PTSD, an acronym for Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder, is a mental health condition that arises after experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event. Often associated with veterans, PTSD can affect anyone who has endured situations that profoundly disturb their sense of safety and well-being. These events could range from natural disasters and accidents to acts of violence or personal assaults. The condition is characterized by a range of symptoms, including flashbacks, severe anxiety, and uncontrollable thoughts about the event, which can significantly impair an individual's ability to function in daily life.
Recognizing the symptoms and understanding what does PTSD mean is crucial for those affected and their loved ones. PTSD symptoms can manifest shortly after the traumatic event or might take years to surface, making early diagnosis and intervention challenging. Treatment often involves a combination of psychotherapy and medication, tailored to help individuals process their trauma and regain control over their lives. Despite its challenges, many individuals with PTSD can lead fulfilling lives with the proper support and treatment.
In recent years, there has been a growing awareness of PTSD, leading to more conversations about mental health and the importance of seeking help. Understanding PTSD is not just about recognizing its symptoms but also about acknowledging the profound impact it can have on an individual's life. This article delves into the complexities of PTSD, exploring its causes, symptoms, treatment options, and the importance of support systems in managing this condition. By enhancing our understanding of PTSD, we can foster a more supportive environment for those affected and promote mental health awareness in our communities.
Read also:All About Chloe Grace Moretz Eye Colors A Detailed Insight
Table of Contents
- What is PTSD?
- Causes of PTSD
- Symptoms of PTSD
- How is PTSD Diagnosed?
- Treatment Options for PTSD
- Psychotherapy in PTSD Treatment
- Medications and PTSD
- Living with PTSD
- The Role of Support Systems
- PTSD and Children
- How Does PTSD Affect Daily Life?
- Can PTSD be Prevented?
- The Future of PTSD Treatment
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
What is PTSD?
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) is a complex mental health condition triggered by experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event. This condition is categorized under anxiety disorders and is characterized by a variety of symptoms that can severely impact an individual's daily functioning. PTSD can affect anyone, regardless of age, gender, or background, and it is not limited to a specific type of trauma. Understanding what does PTSD mean involves recognizing that it is a natural response to abnormal situations, where the brain struggles to process the traumatic experience.
PTSD is not just about reliving the traumatic event; it encompasses a range of emotional and physical responses. Individuals with PTSD may experience flashbacks, nightmares, severe anxiety, and uncontrollable thoughts related to the event. These symptoms can be debilitating and often persist long after the initial trauma has occurred. While PTSD is commonly associated with military veterans, it can also affect survivors of accidents, natural disasters, abuse, and other life-threatening events.
How does PTSD manifest?
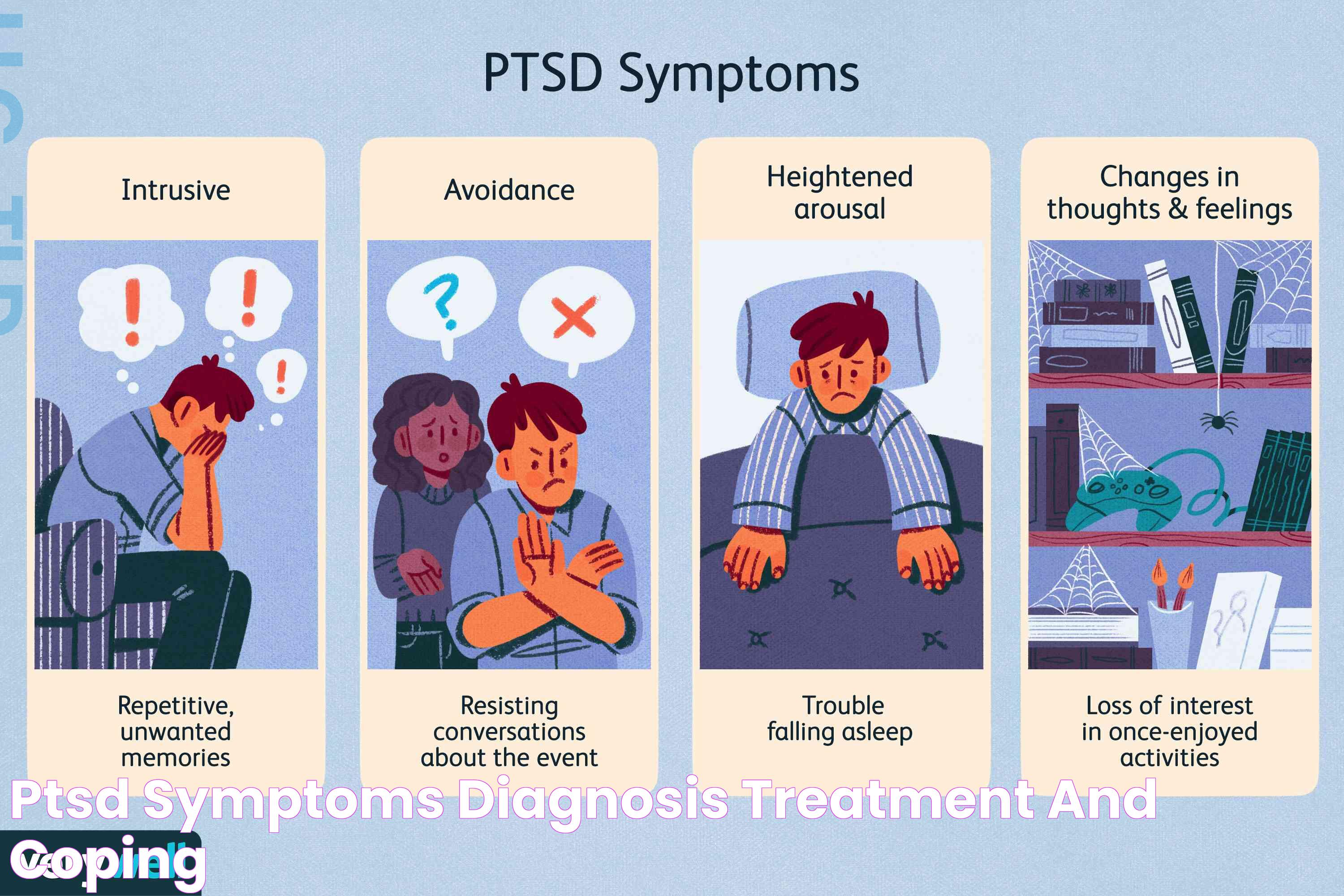
The manifestation of PTSD varies among individuals, but it generally involves intense emotional and physiological reactions to reminders of the trauma. These reactions can include:
- Intrusive memories, such as distressing flashbacks or dreams.
- Avoidance of places, people, or activities that trigger memories of the trauma.
- Negative changes in thinking and mood, leading to feelings of hopelessness or detachment from loved ones.
- Heightened arousal or reactivity, resulting in irritability, difficulty sleeping, or being easily startled.
Understanding these manifestations is crucial in recognizing the signs of PTSD and seeking appropriate treatment.
Causes of PTSD
PTSD is caused by exposure to traumatic events that overwhelm an individual's ability to cope. While the exact cause of PTSD is not fully understood, several factors contribute to its development. These include the nature and severity of the trauma, the individual's personal history, and their overall mental health. Traumatic events that can lead to PTSD include:
- Military combat
- Serious accidents
- Natural disasters
- Physical or sexual assault
- Witnessing violence or death
It is important to note that not everyone who experiences trauma will develop PTSD. Factors such as the individual's resilience, support systems, and coping mechanisms play a significant role in determining their risk of developing the disorder.
Read also:Effortless Elegance Low Maintenance Hair Cut For Women
Are there risk factors for PTSD?
Certain factors can increase the likelihood of developing PTSD after a traumatic event. These risk factors include:
- Experiencing intense or long-lasting trauma
- Having a history of mental health issues, such as anxiety or depression
- Lack of support from family or friends
- Having experienced previous trauma
- Possessing certain personality traits, such as high levels of neuroticism
Understanding these risk factors can help in identifying individuals who may be more susceptible to PTSD and providing them with early interventions.
Symptoms of PTSD
PTSD symptoms are typically grouped into four categories: intrusive memories, avoidance, negative changes in thinking and mood, and changes in physical and emotional reactions. These symptoms can vary in intensity over time and can significantly impact an individual's quality of life.
What do intrusive memories include?
Intrusive memories are one of the hallmark symptoms of PTSD and can manifest as:
- Recurrent, unwanted distressing memories of the traumatic event
- Flashbacks, where the individual feels as though they are reliving the trauma
- Nightmares or vivid dreams about the event
- Severe emotional distress or physical reactions to reminders of the trauma
These memories can be triggered by events, places, or people that remind the individual of the trauma, making it challenging to avoid these stimuli in everyday life.
What does avoidance look like in PTSD?
Avoidance symptoms involve efforts to evade reminders of the trauma and can include:
- Staying away from places, people, or activities that recall memories of the trauma
- Refusing to talk about the traumatic event or suppressing thoughts related to it
- Feeling emotionally numb or detached from loved ones
- Loss of interest in activities once enjoyed
Avoidance can severely limit an individual's ability to engage in daily activities and maintain relationships, contributing to feelings of isolation and loneliness.
How is PTSD Diagnosed?
Diagnosing PTSD involves a comprehensive evaluation by a mental health professional, who will assess the individual's symptoms, medical history, and exposure to trauma. The diagnostic process typically includes:
- A detailed interview to understand the nature and impact of the traumatic event
- A review of the individual's symptoms and their duration
- Screening for other mental health conditions that may present similarly, such as depression or anxiety
What criteria are used for PTSD diagnosis?
The criteria for diagnosing PTSD are outlined in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) and include:
- Exposure to a traumatic event, either by direct experience, witnessing, or learning about it happening to a loved one
- Presence of intrusive symptoms, such as distressing memories or flashbacks, for more than a month
- Avoidance of reminders associated with the trauma
- Negative changes in mood and cognition
- Marked changes in arousal and reactivity
For a PTSD diagnosis, these symptoms must cause significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning.
Treatment Options for PTSD
Treating PTSD involves a multifaceted approach that includes psychotherapy, medication, and support from family and friends. The goal of treatment is to help individuals manage their symptoms, process their trauma, and improve their quality of life.
What are the primary forms of psychotherapy for PTSD?
Several types of psychotherapy have proven effective in treating PTSD, including:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Focuses on identifying and changing negative thought patterns that contribute to PTSD symptoms.
- Exposure Therapy: Helps individuals confront their fears by gradually exposing them to trauma-related memories in a controlled environment.
- Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR): Involves guided eye movements to help process and integrate traumatic memories.
These therapies can be tailored to meet the specific needs of the individual and are often delivered in individual or group settings.
Psychotherapy in PTSD Treatment
Psychotherapy, also known as talk therapy, is a cornerstone of PTSD treatment, providing individuals with a safe space to explore their trauma and develop coping strategies. Different forms of psychotherapy can be used to address the unique needs of each individual, helping them process their experiences and reduce symptoms.
How does Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) help with PTSD?
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is one of the most effective psychotherapies for PTSD. It helps individuals identify and challenge distorted beliefs related to their trauma, leading to changes in their emotional and behavioral responses. CBT focuses on:
- Recognizing and altering negative thought patterns
- Developing skills to manage distressing emotions
- Improving problem-solving and decision-making abilities
Through CBT, individuals learn to reframe their understanding of the trauma, reducing its hold over their thoughts and actions.
Medications and PTSD
Alongside psychotherapy, medications can play a crucial role in managing PTSD symptoms. These medications are used to alleviate symptoms such as anxiety, depression, and insomnia, allowing individuals to engage more effectively in therapeutic interventions.
What types of medications are commonly used for PTSD?
Several classes of medications are commonly prescribed for PTSD, including:
- Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs): Often considered the first-line treatment for PTSD, SSRIs help regulate mood and reduce anxiety.
- Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs): Similar to SSRIs, SNRIs can alleviate symptoms of depression and anxiety.
- Prazosin: An alpha-blocker used to treat nightmares and sleep disturbances associated with PTSD.
These medications are typically prescribed in conjunction with psychotherapy to provide comprehensive symptom management.
Living with PTSD
Living with PTSD can present significant challenges, but with the right support and treatment, individuals can lead fulfilling lives. Managing PTSD involves developing coping strategies, building a strong support network, and engaging in ongoing treatment to address symptoms.
What are some coping strategies for managing PTSD?
Individuals with PTSD can benefit from a variety of coping strategies, such as:
- Practicing relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing or meditation, to reduce stress and anxiety.
- Engaging in regular physical activity to improve mood and overall well-being.
- Establishing a routine to provide structure and stability.
- Connecting with support groups or peer networks for shared experiences and encouragement.
These strategies can empower individuals to take control of their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
The Role of Support Systems
A strong support system is vital for individuals with PTSD, providing emotional, practical, and social support. Family, friends, and mental health professionals play a crucial role in helping individuals navigate their recovery journey.
How can family and friends support someone with PTSD?
Family and friends can provide invaluable support to those with PTSD by:
- Listening without judgment and offering emotional support
- Encouraging them to seek professional help and adhere to treatment plans
- Participating in family therapy sessions to improve understanding and communication
- Providing practical assistance, such as helping with daily tasks and creating a safe environment
By fostering a supportive and understanding environment, loved ones can help individuals with PTSD feel less isolated and more empowered in their recovery.
PTSD and Children
While PTSD is commonly associated with adults, children can also experience this disorder. Childhood PTSD can result from various traumatic events, such as abuse, neglect, or exposure to violence, and its symptoms may differ from those in adults.
What are the signs of PTSD in children?
Common signs of PTSD in children include:
- Re-experiencing the trauma through play or drawings
- Nightmares or sleep disturbances
- Increased irritability or aggression
- Difficulty concentrating or changes in academic performance
- Withdrawal from family and friends
Recognizing these signs is crucial for early intervention and treatment, which can significantly improve a child's long-term mental health outcomes.
How Does PTSD Affect Daily Life?
PTSD can have a profound impact on an individual's daily life, affecting their relationships, work, and overall well-being. The symptoms of PTSD can interfere with an individual's ability to function effectively, leading to difficulties in maintaining employment, social connections, and personal responsibilities.
What challenges do individuals with PTSD face in their daily lives?
Individuals with PTSD may face numerous challenges, such as:
- Struggling to maintain focus and productivity at work or school
- Experiencing difficulties in establishing and maintaining relationships due to emotional detachment or irritability
- Dealing with physical health issues, such as chronic pain or sleep disturbances
- Facing stigma or misunderstanding from others regarding their condition
Addressing these challenges requires a comprehensive approach to treatment and support, empowering individuals to regain control over their lives.
Can PTSD be Prevented?
While it may not be possible to prevent PTSD entirely, certain strategies can reduce the risk of developing the disorder after a traumatic event. These strategies focus on building resilience, seeking early intervention, and fostering a supportive environment.
What steps can be taken to prevent PTSD?
To minimize the risk of PTSD, individuals can:
- Engage in stress-reduction techniques, such as mindfulness and relaxation exercises
- Seek professional help promptly after experiencing trauma
- Build a strong support network of family, friends, and mental health professionals
- Stay physically active and maintain a healthy lifestyle
By taking proactive steps, individuals can enhance their resilience and reduce the likelihood of developing PTSD after a traumatic event.
The Future of PTSD Treatment
Advancements in PTSD treatment continue to evolve, offering new hope for individuals affected by this condition. Emerging therapies and research are paving the way for more effective and personalized treatment options.
What are some promising developments in PTSD treatment?
Recent developments in PTSD treatment include:
- Innovative psychotherapies, such as virtual reality exposure therapy, which allows individuals to confront their fears in a controlled virtual environment
- Research into the use of psychedelics, like MDMA, in conjunction with psychotherapy to facilitate trauma processing
- Advancements in neurofeedback and brain stimulation techniques to target specific brain areas involved in PTSD symptoms
These advancements hold the potential to revolutionize PTSD treatment, providing individuals with more targeted and effective options for managing their symptoms.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does PTSD mean in the context of mental health?
PTSD stands for Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder, a mental health condition triggered by experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event. It is characterized by symptoms such as flashbacks, anxiety, and avoidance behaviors.
Can PTSD affect anyone?
Yes, PTSD can affect anyone who has experienced or witnessed a traumatic event, regardless of age, gender, or background. It is not limited to a specific group of individuals.
How long does it take for PTSD symptoms to appear?
PTSD symptoms can appear within a few weeks of the traumatic event, but in some cases, they may not manifest until months or even years later. The onset and duration of symptoms can vary widely among individuals.
Is PTSD treatable?
Yes, PTSD is treatable. With appropriate therapy, medication, and support, individuals with PTSD can manage their symptoms and lead fulfilling lives.
Can children develop PTSD?
Yes, children can develop PTSD as a result of experiencing or witnessing traumatic events. Symptoms may differ from those in adults and require specialized treatment approaches.
What resources are available for individuals with PTSD?
Individuals with PTSD can access a variety of resources, including mental health professionals, support groups, and online communities. Organizations such as the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) provide valuable information and assistance.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding what does PTSD mean is essential for recognizing the impact of trauma on mental health and supporting those affected. PTSD is a complex condition that can significantly affect an individual's well-being, but with the right treatment and support, recovery is possible. By fostering awareness and empathy, we can create a more supportive environment for individuals with PTSD, enabling them to lead fulfilling lives and contribute positively to their communities. As research and treatment options continue to evolve, there is hope for more effective interventions and improved outcomes for those living with PTSD.