When we think about sun exposure, we often consider the warmth, the tan, and the vitamin D benefits. However, there's a lesser-known condition that can arise from too much sun exposure, known as sun poisoning. Sun poisoning isn't just a severe sunburn; it's a serious medical condition that requires attention. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and prevention methods can help you protect yourself and enjoy the sun safely.
Despite its name, sun poisoning isn't a type of poisoning at all. Rather, it refers to a severe case of sunburn that can lead to symptoms such as skin blistering, pain, nausea, and even dehydration. It's crucial to differentiate between a typical sunburn and sun poisoning to ensure appropriate treatment and care. Sun poisoning can affect anyone who spends prolonged periods in the sun without adequate protection, especially during peak UV radiation hours.
With the increasing awareness of skin health and the dangers of UV radiation, it's essential to be informed about the potential risks associated with sun exposure. This article delves into the details of sun poisoning, covering everything from symptoms and causes to preventive measures and treatments. By the end of this article, you'll have a comprehensive understanding of how to protect yourself from sun poisoning and enjoy the sun responsibly.
Read also:Your Guide To 13 Astrological Signs And Dates
Table of Contents
- What Is Sun Poisoning?
- Symptoms of Sun Poisoning
- Causes of Sun Poisoning
- How Does Sun Poisoning Differ from a Sunburn?
- Risk Factors for Sun Poisoning
- Prevention Tips for Sun Poisoning
- Treatment Options for Sun Poisoning
- When to See a Doctor for Sun Poisoning?
- Natural Remedies for Sun Poisoning
- Sun Poisoning vs. Heat Exhaustion: What's the Difference?
- Impact of Sun Poisoning on the Skin
- Long-Term Effects of Sun Poisoning
- How to Care for Sun-Damaged Skin?
- Frequently Asked Questions about Sun Poisoning
- Conclusion
What Is Sun Poisoning?
Sun poisoning is a severe reaction to prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) rays, particularly from the sun. It is not a formal medical diagnosis but a colloquial term for a serious sunburn with accompanying symptoms that resemble an allergic reaction. The condition is marked by a range of symptoms that are more intense than those of a typical sunburn.
Sun poisoning can occur when the skin is exposed to UV rays for an extended period, often without adequate sunscreen protection. The condition can affect anyone, but individuals with fair skin, light-colored eyes, and light hair are more susceptible. Sun poisoning can lead to significant discomfort and, in some cases, necessitate medical attention.
Symptoms of Sun Poisoning
Recognizing the symptoms of sun poisoning is crucial for timely intervention and treatment. The symptoms can vary in severity and may include:
- Severe skin redness and blistering
- Swelling of the affected areas
- Itching or a burning sensation
- Headache and dizziness
- Nausea and vomiting
- Dehydration
- Fever and chills
- Confusion or disorientation in severe cases
If you experience any of these symptoms after sun exposure, it's important to take immediate steps to cool the skin and rehydrate the body. Persistent or worsening symptoms warrant medical consultation.
Causes of Sun Poisoning
The primary cause of sun poisoning is excessive exposure to UV radiation, which can damage the skin's cells and lead to severe inflammation. Factors that contribute to sun poisoning include:
- Spending extended time outdoors during peak UV radiation hours (10 a.m. to 4 p.m.)
- Not using sunscreen or using a sunscreen with inadequate SPF
- Having a fair skin type that burns easily
- Exposure to reflective surfaces like water, sand, or snow, which can intensify UV exposure
- Using certain medications that increase sun sensitivity
- Having a history of sunburns, which can increase susceptibility
Understanding these causes can help you take preventive measures to reduce the risk of sun poisoning.
Read also:Equilibrium Meaning Balance And Harmony In Various Contexts
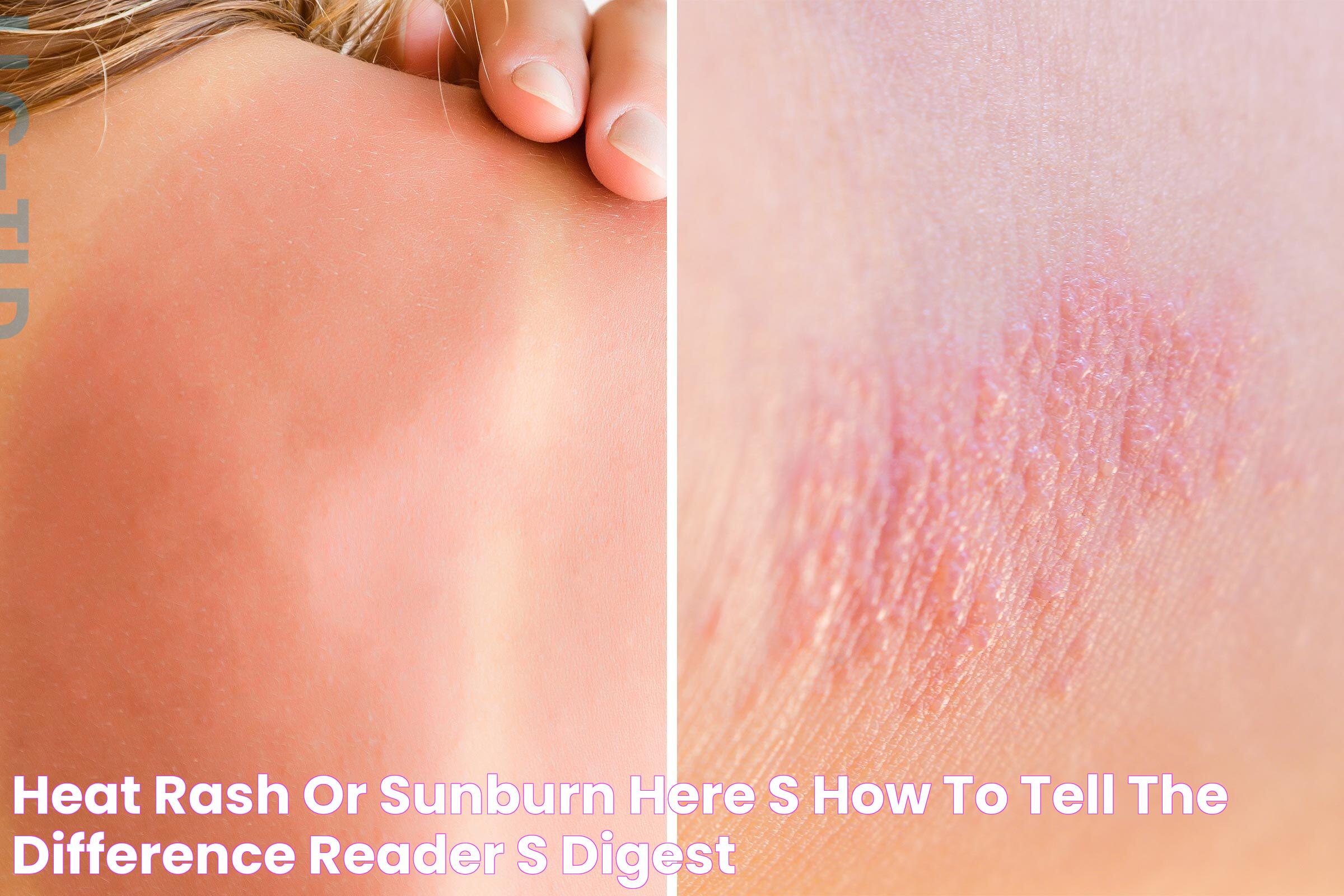
How Does Sun Poisoning Differ from a Sunburn?
While sun poisoning and sunburn both result from UV exposure, they differ significantly in their severity and symptoms. A sunburn is a common skin reaction characterized by redness, pain, and sometimes peeling. In contrast, sun poisoning involves more severe symptoms that extend beyond the skin.
Sun poisoning may present with:
- Intense redness and blistering of the skin
- Systemic symptoms such as fever, chills, nausea, and confusion
- Longer recovery time compared to a typical sunburn
The key distinction lies in the systemic involvement and severity of symptoms, making sun poisoning a more serious condition that requires immediate attention and care.
Risk Factors for Sun Poisoning
Certain individuals are at a higher risk of developing sun poisoning due to their skin type, lifestyle, or medical history. Risk factors include:
- Having fair skin, light hair, and light-colored eyes
- Living in or visiting regions with high UV index levels
- Participating in outdoor activities without adequate sun protection
- Taking medications such as antibiotics or oral contraceptives that increase sun sensitivity
- Having a history of skin conditions or sunburns
Being aware of these risk factors can help in taking proactive steps to prevent sun poisoning.
Prevention Tips for Sun Poisoning
Preventing sun poisoning involves adopting sun-safe practices and being vigilant about sun exposure. Here are some tips to protect yourself:
- Apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen with at least SPF 30, and reapply every two hours or after swimming or sweating.
- Wear protective clothing, including a wide-brimmed hat and UV-blocking sunglasses.
- Seek shade during peak UV hours, especially between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m.
- Use additional sun protection measures when near reflective surfaces such as water or sand.
- Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water, especially in hot conditions.
By incorporating these preventive measures, you can reduce your risk of sun poisoning and enjoy outdoor activities safely.
Treatment Options for Sun Poisoning
If you suspect sun poisoning, it's important to begin treatment immediately to alleviate symptoms and prevent further complications. Treatment options include:
- Moving indoors or into the shade to prevent further UV exposure
- Applying cool compresses to the affected areas to soothe the skin
- Taking over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen to reduce pain and inflammation
- Using aloe vera gel or moisturizing lotions to hydrate the skin
- Staying hydrated by drinking water and electrolyte-rich fluids
For severe cases with symptoms like fever, chills, or confusion, seek medical attention promptly. A healthcare professional can provide additional treatment options, including prescription medications if necessary.
When to See a Doctor for Sun Poisoning?
While many cases of sun poisoning can be managed at home, certain symptoms necessitate medical evaluation. Contact a healthcare provider if you experience:
- Severe blistering or swelling of the skin
- Persistent fever, chills, or dizziness
- Signs of dehydration, such as dark urine or extreme thirst
- Symptoms that do not improve with home care
- Confusion or disorientation
Prompt medical attention is crucial to prevent complications and ensure proper recovery.
Natural Remedies for Sun Poisoning
In addition to conventional treatments, some individuals find relief from sun poisoning symptoms using natural remedies. These may include:
- Aloe Vera: Known for its soothing and cooling properties, aloe vera gel can help reduce inflammation and hydrate the skin.
- Oatmeal Baths: Adding colloidal oatmeal to a lukewarm bath can alleviate itching and irritation.
- Cucumber Slices: Placing chilled cucumber slices on the affected areas can provide a cooling effect and reduce swelling.
- Coconut Oil: Applying coconut oil may help moisturize and protect the skin from further damage.
While natural remedies can be beneficial, it's important to use them in conjunction with medical treatments and consult a healthcare provider if symptoms persist.
Sun Poisoning vs. Heat Exhaustion: What's the Difference?
Sun poisoning and heat exhaustion are both related to sun exposure, but they are distinct conditions with different causes and symptoms. Sun poisoning is primarily a skin reaction to UV rays, while heat exhaustion is a result of the body's inability to cope with high temperatures and humidity.
Heat exhaustion symptoms include:
- Heavy sweating and pale skin
- Weakness and fatigue
- Muscle cramps
- Headache and dizziness
- Nausea or vomiting
Preventing both conditions involves staying hydrated, seeking shade, and wearing appropriate protective clothing. Understanding the differences can help in providing the correct treatment and care.
Impact of Sun Poisoning on the Skin
Sun poisoning can have significant short-term and long-term effects on the skin. In the immediate aftermath, the skin may experience severe redness, blistering, and peeling. The damage can extend beyond the surface, affecting deeper layers of the skin and increasing the risk of complications.
Long-term effects of repeated or severe sun poisoning can include:
- Increased risk of skin cancer, including melanoma
- Premature aging, such as wrinkles and age spots
- Changes in skin texture and elasticity
- Persistent hyperpigmentation or discoloration
Protecting your skin from sun poisoning is not only important for immediate relief but also for long-term skin health and cancer prevention.
Long-Term Effects of Sun Poisoning
The long-term effects of sun poisoning can be serious and lasting. Prolonged UV exposure and repeated instances of sun poisoning increase the risk of developing skin cancer, particularly melanoma, which is the most aggressive form of skin cancer.
Other potential long-term effects include:
- Chronic skin conditions such as actinic keratosis, which can progress to cancer
- Photoaging, characterized by wrinkles, sagging, and a leathery texture
- Persistent changes in skin pigmentation, such as sunspots or freckles
Taking preventive measures against sun poisoning is crucial to minimizing these long-term risks and maintaining healthy skin.
How to Care for Sun-Damaged Skin?
Caring for sun-damaged skin involves a combination of protective and restorative measures. If you've experienced sun poisoning or significant sunburn, follow these steps to aid recovery and prevent further damage:
- Continue using sunscreen daily, even on cloudy days, to protect the skin from additional UV exposure.
- Moisturize regularly to restore hydration and improve skin barrier function.
- Consider using products with antioxidants, such as vitamin C or E, to combat free radical damage.
- Exfoliate gently to remove dead skin cells and promote skin renewal.
- Avoid tanning beds and prolonged sun exposure to prevent exacerbating skin damage.
By taking these steps, you can help your skin recover from sun damage and protect it from future harm.
Frequently Asked Questions about Sun Poisoning
What should I do if I suspect sun poisoning?
If you suspect sun poisoning, seek shade immediately, cool the skin with damp cloths, and hydrate. Over-the-counter pain relievers can help with discomfort. If symptoms are severe, consult a healthcare provider.
Can sun poisoning lead to skin cancer?
Yes, severe or repeated instances of sun poisoning can increase the risk of skin cancer, including melanoma. It's important to protect your skin and monitor for any changes or abnormalities.
How long does it take for sun poisoning symptoms to appear?
Symptoms of sun poisoning can appear within a few hours of exposure, but in some cases, they may take up to 24 hours to manifest fully.
Is there a difference between sun poisoning and sun allergy?
Yes, sun poisoning is a severe sunburn, while sun allergy (or photosensitivity) is an immune system reaction to sunlight, often causing a rash or hives.
Can I treat sun poisoning at home?
Mild cases of sun poisoning can often be treated at home with cooling measures, hydration, and over-the-counter medications. However, severe symptoms require medical attention.
What is the best sunscreen to prevent sun poisoning?
Choose a broad-spectrum sunscreen with at least SPF 30, water resistance, and reapply every two hours or after swimming or sweating for optimal protection.
Conclusion
Sun poisoning is a serious condition that results from excessive UV exposure and can have both immediate and long-term effects on the skin. By understanding the symptoms, causes, and preventive measures, you can protect yourself and enjoy the sun safely. Remember to take proactive steps in using sunscreen, wearing protective clothing, and staying hydrated to minimize the risk of sun poisoning. If you experience severe symptoms, seek medical attention promptly to ensure proper care and recovery.