The human skin is a marvel of nature, constantly engaging in a delicate balancing act to maintain its health and functionality. Among its many roles, the production of lactic acid stands out as a crucial process, playing an essential part in skin health and regeneration. Lactic acid, a type of alpha hydroxy acid (AHA), is naturally produced by the skin and is vital for maintaining its pH balance, hydration, and cell turnover. Understanding how the skin synthesizes this compound not only unravels the intricacies of skin biology but also offers insights into enhancing skincare routines. In today's quest for radiant and healthy skin, lactic acid has emerged as a pivotal component, underscoring its significance in dermatology and cosmetic science.
In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the mechanisms by which the skin produces lactic acid, its multifaceted roles, and the factors influencing its synthesis. By examining the biochemical pathways and cellular interactions, we aim to shed light on the integral role lactic acid plays in skin physiology. From its moisturizing properties to its impact on skin renewal, lactic acid is indispensable in achieving optimal skin health. Furthermore, understanding these processes can lead to targeted skincare interventions, ultimately promoting better skin health and appearance.
As we navigate through this intricate topic, we will also address common questions surrounding lactic acid, its benefits, and how to harness its potential in skincare. Whether you're a skincare enthusiast or a professional in the field, gaining a deeper understanding of how the skin makes lactic acid is invaluable. Join us as we explore the science and significance of lactic acid production in the skin, offering practical insights and empowering knowledge to enhance your skincare journey.
Read also:Effective Hair Growth Supplements For Men A Comprehensive Guide
Table of Contents
- What are the biochemical pathways involved in lactic acid production?
- Why is lactic acid important for skin health?
- Cellular Processes: How lactic acid is synthesized in the skin
- Factors influencing lactic acid production in the skin
- Role of Lactic Acid in Skincare Regimens
- Natural sources of lactic acid for the skin
- How does lactic acid compare to other skincare acids?
- Impact of environmental factors on lactic acid synthesis
- Benefits of lactic acid for aging skin
- Can dietary choices affect skin's lactic acid levels?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
What are the biochemical pathways involved in lactic acid production?
Lactic acid production in the skin involves several intricate biochemical pathways. At the heart of this process is the breakdown of glucose through glycolysis, a metabolic pathway that converts glucose into pyruvate. Under certain conditions, such as when oxygen levels are low, pyruvate is further converted into lactic acid by the enzyme lactate dehydrogenase (LDH). This conversion is a pivotal step in producing lactic acid within the skin.
The process begins with the uptake of glucose by skin cells, facilitated by glucose transporters. Once inside the cell, glucose undergoes a series of enzymatic reactions in the cytoplasm, collectively known as glycolysis. This pathway not only provides energy for cellular functions but also generates pyruvate, the precursor for lactic acid. The conversion of pyruvate to lactic acid is anaerobic and occurs in the cytosol, offering a quick energy source and contributing to the acidification of the microenvironment, which is crucial for maintaining optimal skin conditions.
Several factors influence this biochemical pathway, including the availability of glucose, the activity of glycolytic enzymes, and the presence of cofactors such as NAD+. Additionally, hormonal signals and skin's metabolic state can modulate glycolysis and subsequent lactic acid production. Understanding these pathways provides insight into how the skin regulates its pH and maintains its barrier function, highlighting the importance of lactic acid in skin health.
Why is lactic acid important for skin health?
Lactic acid plays several vital roles in maintaining skin health. As a natural component of the skin's acid mantle, it helps regulate pH levels, which is essential for barrier function and microbial defense. The acid mantle is a thin film on the skin's surface that maintains a slightly acidic environment, deterring pathogenic microorganisms and promoting the growth of beneficial skin flora.
Beyond its role in pH regulation, lactic acid is a potent humectant, attracting and retaining moisture in the skin. This moisturizing property is crucial for maintaining skin hydration, elasticity, and softness, contributing to a healthy and youthful appearance. Moreover, lactic acid facilitates gentle exfoliation by dissolving the bonds between dead skin cells, promoting their shedding and revealing fresher, smoother skin underneath.
Furthermore, lactic acid stimulates collagen production, supporting skin structure and reducing the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles. Its exfoliating action also enhances the penetration of other skincare ingredients, improving their efficacy. By supporting cell turnover and renewal, lactic acid helps to maintain a vibrant and even skin tone, making it an invaluable component in skincare formulations.
Read also:Migraines During Menstruation Causes Remedies And Management
Cellular Processes: How lactic acid is synthesized in the skin
The synthesis of lactic acid in the skin is a complex process involving multiple cellular mechanisms. At the cellular level, skin cells, particularly keratinocytes and fibroblasts, play crucial roles in lactic acid production. These cells are adept at metabolizing glucose through glycolysis, leading to lactic acid formation as a byproduct.
Keratinocytes, the predominant cell type in the epidermis, are particularly active in glycolysis. They convert glucose to pyruvate, which is then transformed into lactic acid under anaerobic conditions. This process is crucial during hypoxic conditions, such as those found in the deeper layers of the skin, where oxygen availability is limited. The production of lactic acid helps to lower the pH in these areas, creating an environment conducive to skin health and function.
Fibroblasts, located in the dermis, also contribute to lactic acid production. These cells are involved in collagen synthesis and tissue repair, processes that require energy and produce lactic acid as a metabolic byproduct. The collaboration between different skin cell types ensures a steady supply of lactic acid, vital for maintaining the skin's structural integrity and hydration levels.
Factors influencing lactic acid production in the skin
Several factors can influence the production of lactic acid in the skin. These include genetic predisposition, lifestyle choices, and environmental conditions. Genetics play a significant role in determining the baseline levels of enzymes involved in glycolysis and lactic acid synthesis, affecting individual variation in lactic acid production.
Lifestyle factors, such as diet and exercise, can also impact lactic acid levels. A diet rich in carbohydrates provides the necessary fuel for glycolysis, potentially enhancing lactic acid production. Regular physical activity boosts circulation and oxygen delivery to the skin, supporting aerobic metabolism and influencing lactic acid synthesis.
Environmental factors, including temperature, humidity, and UV exposure, also affect lactic acid production. High temperatures and humidity can increase perspiration and lactic acid secretion, while UV exposure can alter skin metabolism and enzyme activity. Understanding these factors can guide skincare practices and interventions aimed at optimizing lactic acid levels for skin health.
Role of Lactic Acid in Skincare Regimens
Lactic acid is a popular ingredient in many skincare products, valued for its exfoliating, hydrating, and anti-aging properties. As an AHA, lactic acid effectively removes dead skin cells and promotes cell turnover, resulting in a smoother and more radiant complexion. Its ability to penetrate the skin's surface and stimulate collagen production makes it a sought-after ingredient in anti-aging formulations.
In addition to its exfoliating benefits, lactic acid is a powerful moisturizer. It enhances the skin's natural moisturizing factor (NMF), helping to maintain hydration and prevent transepidermal water loss (TEWL). This dual action of exfoliation and hydration makes lactic acid suitable for various skin types, including sensitive and acne-prone skin.
To incorporate lactic acid into a skincare regimen, it is essential to choose products with appropriate concentrations and formulations. Lactic acid serums, creams, and masks are available in varying strengths, allowing users to tailor their skincare routine to their specific needs. Regular use of lactic acid products can improve skin texture, tone, and overall appearance, making it a valuable addition to any skincare arsenal.
Natural sources of lactic acid for the skin
Lactic acid can be derived from several natural sources, making it an accessible and sustainable ingredient for skincare. Fermented foods, such as yogurt, kefir, and sauerkraut, are rich in lactic acid, produced by lactic acid bacteria during fermentation. These foods not only provide dietary lactic acid but also contain probiotics that support skin health from within.
In addition to fermented foods, certain fruits, such as grapes and tomatoes, contain natural lactic acid and other AHAs. These fruits can be used in DIY skincare treatments or consumed as part of a balanced diet to support skin health. Milk and buttermilk are also traditional sources of lactic acid, historically used in milk baths and masks for their soothing and exfoliating properties.
Utilizing natural sources of lactic acid in skincare offers a holistic approach to skin health, combining the benefits of topical application and dietary intake. By incorporating these sources into daily routines, individuals can harness the power of lactic acid for a more vibrant and youthful complexion.
How does lactic acid compare to other skincare acids?
Lactic acid is one of several alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs) commonly used in skincare. Compared to other AHAs, such as glycolic acid, lactic acid is milder and less likely to cause irritation, making it suitable for sensitive skin. Its larger molecular size limits its penetration into the skin, reducing the risk of irritation while still providing effective exfoliation and hydration.
In contrast, glycolic acid is smaller and penetrates the skin more deeply, offering more intense exfoliation. However, this can also increase the potential for irritation, especially in sensitive skin types. Lactic acid's gentle nature makes it a preferred choice for those new to AHAs or with sensitive skin, while glycolic acid may be more suitable for individuals seeking more dramatic exfoliation results.
Other acids, such as salicylic acid, are beta hydroxy acids (BHAs) and differ from AHAs in their oil-solubility, making them effective for treating acne-prone skin. Lactic acid, with its hydrating properties, complements BHAs by maintaining moisture levels while addressing surface texture and tone. By understanding the unique properties of each acid, individuals can choose the most appropriate options for their skincare needs and goals.
Impact of environmental factors on lactic acid synthesis
Environmental factors play a significant role in lactic acid synthesis within the skin. Temperature and humidity levels can influence the rate of perspiration and the secretion of lactic acid. In hot and humid conditions, increased sweating can lead to higher lactic acid levels on the skin's surface, affecting its pH and barrier function.
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun can also impact lactic acid synthesis. UV exposure can alter skin metabolism, affecting enzyme activity and disrupting the balance of lactic acid production. Prolonged UV exposure can lead to skin damage, underscoring the importance of sun protection to maintain healthy lactic acid levels and overall skin health.
Pollutants and chemicals in the environment can further influence lactic acid production by affecting skin metabolism and barrier function. These factors highlight the importance of environmental awareness in skincare, as protecting the skin from external stressors can support optimal lactic acid synthesis and skin health.
Benefits of lactic acid for aging skin
Aging skin can greatly benefit from the incorporation of lactic acid in skincare routines. As the skin ages, cellular turnover slows down, leading to a buildup of dead skin cells on the surface. This can result in a dull and uneven complexion, emphasizing the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
Lactic acid's exfoliating action helps to remove these dead skin cells, promoting cell renewal and revealing fresher, more radiant skin. Its ability to stimulate collagen production further supports skin structure, reducing the visibility of fine lines and enhancing skin firmness and elasticity.
Additionally, lactic acid's moisturizing properties are particularly beneficial for aging skin, which tends to become drier over time. By enhancing hydration and maintaining the skin's natural moisture balance, lactic acid helps to keep the skin plump and supple, contributing to a youthful appearance.
Can dietary choices affect skin's lactic acid levels?
Dietary choices can indeed influence lactic acid levels in the skin. Consuming a diet rich in carbohydrates provides the necessary substrates for glycolysis, potentially enhancing lactic acid production. Foods high in sugars and starches can increase glucose availability, supporting the metabolic pathways that lead to lactic acid synthesis.
In addition to carbohydrate intake, the consumption of fermented foods, such as yogurt and kefir, can directly provide lactic acid and probiotics that benefit skin health. These foods support a healthy gut microbiome, which is closely linked to skin health and can influence lactic acid production indirectly.
Hydration is another critical dietary factor, as adequate water intake supports overall skin health and function. By maintaining optimal hydration levels, the skin can effectively regulate lactic acid production and maintain its barrier function, contributing to a balanced and healthy complexion.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can lactic acid cause skin irritation?
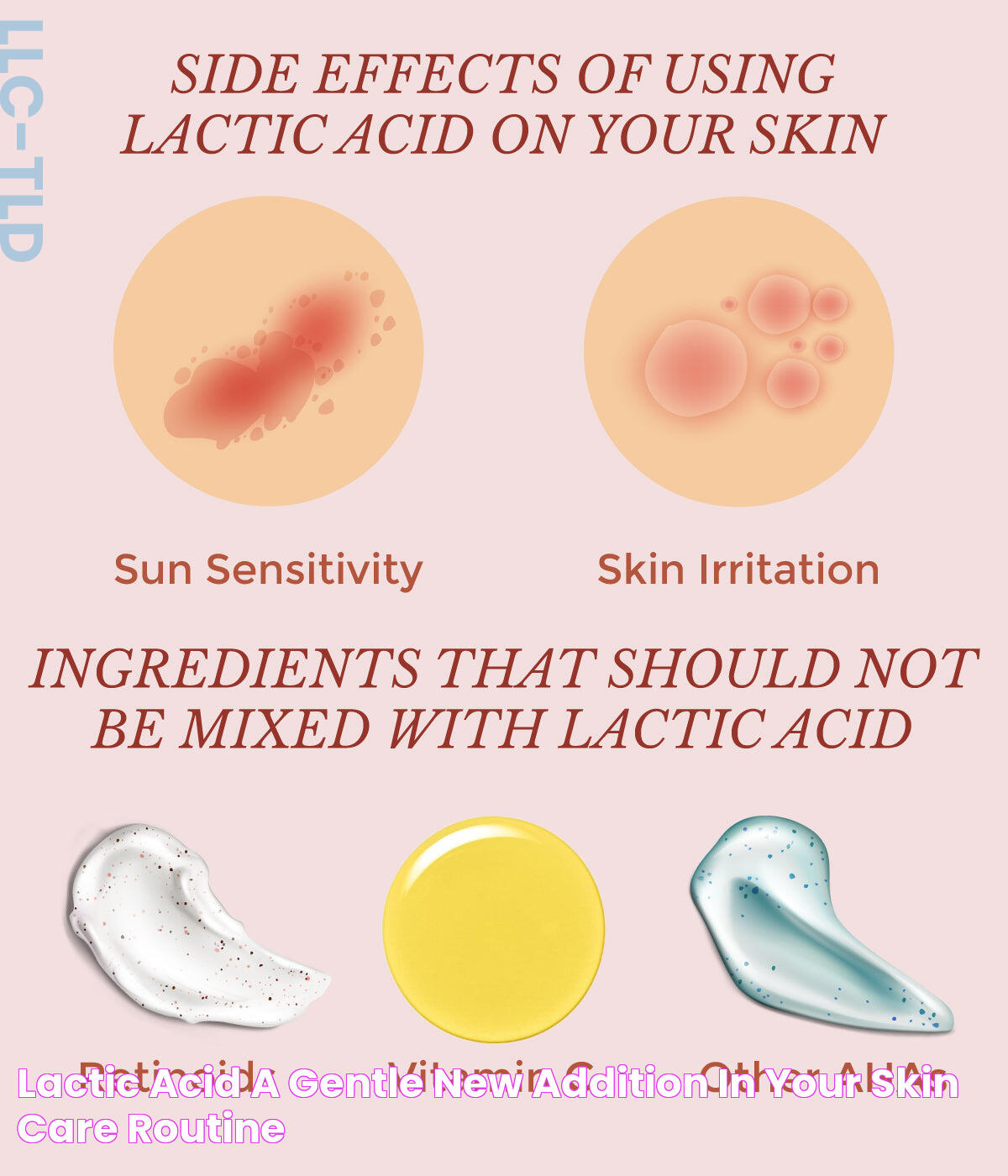
While lactic acid is generally well-tolerated, it can cause irritation in some individuals, especially at higher concentrations. It's essential to patch test new products and start with lower concentrations to assess tolerance.
2. How often should I use lactic acid in my skincare routine?
Frequency of use depends on skin type and product formulation. Generally, lactic acid can be used 1-3 times per week. It's important to follow the product's instructions and monitor skin response.
3. Is lactic acid safe for sensitive skin?
Lactic acid is one of the gentler AHAs and is often suitable for sensitive skin. However, patch testing and gradual introduction are recommended to ensure tolerance.
4. Can lactic acid be used with other skincare ingredients?
Lactic acid can be combined with other ingredients, such as hyaluronic acid and ceramides, to enhance hydration and barrier function. Avoid using with other potent acids or retinoids to minimize irritation risk.
5. Does lactic acid help with acne?
Lactic acid can help with acne by exfoliating dead skin cells and unclogging pores. Its hydrating properties also prevent excessive dryness, supporting skin balance.
6. Should I use sunscreen when using lactic acid?
Yes, it's crucial to use sunscreen when using lactic acid as it can increase photosensitivity. Apply broad-spectrum sunscreen daily to protect the skin from UV damage.
Conclusion
In conclusion, lactic acid is a pivotal component in the realm of skincare, offering a multitude of benefits that enhance skin health and appearance. Through its production in the skin, lactic acid plays a vital role in maintaining pH balance, hydration, and exfoliation, contributing to a healthy and radiant complexion. By understanding the mechanisms and factors influencing its synthesis, individuals can harness its potential in their skincare routines.
Whether through topical application or dietary choices, incorporating lactic acid into daily practices can support skin structure, improve texture, and address signs of aging. Its gentle nature makes it suitable for a wide range of skin types, offering a versatile solution for various skincare needs. As research continues to unveil the complexities of lactic acid production and function, its significance in skincare remains undeniable, promising continued innovations and applications in the pursuit of optimal skin health.
For further reading and resources on skincare and lactic acid, consider visiting reputable dermatology websites and consulting with skincare professionals to tailor a regimen that suits your individual needs and goals.