.
In our quest to explore "when do you need more melinana," we will cover various aspects, including the biology of melanin, factors affecting its production, and the potential health benefits of increased melanin levels. By the end of this article, you'll have a clearer understanding of how melanin works and when boosting its production might be beneficial for you.
Read also:From Platinum To Blonde Ultimate Guide To Hair Transformation
Table of Contents
- What is Melanin?
- How is Melanin Produced?
- Factors Affecting Melanin Production
- Why Might You Need More Melanin?
- When Do You Need More Melinana?
- Health Benefits of Increased Melanin
- Melanin and Skin Protection
- Melanin and Eye Health
- Melanin and Hair Color
- Foods That Boost Melanin Production
- Supplements for Melanin Production
- Lifestyle Changes to Enhance Melanin
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
What is Melanin?
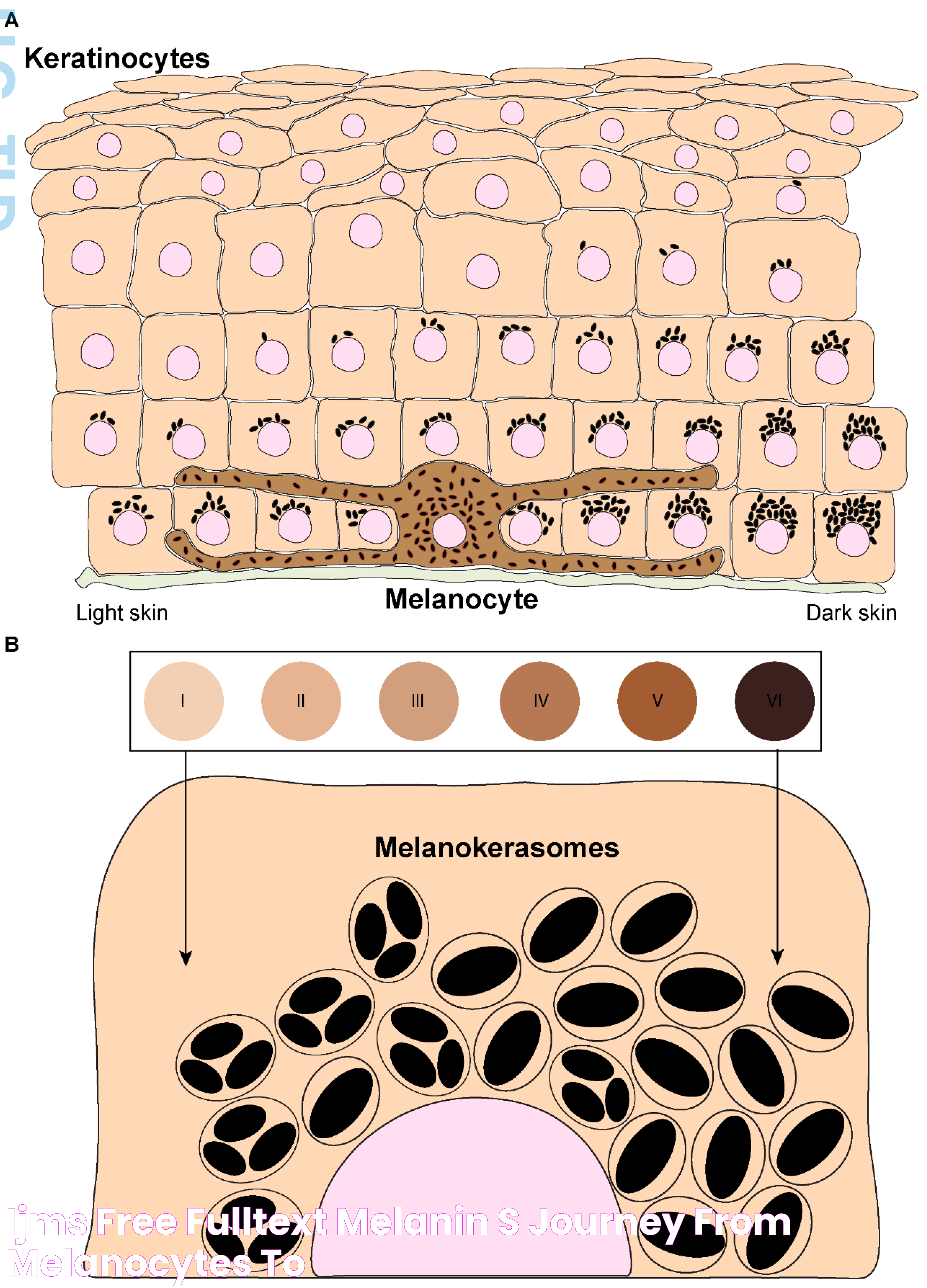
Melanin is a naturally occurring pigment found in most organisms, responsible for the color of skin, hair, and eyes. This pigment is produced by cells known as melanocytes, located primarily in the skin's epidermis. Melanin is categorized into three main types: eumelanin, pheomelanin, and neuromelanin, each contributing distinct colors and serving various functions.
Eumelanin is the most prevalent type, providing black and brown hues, and is found in higher concentrations in individuals with darker skin tones. Pheomelanin imparts red and yellow shades, commonly seen in individuals with lighter skin and red hair. Neuromelanin, although less understood, is located in different parts of the brain and is thought to play a role in brain function.
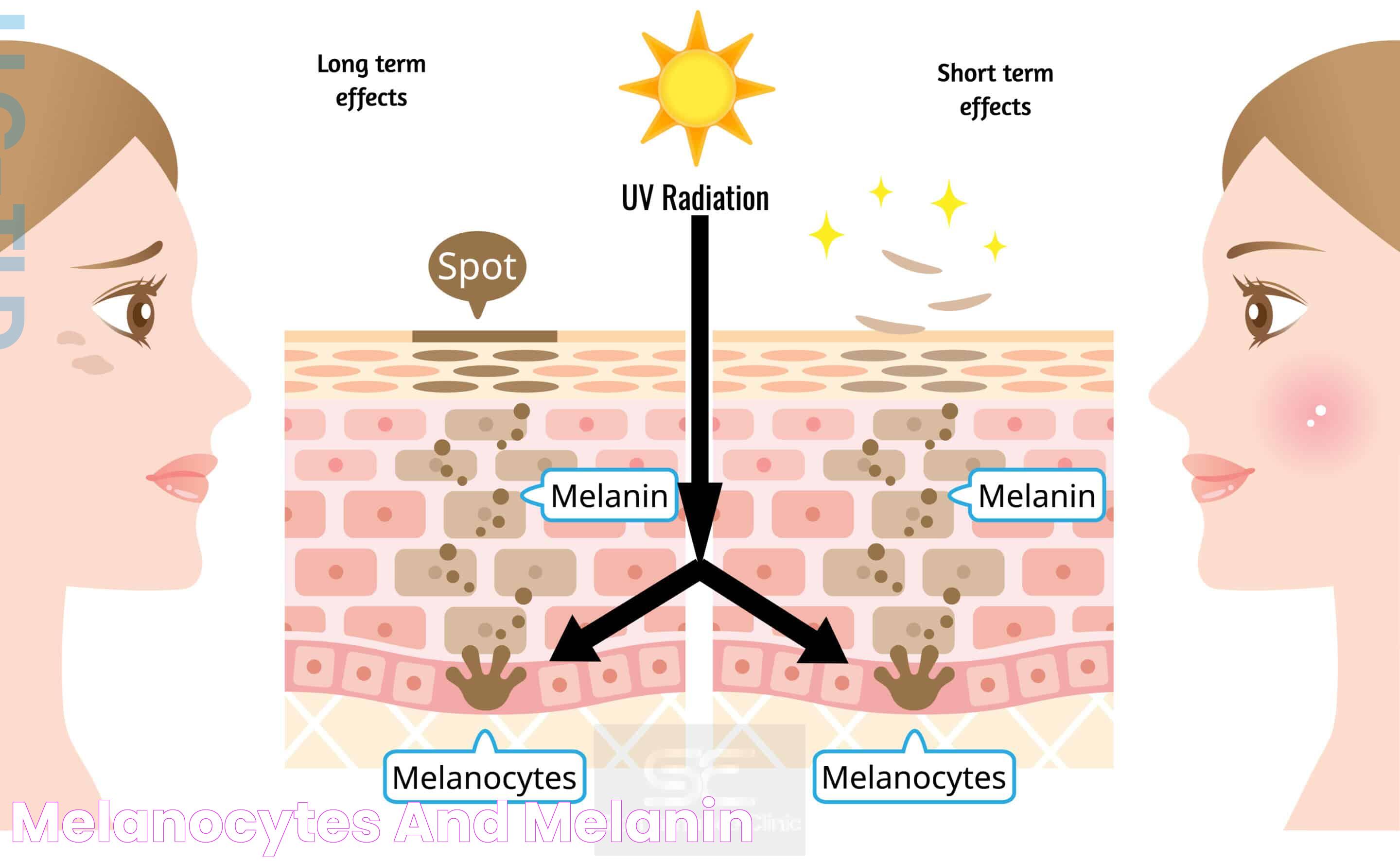
In addition to determining physical appearance, melanin serves as a protective barrier against UV radiation. It absorbs sunlight and dissipates it as heat, reducing the risk of DNA damage that can lead to skin cancer. This protective feature of melanin highlights its vital role in maintaining skin health and underscores the importance of understanding when you might need more of it.
How is Melanin Produced?
The production of melanin, known as melanogenesis, is a complex process initiated by the exposure of skin to UV radiation. When UV rays penetrate the skin, they stimulate the melanocytes to produce more melanin as a defense mechanism. This process involves the conversion of the amino acid tyrosine into melanin through a series of biochemical reactions catalyzed by the enzyme tyrosinase.
Several factors influence the rate of melanin production, including genetics, hormonal changes, and environmental exposure. Genetic predisposition determines baseline melanin levels, while hormonal fluctuations during puberty, pregnancy, or conditions like Addison's disease can alter melanin production. Environmental factors, such as sun exposure and pollution, can also impact melanin synthesis.
Understanding how melanin is produced and the factors influencing its production is crucial for recognizing when you might need more melanin. By identifying these triggers, individuals can take proactive steps to enhance melanin levels and protect their skin from potential damage.
Read also:All You Need To Know About Black Mascara A Beauty Staple
Factors Affecting Melanin Production
Several intrinsic and extrinsic factors can affect melanin production, influencing the amount of melanin present in the skin, hair, and eyes. Intrinsic factors are primarily related to genetics and hormonal changes, while extrinsic factors include environmental influences and lifestyle choices.
Intrinsic Factors
- Genetics: Genetic makeup plays a significant role in determining baseline melanin levels. Individuals with a family history of lighter or darker skin tones are likely to inherit similar melanin levels.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormones can impact melanin production, with fluctuations occurring during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause. Conditions like Addison's disease can also lead to increased melanin production.
Extrinsic Factors
- Sun Exposure: UV radiation is a significant trigger for melanin production, leading to tanning as the skin produces more melanin to protect against damage.
- Pollution: Environmental pollutants can affect skin health and melanin production by inducing oxidative stress and inflammation.
- Lifestyle Choices: Diet, stress levels, and skincare routines can all influence melanin production. A diet rich in antioxidants and vitamins can support healthy melanin levels.
Recognizing these factors can help individuals make informed decisions about their skincare routines and lifestyle choices to support optimal melanin production.
Why Might You Need More Melanin?
There are several reasons why an individual might require increased melanin production. These reasons can be related to health, aesthetics, or environmental considerations, each presenting unique challenges and benefits.
Health Benefits
- Protection Against UV Radiation: Increased melanin levels provide better protection against UV rays, reducing the risk of skin cancer and photoaging.
- Preventing Skin Disorders: Conditions like vitiligo and albinism, characterized by a lack of melanin, can benefit from increased melanin production.
Aesthetic Considerations
- Achieving a Desired Skin Tone: Some individuals seek to enhance their skin tone for personal or cultural reasons, finding a more even complexion desirable.
- Camouflaging Skin Imperfections: Increased melanin can help mask blemishes, scars, or hyperpigmentation, leading to a more uniform skin appearance.
Environmental Factors
- Living in High UV Areas: Individuals residing in regions with high UV exposure, such as near the equator, may require more melanin for adequate protection.
- Occupational Hazards: Jobs involving prolonged sun exposure, such as construction or outdoor sports, may necessitate higher melanin levels for skin protection.
Understanding these reasons and the potential benefits of increased melanin production can guide individuals in making informed decisions about their skin health and overall well-being.
When Do You Need More Melinana?
Determining "when do you need more melinana" involves evaluating several factors, including personal health, lifestyle, and environmental conditions. Here are some scenarios in which increased melanin may be beneficial:
Health-Related Scenarios
- Skin Conditions: Individuals with conditions like vitiligo or albinism, which result in reduced melanin levels, may need more melanin to achieve skin uniformity.
- Risk of Skin Cancer: Those with a family history of skin cancer or who have experienced significant UV exposure may benefit from increased melanin for better protection.
Lifestyle and Environmental Factors
- High UV Exposure: People living in regions with intense UV radiation might need more melanin to safeguard their skin from damage.
- Outdoor Occupations: Jobs requiring prolonged outdoor exposure can increase the need for more melanin to protect against UV rays.
By considering these factors, individuals can assess their need for increased melanin and take appropriate measures to support melanin production.
Health Benefits of Increased Melanin
Boosting melanin levels can offer numerous health benefits, particularly related to skin protection and overall well-being. Understanding these benefits can highlight the importance of maintaining optimal melanin levels.
UV Protection
- Reduced Risk of Skin Cancer: Increased melanin provides better protection against UV radiation, lowering the risk of developing skin cancer.
- Prevention of Photoaging: By absorbing and dissipating UV rays, melanin helps prevent the premature aging of the skin, maintaining a youthful appearance.
Support for Skin Health
- Even Skin Tone: Enhanced melanin levels can lead to a more uniform skin tone, reducing the appearance of blemishes and hyperpigmentation.
- Protection Against Skin Disorders: Conditions like vitiligo and melasma can benefit from increased melanin production, improving skin uniformity.
These health benefits underscore the importance of understanding when increased melanin might be necessary and how it contributes to overall skin health.
Melanin and Skin Protection
Melanin's primary function is to protect the skin from the harmful effects of UV radiation. By absorbing sunlight and dissipating it as heat, melanin reduces the risk of DNA damage and subsequent skin cancer. This protective barrier is crucial for maintaining healthy skin and preventing various skin disorders.
In addition to its protective role, melanin contributes to skin tone and appearance. A balanced melanin level ensures an even complexion and reduces the visibility of skin imperfections. This aesthetic benefit highlights the importance of maintaining optimal melanin levels for both health and appearance.
Understanding melanin's role in skin protection can help individuals make informed decisions about their sun exposure and skincare routines. By recognizing the importance of melanin, individuals can take proactive steps to enhance their skin's natural defense mechanisms.
Melanin and Eye Health
Melanin also plays a vital role in eye health, particularly in protecting the eyes from UV radiation. The pigment is present in the iris and retinal pigment epithelium, providing a shield against harmful light exposure. This protection is essential for maintaining vision and preventing eye disorders such as cataracts and age-related macular degeneration (AMD).
In addition to its protective function, melanin contributes to eye color, influencing the amount of light that enters the eye. Darker irises, which contain more melanin, offer greater protection against bright light, reducing glare and enhancing visual comfort.
Understanding melanin's role in eye health emphasizes the need for adequate melanin levels to safeguard vision and prevent eye-related conditions. By recognizing the importance of melanin in eye health, individuals can take steps to maintain optimal levels and protect their eyes from damage.
Melanin and Hair Color
Melanin is responsible for the color of hair, with eumelanin and pheomelanin determining whether hair is black, brown, blonde, or red. The amount and type of melanin present in hair follicles influence hair color, with higher eumelanin levels resulting in darker hair and increased pheomelanin levels leading to lighter or red hair.
As individuals age, melanin production in hair follicles decreases, leading to the gradual graying of hair. This natural process is influenced by genetic factors and environmental exposure. While reduced melanin levels are a normal part of aging, some individuals may seek to enhance melanin production to maintain their natural hair color for longer.
Understanding melanin's role in hair color can guide individuals in making informed decisions about hair care and coloring options. By recognizing the importance of melanin, individuals can take steps to support healthy hair pigmentation and delay the onset of graying.
Foods That Boost Melanin Production
Diet plays a crucial role in supporting melanin production, with certain foods providing the nutrients necessary for optimal melanin synthesis. Incorporating these foods into your diet can enhance melanin levels and support overall skin health.
- Foods Rich in Vitamin A: Carrots, sweet potatoes, and spinach are excellent sources of vitamin A, which supports melanin production by promoting healthy skin cell turnover.
- Foods High in Vitamin C: Citrus fruits, strawberries, and bell peppers are rich in vitamin C, which aids in collagen production and supports melanin synthesis.
- Foods with Vitamin E: Nuts, seeds, and avocados provide vitamin E, an antioxidant that protects skin cells and supports melanin production.
- Copper-Rich Foods: Shellfish, nuts, and seeds contain copper, a mineral essential for the production of melanin.
- Iron-Rich Foods: Red meat, lentils, and spinach are good sources of iron, which supports healthy blood flow and melanin production.
Incorporating these foods into your diet can help support melanin production, promoting healthy skin, hair, and eye pigmentation.
Supplements for Melanin Production
In addition to a balanced diet, supplements can provide additional support for melanin production. These supplements can help individuals who may have difficulty obtaining sufficient nutrients from food alone or who require enhanced melanin levels for specific health or aesthetic reasons.
- Vitamin A Supplements: Vitamin A is crucial for healthy skin cell turnover and melanin production. Supplements can help individuals meet their daily requirements.
- Vitamin C Supplements: As an antioxidant, vitamin C supports collagen production and melanin synthesis, making supplements beneficial for those with dietary restrictions.
- Vitamin E Supplements: Vitamin E protects skin cells from oxidative stress, supporting melanin production and overall skin health.
- Copper Supplements: Copper is essential for melanin synthesis, and supplements can help individuals with deficiencies meet their needs.
- Iron Supplements: Iron supports healthy blood flow and melanin production, making supplements beneficial for individuals with low iron levels.
Before starting any supplement regimen, it's essential to consult with a healthcare professional to ensure safety and appropriateness based on individual health needs.
Lifestyle Changes to Enhance Melanin
In addition to diet and supplements, certain lifestyle changes can support melanin production and enhance overall skin health. By incorporating these changes into daily routines, individuals can promote healthy melanin levels and protect their skin from damage.
- Sun Exposure: Moderate sun exposure can stimulate melanin production, but it's essential to balance exposure with sun protection to prevent skin damage.
- Hydration: Staying hydrated supports skin health and promotes optimal melanin production.
- Stress Management: Reducing stress through relaxation techniques, exercise, or mindfulness can support healthy melanin levels.
- Skincare Routine: Using skincare products with antioxidants and UV protection can enhance melanin production and protect the skin.
- Healthy Sleep Patterns: Adequate sleep supports skin health and melanin production, promoting a healthy complexion.
By implementing these lifestyle changes, individuals can enhance melanin production and maintain healthy skin, hair, and eye pigmentation.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is melanin, and why is it important?
Melanin is a natural pigment responsible for the color of skin, hair, and eyes. It protects the skin from UV radiation and is crucial for maintaining skin health and preventing skin disorders.
2. Can diet influence melanin production?
Yes, diet plays a significant role in melanin production. Foods rich in vitamins A, C, and E, as well as copper and iron, support melanin synthesis and promote healthy skin pigmentation.
3. How does sun exposure affect melanin levels?
Sun exposure stimulates melanin production, leading to tanning as the skin produces more melanin to protect against UV damage. However, excessive exposure can be harmful, so balance is key.
4. Are there any supplements that can boost melanin production?
Yes, supplements such as vitamins A, C, and E, as well as copper and iron, can support melanin production. It's essential to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any supplement regimen.
5. How does melanin protect the skin and eyes?
Melanin absorbs and dissipates UV radiation, reducing the risk of DNA damage and skin cancer. In the eyes, melanin protects against harmful light exposure, preventing conditions like cataracts and AMD.
6. Can lifestyle changes enhance melanin production?
Yes, lifestyle changes such as moderate sun exposure, hydration, stress management, and a healthy skincare routine can support melanin production and maintain healthy skin pigmentation.
Conclusion
Understanding "when do you need more melinana" involves evaluating personal health, lifestyle, and environmental factors. By recognizing the importance of melanin in protecting skin, hair, and eyes, individuals can make informed decisions to support optimal melanin levels. Through a combination of diet, supplements, and lifestyle changes, it's possible to enhance melanin production and maintain overall skin health and well-being.
By taking proactive steps to support melanin production, individuals can protect themselves from UV damage, achieve their desired skin tone, and enjoy the numerous health benefits associated with increased melanin levels.