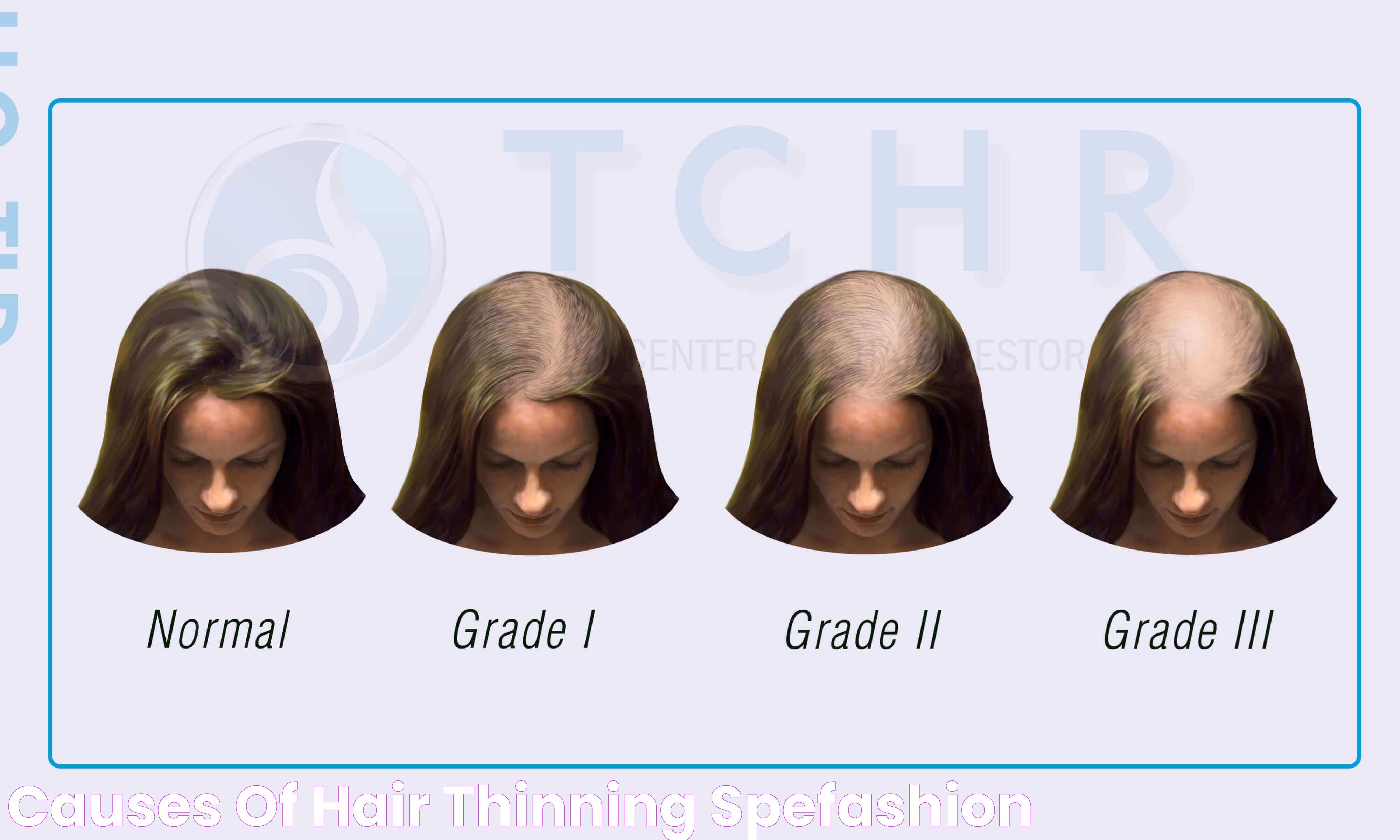
Hair loss in women can be a distressing experience, affecting self-esteem and quality of life. While it's common to shed some hair daily, excessive hair loss can be alarming and may indicate underlying health issues or lifestyle factors. Understanding the root causes of hair loss in women is crucial for finding effective solutions and preventing further damage.
Several factors can contribute to hair loss in women, ranging from genetics to environmental influences. Hormonal imbalances, nutritional deficiencies, and medical conditions are some of the primary culprits. Additionally, stress, hairstyling practices, and certain medications can exacerbate the problem. Identifying the specific cause of hair loss is the first step toward finding an appropriate treatment plan.
Fortunately, various remedies and treatments are available to help women combat hair loss and promote healthy hair growth. From medical interventions and lifestyle changes to natural remedies and dietary adjustments, women have multiple options to explore. This comprehensive guide will delve into the different causes of hair loss in women and provide actionable insights to restore and maintain luscious locks.
Read also:What To Avoid Tips For Cutting Down A Tree Safely
Table of Contents
- Genetic Factors and Hair Loss
- Hormonal Imbalances: The Hidden Culprit?
- Are Nutritional Deficiencies to Blame?
- How Do Medical Conditions Affect Hair Loss?
- Stress and Hair Loss: What's the Connection?
- Hairstyling Practices: A Double-Edged Sword
- Can Medications Cause Hair Loss?
- Pregnancy and Postpartum Hair Loss
- Does Age Play a Role in Hair Loss?
- Environmental Factors: A Silent Threat?
- Lifestyle Changes for Healthier Hair
- What Dietary Adjustments Can Help?
- Natural Remedies for Hair Loss
- Exploring Medical Treatments for Hair Loss
- FAQs About Hair Loss in Women
- Conclusion
Genetic Factors and Hair Loss
A significant portion of hair loss cases in women can be attributed to genetic factors. Hereditary hair loss, also known as female-pattern baldness or androgenetic alopecia, is the most common cause of hair loss in women. This condition is characterized by a gradual thinning of hair across the scalp, often starting at the part line. Unlike male-pattern baldness, which typically results in complete baldness, female-pattern baldness rarely leads to total hair loss.
The genetic predisposition to hair loss is usually passed down from either parent. It involves the sensitivity of hair follicles to androgens, a group of hormones that includes testosterone. This sensitivity results in the shrinking of hair follicles, leading to shorter and thinner hair strands over time. While genetic hair loss is a natural part of aging, it can start as early as in one's 20s or 30s.
Women with a family history of hair loss are more likely to experience similar patterns of thinning. Despite the genetic component, environmental and lifestyle factors can influence the severity and progression of hair loss. Understanding one's genetic predisposition can help in managing expectations and exploring preventive measures.
Hormonal Imbalances: The Hidden Culprit?
Hormones play a critical role in regulating hair growth and loss. Any disruption in hormonal balance can significantly impact hair health. Conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), menopause, and thyroid disorders are common hormonal issues that can lead to hair loss in women.
During menopause, the decline in estrogen levels can result in increased hair thinning. Similarly, thyroid hormones, which regulate metabolism and growth, can cause hair loss when levels are too high or too low. Women with PCOS often experience hair loss due to elevated androgen levels, which can lead to male-pattern baldness.
Hormonal changes during pregnancy can also cause temporary hair loss. While many women experience thicker hair during pregnancy due to increased estrogen levels, hair shedding can occur postpartum as hormone levels return to normal. Identifying and treating the underlying hormonal imbalance can help manage hair loss effectively.
Read also:Top Choices For Essential Oil Brands Quality And Purity Unveiled
Are Nutritional Deficiencies to Blame?
Proper nutrition is essential for maintaining healthy hair. Deficiencies in key nutrients can lead to hair thinning and loss. Iron, vitamin D, zinc, and biotin are particularly important for hair health. Iron deficiency, often caused by anemia, is a well-known factor contributing to hair loss in women. It affects the hair growth cycle by limiting the oxygen supply to hair follicles.
Vitamin D plays a role in hair follicle cycling, and its deficiency has been linked to hair loss. Zinc is crucial for cell growth and repair, and a lack of it can lead to hair loss and scalp problems. Biotin, a B-vitamin, is often associated with hair, skin, and nail health. Its deficiency can cause hair thinning and brittle hair.
Addressing nutritional deficiencies through a balanced diet or supplements can significantly improve hair health. Consulting with a healthcare professional can help identify specific deficiencies and develop a tailored nutritional plan.
How Do Medical Conditions Affect Hair Loss?
Various medical conditions can lead to hair loss in women. Autoimmune disorders, such as alopecia areata, cause the immune system to attack hair follicles, leading to patchy hair loss. Lupus, an autoimmune disease, can also cause hair thinning and loss due to its impact on the skin and hair follicles.
Scalp infections, such as ringworm, can result in temporary hair loss. These infections can cause inflammation and damage to hair follicles, leading to hair shedding. Treating the underlying infection is crucial for restoring hair growth.
Other medical conditions, such as diabetes and anemia, can indirectly affect hair health. Diabetes can impair blood circulation and nutrient delivery to hair follicles, while anemia reduces oxygen supply. Managing these conditions with appropriate medical care can help mitigate hair loss.
Stress and Hair Loss: What's the Connection?
Stress is a common trigger for hair loss in women. Emotional or physical stress can disrupt the hair growth cycle, leading to a condition known as telogen effluvium. This condition causes a significant number of hair follicles to enter the resting phase prematurely, resulting in increased hair shedding.
Traumatic events, such as surgery, illness, or significant life changes, can also trigger stress-related hair loss. Typically, hair loss due to stress is temporary, and hair growth resumes once the stressor is eliminated.
Managing stress through relaxation techniques, exercise, and proper sleep can help promote hair health. Additionally, seeking support from mental health professionals can aid in addressing underlying stressors and improving overall well-being.
Hairstyling Practices: A Double-Edged Sword
While hairstyling can enhance one's appearance, certain practices can contribute to hair loss in women. Excessive use of heat styling tools, such as hairdryers, straighteners, and curling irons, can weaken hair strands and cause breakage.
Hairstyles that pull tightly on the scalp, such as ponytails, braids, and buns, can lead to a condition known as traction alopecia. This condition results from prolonged tension on hair follicles, causing hair loss around the hairline.
Chemical treatments, such as coloring, perming, and relaxing, can also damage hair and lead to thinning. It's essential to minimize the use of harsh chemicals and heat styling to maintain healthy hair. Opting for gentle hair care products and styles can help prevent hair loss due to styling practices.
Can Medications Cause Hair Loss?
Some medications can have hair loss as a side effect. Drugs used to treat conditions like high blood pressure, depression, and cancer may lead to hair thinning or shedding. Chemotherapy, in particular, is known for causing temporary hair loss due to its impact on rapidly dividing cells, including hair follicles.
Other medications, such as contraceptive pills and hormone replacement therapy, can also affect hormone levels and contribute to hair loss. If medication-induced hair loss is a concern, discussing alternative options with a healthcare provider is advisable.
In most cases, hair loss due to medication is reversible once the drug is discontinued or adjusted. However, it's important not to stop taking any prescribed medication without consulting a doctor.
Pregnancy and Postpartum Hair Loss
Pregnancy and childbirth can lead to changes in hair growth patterns. During pregnancy, many women experience thicker, fuller hair due to elevated estrogen levels. However, after childbirth, hormone levels drop, leading to increased hair shedding, commonly known as postpartum hair loss.
This type of hair loss is usually temporary and resolves within a few months. Maintaining a healthy diet and taking prenatal vitamins can support hair health during and after pregnancy. If hair loss persists, consulting with a healthcare professional can help identify any underlying issues.
Does Age Play a Role in Hair Loss?
Aging is a natural factor that contributes to hair loss in women. As women age, hair follicles can shrink, leading to thinner and finer hair strands. The hair growth cycle also slows down, resulting in less hair growth and increased shedding.
Menopause often coincides with age-related hair loss, as hormonal changes can exacerbate thinning. While age-related hair loss is a normal part of aging, maintaining a healthy lifestyle and hair care routine can help minimize its impact.
Regular scalp massages, using gentle hair care products, and protecting hair from environmental damage can promote hair health as women age. Additionally, exploring hair restoration treatments may be beneficial for those seeking to address age-related hair loss.
Environmental Factors: A Silent Threat?
Environmental factors can significantly impact hair health. Exposure to pollutants, such as dust, smoke, and chemicals, can damage hair and scalp, leading to hair loss. UV radiation from the sun can also weaken hair strands and cause color fading.
Hard water, which contains high levels of minerals, can lead to hair dryness and breakage. Similarly, chlorine in swimming pools can strip hair of its natural oils, leaving it brittle and prone to damage.
Protecting hair from environmental stressors is crucial for maintaining its health and vitality. Using protective hair products, wearing hats, and rinsing hair after swimming can help mitigate the effects of environmental factors.
Lifestyle Changes for Healthier Hair
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can have a positive impact on hair health. Regular exercise promotes blood circulation, delivering essential nutrients to hair follicles. Staying hydrated ensures that hair remains moisturized and less prone to breakage.
A balanced diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and proteins is vital for hair growth and strength. Foods such as leafy greens, nuts, fish, and eggs provide essential nutrients that support hair health.
Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can also benefit hair. These habits can constrict blood vessels and reduce nutrient delivery to hair follicles, leading to hair thinning.
What Dietary Adjustments Can Help?
Dietary adjustments can play a significant role in addressing hair loss in women. Incorporating foods rich in iron, biotin, and omega-3 fatty acids can promote hair growth and strength. Spinach, lentils, and beans are excellent sources of iron, while eggs and nuts provide biotin.
Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fatty fish like salmon and mackerel, help nourish hair follicles and promote a healthy scalp. Vitamin C-rich foods, such as citrus fruits and berries, support collagen production, strengthening hair strands.
Limiting processed foods and sugary snacks can also benefit hair health. These foods can contribute to inflammation and hormonal imbalances, affecting hair growth negatively. Consulting with a nutritionist can help develop a personalized dietary plan to support hair health.
Natural Remedies for Hair Loss
Natural remedies offer a holistic approach to combating hair loss in women. Essential oils, such as rosemary and lavender, are known for their hair-strengthening properties. Massaging the scalp with these oils can improve blood circulation and stimulate hair growth.
Aloe vera, a natural moisturizer, can soothe the scalp and promote healthy hair growth. Applying aloe vera gel directly to the scalp can reduce dandruff and strengthen hair strands.
Herbal supplements, such as saw palmetto and ginseng, are believed to block the production of DHT, a hormone linked to hair loss. While natural remedies can be effective, it's important to consult with a healthcare professional before trying new treatments.
Exploring Medical Treatments for Hair Loss
Medical treatments for hair loss offer scientifically backed solutions for women experiencing significant hair thinning. Topical treatments, such as minoxidil, are FDA-approved for promoting hair growth and thickness. Minoxidil works by prolonging the growth phase of hair follicles, leading to increased hair density.
Oral medications, such as spironolactone, can help reduce androgen levels and improve hair growth in women with hormonal imbalances. Hair transplant surgery is another option for women with significant hair loss, offering natural-looking results by relocating hair follicles to thinning areas.
Consulting with a dermatologist or hair specialist is essential for determining the most suitable medical treatment. They can provide personalized recommendations based on the underlying cause of hair loss.
FAQs About Hair Loss in Women
- Can hair loss in women be reversed?
In many cases, hair loss can be reversed or managed with appropriate treatments, especially if addressed early. Identifying the underlying cause is crucial for effective intervention.
- How long does it take for hair to regrow after hair loss?
Hair regrowth can take several months, depending on the cause and treatment. Patience and consistency with treatment are key to seeing results.
- Are hair supplements effective for hair loss?
Hair supplements can be beneficial if hair loss is due to nutritional deficiencies. However, they should be used in conjunction with a balanced diet and under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
- Is it normal to lose hair daily?
Yes, losing 50 to 100 hairs a day is considered normal. Excessive shedding may indicate an underlying issue that requires attention.
- Can stress-related hair loss be permanent?
Stress-related hair loss is usually temporary and resolves once the stressor is removed. Long-term stress, however, can lead to more persistent hair loss.
- What role does genetics play in hair loss?
Genetics significantly influence hair loss patterns. Women with a family history of hair loss are more likely to experience similar issues. Genetic hair loss typically involves gradual thinning rather than complete baldness.
Conclusion
Hair loss in women is a multifaceted issue with various causes, ranging from genetics and hormonal imbalances to lifestyle and environmental factors. While it can be a challenging experience, understanding the underlying causes is the first step toward finding effective solutions. By exploring a combination of lifestyle changes, dietary adjustments, natural remedies, and medical treatments, women can combat hair loss and promote healthy hair growth. Consulting with healthcare professionals and hair specialists can provide personalized guidance and support on this journey.
With the right approach, women can regain their confidence and enjoy the beauty of healthy, vibrant hair.